George Cross facts for kids
Quick facts for kids George Cross |
|
|---|---|
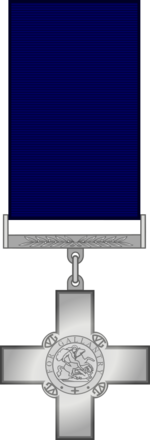
Obverse of the cross. Ribbon: 1½", dark blue
|
|
| Awarded for | Height 48 mm, max. width 45 mm; (Obverse) plain silver cross with circular medallion in the centre depicting the effigy of St George and the Dragon, surrounded by the words "FOR GALLANTRY". In the angle of each limb is the Royal Cypher GVI; (Reverse) plain, centre engraved with name of recipient and date of award. Cross attached by ring to bar ornamented with laurel leaves, through which the ribbon passes. |
| Presented by | Monarch of the United Kingdom |
The George Cross (GC) is the highest award given by the British government for amazing bravery. This bravery is shown when there isn't an enemy around. In the British honours system, the George Cross is just as important as the Victoria Cross. The Victoria Cross is the highest military award for courage.
The George Cross is given "for acts of the greatest heroism or for most conspicuous courage in circumstances of extreme danger." This means for incredibly brave actions in very risky situations. It is awarded to members of the British Armed Forces and to British civilians. It can be given to people even after they have passed away.
The award used to be given to people in Commonwealth countries. One famous award was to Malta, which was a British colony. Many Commonwealth countries now have their own awards. The George Cross can be given to anyone in the military. It can also be given to civilians like police, emergency workers, and sailors. The British King or Queen often gives the award in person. These ceremonies usually happen at Buckingham Palace.
Contents
Creating the George Cross
The George Cross was created on 24 September 1940 by King George VI. This was during the Blitz, when German planes were bombing Britain. Many civilians were showing great courage during these attacks. The King wanted a special way to recognize their bravery.
He decided to create the George Cross and the George Medal. These awards would honor brave actions by civilians. They would also recognize brave deeds more generally.
When announcing the new award, King George VI said:
In order that they should be worthily and promptly recognised, I have decided to create, at once, a new mark of honour for men and women in all walks of civilian life. I propose to give my name to this new distinction, which will consist of the George Cross, which will rank next to the Victoria Cross, and the George Medal for wider distribution.
The medal was designed by Percy Metcalfe. The official document for the George Cross was published on 31 January 1941.
The King said the George Cross would be second in importance only to the Victoria Cross. This placed it much higher than other awards for bravery not involving an enemy. Before the GC, the highest such award was the Albert Medal (AM). The Empire Gallantry Medal (EGM) was the lowest.
Holders of the EGM had to exchange their medal for the George Cross. Most received their new GC at a special ceremony. In 1971, people who had received the Albert Medal or the Edward Medal (EM) could also become George Cross recipients. They could choose to keep their original medal or exchange it.
How the George Cross Is Awarded
The George Cross can be given to someone even after they have died. It recognizes:
acts of the greatest heroism or of the most conspicuous courage in circumstances of extreme danger.
This award is mainly for civilians. But it can also be given to military personnel. This happens when their brave actions are not in battle. The rules state:
The Cross is intended primarily for civilians and award in Our military services is to be confined to actions for which purely military Honours are not normally granted.
The George Cross is worn on the left side of the chest. It hangs from a dark blue ribbon. It is worn right after the Victoria Cross. If a woman receives the award, she can wear it on her left shoulder. It hangs from a ribbon tied into a bow.
If someone performs another act of bravery worthy of the GC, they can receive a "bar." This is a small metal bar added to the ribbon. So far, no one has received a bar for the George Cross.
Recipients can use the letters "GC" after their name. All individual George Cross awards are officially announced. The latest collective award to the National Health Service was also announced in The London Gazette.
George Cross Committee
A special group called the George Cross Committee looks at cases of bravery. This committee is part of the Cabinet Office. They decide who should receive the George Cross.
Who Has Received the George Cross?
Since 1940, the George Cross has been awarded 416 times. This includes 401 awards to men and 12 to women. It has also been given to three groups of people. About 30% of the individual awards have gone to civilians. Many awards were exchanges for older medals like the Empire Gallantry Medal.
