Frank R. Lautenberg Deep-Sea Coral Protection Area facts for kids
The Frank R. Lautenberg Deep-Sea Coral Protection Area is a special part of the ocean that protects deep-sea corals. It's located off the coast of the Mid-Atlantic states of the United States. Think of it like a national park, but underwater!
On September 26, 2016, a government group called the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Fisheries, along with the Mid-Atlantic Fishery Management Council, decided to create this large protected area. The rules for this area officially started on January 13, 2017. This special place was named after Senator Frank Lautenberg, a U.S. Senator from New Jersey. He worked hard to create many policies that help protect our oceans.
Where is This Special Area?
This protected area focuses on spots where many deep-sea corals are known to live. These corals are often found in underwater canyons or along the edge of the continental shelf, which is where the land slopes down into the deep ocean.
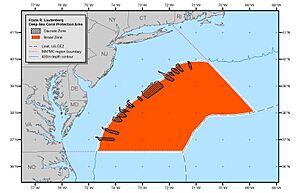
The area stretches from the Mid-Atlantic states (like New York to North Carolina) all the way to the edge of the U.S.'s Exclusive Economic Zone, which is a large ocean area where the U.S. has special rights. It starts at depths of about 450 meters (about 1,476 feet) and includes 15 separate zones. In total, it covers about 38,000 square miles of federal waters. That's roughly the same size as the state of Virginia! An environmental group called the Natural Resources Defense Council says it's the "largest area in the U.S. Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico protected from a range of destructive fishing gear."
What Rules Protect the Corals?
To keep the deep-sea corals safe, certain types of fishing gear are not allowed in this area. These include:
- Bottom-tending trawls (nets dragged along the seafloor)
- Hydraulic dredges and non-hydraulic dredges (tools that scoop up things from the bottom)
- Seines (large nets that hang vertically in the water)
- Longlines (very long lines with many hooks)
- Pots and traps (like those used for crabs, but not for all types)
- Sink or gill nets (nets that catch fish by their gills)
However, some fishing activities are still allowed. These include:
- Recreational fishing (fishing for fun)
- Commercial fishing gear that does not touch the seafloor
- Fishing for American lobster using traps
- Fishing for deep sea red crab using traps
If a fishing boat needs to travel through the protected area, it can. But all fishing gear must be stored away and not ready for use.
Also, vessels that have a special permit for Illex squid must have a vessel monitoring system (VMS) installed. This system helps track their location. Operators of these vessels also need to report their squid fishing trips if they plan to catch 10,000 pounds or more of Illex squid.
Why Was This Area Created?
This protection area was created because NOAA’s National Marine Fisheries Service approved something called Amendment 16. This amendment is part of a larger plan to manage fishing for Atlantic Mackerel, Squid, and Butterfish. Its main goal is to protect deep-sea corals from being harmed by commercial fishing gear.
This action also follows the main ideas of the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act. This important law helps make sure that U.S. coastal fisheries are used wisely and in a way that keeps them healthy for a long time.
The Regional Fishery Management Councils, which are groups that help manage fishing, have the power to:
- Decide where and when fishing can be limited or not allowed. They can also say which types of boats or gear can be used.
- Create protected zones in areas where deep-sea corals live. This is to stop fishing gear from damaging the corals or to prevent gear from getting lost or damaged by corals. They also think about how to use fish resources sustainably in these areas.
- Make sure that any area closed to fishing is based on the best scientific information available. They also set goals for how well the closed area is working and plan reviews to check its success. Finally, they look at the good and bad effects of closing an area, including how it affects fishermen, science, and ocean conservation.