Goldman's nectar bat facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Goldman's nectar bat |
|
|---|---|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Phyllostomidae |
| Genus: | Lonchophylla |
| Species: |
L. mordax
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lonchophylla mordax Thomas et al., 1903
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Goldman's nectar bat (Lonchophylla mordax) is a special type of bat. It lives in warm, tropical areas of Central and South America. These bats are known for their unique diet. They mainly feed on nectar and pollen from flowers. This makes them very important helpers for plants, just like bees!
Contents
Discover Goldman's Nectar Bat
Goldman's nectar bat is a small mammal. It belongs to a group of bats called "leaf-nosed bats." This name comes from a small, leaf-shaped growth on their noses. Scientists believe this helps them with echolocation. Echolocation is how bats use sound to "see" their surroundings.
What Makes This Bat Special?
Goldman's nectar bats have a few cool features. They have a long, pointed snout. This helps them reach deep into flowers. They also have a very long tongue. It can stretch out far to lap up nectar. Their fur is usually a reddish-brown color. They are quite small, weighing only a few grams.
These bats are nocturnal. This means they are active at night. During the day, they rest in safe places. They might sleep in caves, hollow trees, or even old buildings. They often roost in groups.
Where Do Goldman's Nectar Bats Live?
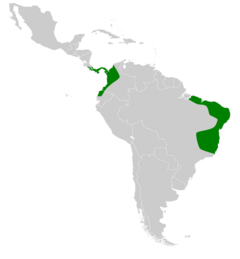
You can find Goldman's nectar bats in several countries. They live in Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, and Panama. They prefer tropical forests. These forests have many flowering plants. This provides plenty of food for the bats. They can live in both wet rainforests and drier forests.
What Do They Eat?
As their name suggests, nectar bats love nectar. Nectar is a sweet liquid found in flowers. They also eat pollen, which is full of protein. Sometimes, they might eat small insects too. This diet makes them excellent pollinators. When they visit flowers for nectar, pollen sticks to their fur. Then, they carry this pollen to other flowers. This helps the plants make seeds and grow.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Like all mammals, Goldman's nectar bats give birth to live young. A mother bat usually has one baby at a time. The baby bat is called a pup. Pups are born without fur and cannot see. The mother bat cares for her pup. She feeds it milk until it is old enough to fly and find its own food.
Young bats learn to fly and hunt for food. They learn from their mothers and other bats in their colony. As they grow, their bodies develop. Their wings get stronger, and their echolocation skills improve. Soon, they can join the adults in their nightly search for food.
Are They in Danger?
The conservation status of Goldman's nectar bat is "Near Threatened." This means they are not in immediate danger of disappearing. However, their numbers could decrease in the future. The biggest threat to these bats is habitat loss. Forests are sometimes cut down for farming or building. This reduces the places where bats can live and find food. Protecting their forest homes is important. It helps ensure these amazing pollinators continue to thrive.
See also
 In Spanish: Lonchophylla mordax para niños
In Spanish: Lonchophylla mordax para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |


