Geodesic facts for kids
A geodesic is like the shortest path you can take between two points on a curved surface. Imagine you are an ant walking on a balloon. If you want to get from one spot to another, the geodesic is the straightest, shortest way to go, even though the balloon itself is curved. In mathematics, a geodesic is a special kind of curve that represents the shortest length between two points on a surface.
Contents
What is a Geodesic?
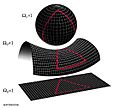
Think of a geodesic as the "straight line" on a curved surface. On a flat piece of paper, the shortest distance between two points is a straight line. But what if the surface isn't flat? What if it's a ball, a donut, or a mountain? A geodesic helps us find that shortest path.
Geodesics on Different Shapes
The way a geodesic looks depends on the shape of the surface it's on.
On a Sphere
On a sphere, like our Earth, geodesics are called great circles. A great circle is any circle drawn on the surface of a sphere that divides it into two equal halves. The equator is a great circle, and so are all lines of longitude. If you fly an airplane from one city to another, the pilot often follows a path that looks curved on a flat map, but it's actually the shortest path (a geodesic or great circle) on the curved surface of the Earth.
On Other Surfaces
- On a flat surface, a geodesic is simply a straight line.
- On a cylinder, a geodesic can be a straight line, a circle, or a spiral.
- On a more complex shape, like a donut (called a torus in mathematics), a geodesic can twist and turn in interesting ways.
Finding the Shortest Path
Sometimes, there can be more than one geodesic between two points. For example, on a sphere, if you pick two points exactly opposite each other (like the North Pole and the South Pole), you can draw many great circles connecting them. All of them are geodesics because they are "straight" on the sphere.
However, there's a special type called a minimal geodesic. This is the geodesic that has the absolute shortest length among all possible geodesics connecting two points. So, even if there are many "straight" paths, the minimal geodesic is the very shortest one.
Geodesics in Real Life
Geodesics are not just a math concept; they are used in many real-world applications:
- Navigation: Pilots and ship captains use geodesics (great circles) to find the shortest routes for travel around the world.
- Physics: In Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity, objects like planets and light rays follow geodesics through the curved spacetime created by massive objects. This means gravity isn't a force pulling things, but rather objects following the "straightest" path in a curved universe.
- Engineering: Architects and engineers use geodesic principles when designing structures like geodesic domes, which are very strong and efficient.
Geodesics help us understand how to find the most direct path, even when the world around us is curved!
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Geodésica para niños
In Spanish: Geodésica para niños