Awards to Groups

The George Cross has been awarded to three groups: the Island of Malta, the Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC), and the National Health Service (NHS) of the United Kingdom.
Malta
The George Cross was given to the island of Malta on 15 April 1942. This was during the Second World War. Malta was heavily bombed by enemy planes. King George VI sent a letter to Malta's Governor, Sir William Dobbie. The letter said:
To honour her brave people, I award the George Cross to the Island Fortress of Malta to bear witness to a heroism and devotion that will long be famous in history.
The people of Malta showed amazing strength during the bombings. They also faced a naval blockade, which almost starved them. Their courage was admired by Britain and other Allied nations. The George Cross was added to the Flag of Malta in 1943. It is still on the flag today.
Royal Ulster Constabulary
The George Cross was awarded to the RUC in 1999 by Queen Elizabeth II. The RUC was the police force in Northern Ireland. They had faced a long and violent period of conflict. The award recognized their "collective courage and dedication to duty." Over 300 officers had been killed. Thousands more were injured.
Queen Elizabeth II presented the George Cross on 12 April 2000. The ceremony was held at Hillsborough Castle. Constable Paul Slaine accepted the cross. He had lost both legs in an attack in 1992. The RUC is often called "RUC GC" because of this award.
National Health Service
On 5 July 2021, Queen Elizabeth II announced that the four NHS organizations in the UK would receive the George Cross. This was on the 73rd anniversary of the NHS. The award was given after the health service had been at the front of the fight against the coronavirus pandemic.
The Queen's message said:
It is with great pleasure, on behalf of a grateful nation, that I award the George Cross to the National Health Services of the United Kingdom. This award recognises all NHS staff, past and present, across all disciplines and all four nations. Over more than seven decades, and especially in recent times, you have supported the people of our country with courage, compassion and dedication, demonstrating the highest standards of public service. You have our enduring thanks and heartfelt appreciation. Elizabeth R.
Awards to Commonwealth Countries
Canada
Ten George Crosses have been awarded to Canadians. This includes awards that replaced older medals. The recipients were nine men and one woman. Canada now has its own award, the Cross of Valour. So, the King of Canada no longer awards the George Cross to Canadians.
Australia
The George Cross was awarded to 23 Australians. Eleven awards went to Australian military members. Twelve went to civilians. It is the highest bravery award in the Australian honours system after the Victoria Cross. Australia created its own Cross of Valour in 1975. However, Australia continued to recommend British honors until 1992.
Four awards went to officers who cleared mines during the Second World War. Privates Benjamin Gower Hardy and Ralph Jones received the George Cross after they died. They bravely fought during a Japanese prisoner of war escape in 1944. They stopped the prisoners from using a machine gun.
Captain Lionel Colin Matthews was another brave recipient. He built a resistance network during the Second World War. He was later executed by his captors. Private Horace William Madden was captured in Korea in 1951. He helped other prisoners and resisted the enemy. He died from the harsh conditions.
The last Australian to receive the GC was Constable Michael Kenneth Pratt in 1978. He was a police officer in Melbourne. He arrested two armed bank robbers in 1976.
A memorial to Australian recipients, George Cross Park, opened in Canberra in 2001.
New Zealand
In 1999, the New Zealand Cross took over the role of the George Cross. The last George Cross awarded to a New Zealander was to Sgt Stewart Guthrie. He was a police officer. He received it after he died for his bravery during the Aramoana massacre.
Annuity for Recipients
People who hold the Victoria Cross or the George Cross receive a yearly payment. This payment is called an annuity. The amount is decided by the government that gave the award. For example, the British government paid £10,000 per year as of 2015.
Rules for Using the George Cross
Since 1943, there have been rules in Malta about using the George Cross. It is against the law to use the George Cross, or anything that looks like it, for business. This is unless the Prime Minister gives permission.
See also
- British and Commonwealth orders and decorations
- Category:Recipients of the George Cross
- List of George Cross recipients
- George Medal
- Cross of St. George, a Russian award
- St. George's cross, the flag of England
- Flag of Malta, a flag bearing the cross
- Soham rail disaster – 2 June 1944
- The Victoria Cross and George Cross Association
- Elizabeth Cross
- PDSA Gold Medal – seen as the animal equivalent of the GC
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |



