Atlantic cod facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Atlantic cod |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
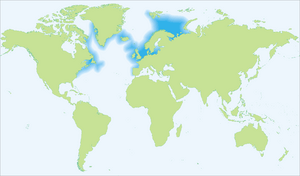
| Distribution of Atlantic cod | |
| Synonyms | |
|
The Atlantic cod is a well-known type of fish. It lives in the cool waters of the northern Atlantic Ocean. These fish are an important part of the ocean's ecosystem. They are also very important to humans as a food source.
Young Atlantic cod usually swim closer to the ocean's surface. As they grow older and bigger, they move to live near the seafloor. This fish eats other, smaller fish, like herring, and also molluscs.
Contents
What is an Atlantic Cod?
Atlantic cod are strong, medium-sized fish. They usually have a greenish-brown or grey color. This helps them blend in with the ocean floor. They have a distinctive white line along their side, called a lateral line. They also have a barbel, which is a whisker-like organ, under their chin. They use this barbel to feel around and find food in the dark seafloor.
Size and Appearance
Atlantic cod can grow quite large. Some can reach up to 200 cm (6 ft 7 in) (about 6.5 feet) in length. They can weigh over 96 kg (212 lb) (about 212 pounds). However, most cod caught today are much smaller. They are usually around 50 cm (20 in) (20 inches) long. Their size depends on where they live and how old they are.
Where They Live
Atlantic cod are found across a wide area. They live in the cold waters of the North Atlantic. This includes areas from the coast of North America to Europe. You can find them in the Arctic Ocean, North Sea, and Baltic Sea. They prefer water temperatures between 0 and 15 °C (32 and 59 °F).
Life and Habits of Atlantic Cod
Atlantic cod are active predators. They play a key role in the ocean's food web. They hunt for food both near the surface and on the seafloor.
What They Eat
Atlantic cod have a varied diet. Young cod eat small crustaceans and tiny fish. As they get bigger, their diet changes. Adult cod eat many different kinds of prey. This includes smaller fish like herring, capelin, and sand eels. They also eat crabs, shrimp, and other invertebrates.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Atlantic cod can live for many years. Some have been known to live for over 20 years. They usually start reproducing when they are about 2 to 4 years old. Female cod can lay millions of eggs in one spawning season. These eggs float near the surface of the ocean. After hatching, the tiny cod larvae drift with the currents. They slowly grow into juvenile fish.
Atlantic Cod and Humans
Atlantic cod has been a very important fish for humans for centuries. It has been a major source of food and income.
Fishing for Cod
For hundreds of years, fishing for Atlantic cod was a huge industry. People from Europe and North America relied on cod. It was a staple food, especially when preserved by salting or drying. This allowed it to be stored for long journeys and times when fresh food was scarce.
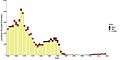
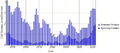
However, heavy fishing has caused problems. In some areas, the number of cod has dropped dramatically. This is called overfishing. Scientists and governments are working to manage fishing better. They want to make sure there are enough cod for the future.
Conservation Status
Because of overfishing, the Atlantic cod is currently listed as "Vulnerable." This means it faces a high risk of becoming endangered in the wild. Efforts are being made to protect cod populations. These efforts include setting fishing limits and creating protected areas. The goal is to help the cod numbers recover.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bacalao para niños
In Spanish: Bacalao para niños