Governor of Wisconsin facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Governor of Wisconsin |
|
|---|---|

|
|

Privy Seal of the State of Wisconsin
|
|
| Government of Wisconsin | |
| Style | His Excellency. The Honorable |
| Residence | Wisconsin Governor's Mansion |
| Seat | Madison, WI |
| Term length | Four years, no term limits |
| Inaugural holder | Nelson Dewey |
| Formation | June 7, 1848 |
| Succession | Line of succession |
| Deputy | Lieutenant Governor of Wisconsin |
| Salary | $152,756 (2022) |
The governor of Wisconsin is like the chief executive officer for the state of Wisconsin. This person is the main leader of the state government. They are also the boss of Wisconsin's army and air forces.
The governor's job is to make sure state laws are followed. They can also approve or reject new laws passed by the Wisconsin Legislature. The governor can call the legislature together for special meetings. They can also grant pardons, which means forgiving someone for a crime. However, they cannot do this for cases of treason or impeachment.
The current governor is Tony Evers. He is a Democrat and is serving his second term. He started his job on January 7, 2019.
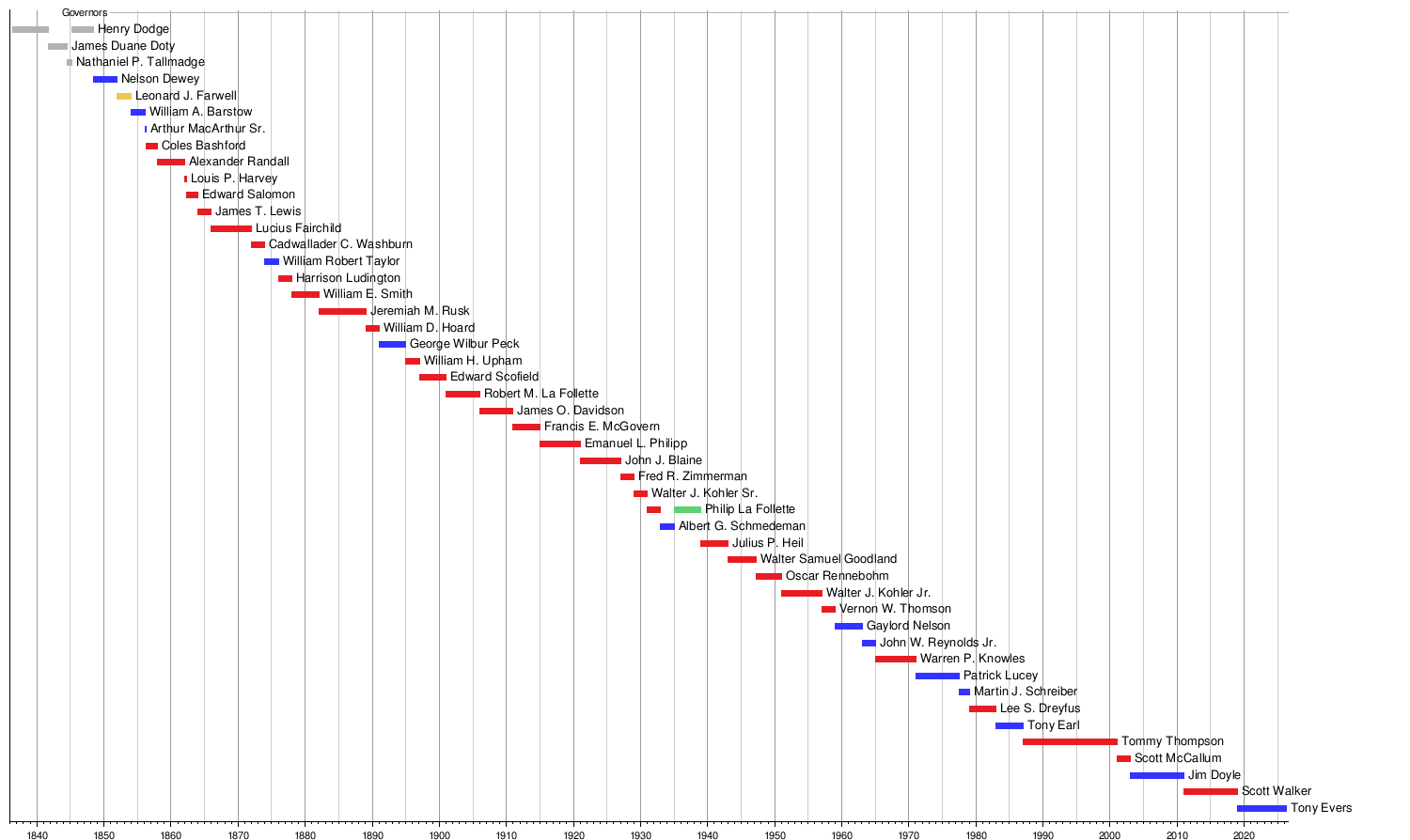
The first person to be governor was Nelson Dewey. He took office on June 7, 1848. This was the same year Wisconsin officially became a state. Before Wisconsin was a state, there were four governors for the Wisconsin Territory.
Contents
Governor's Important Powers
The governor of Wisconsin has special powers. Some powers come from the Wisconsin Constitution. Other powers are given by laws passed by the state legislature.
Key Powers of the Governor
The main powers of the governor are explained in the Wisconsin Constitution. Generally, the governor makes sure that all of Wisconsin's laws are put into action.
Veto Power: Saying No to Laws
The governor of Wisconsin has a very strong power called the veto. This means they can reject a bill (a proposed law) that the Wisconsin State Legislature has passed. Every bill passed by the legislature must go to the governor. The governor either signs it, making it a law, or vetoes it.
If the governor vetoes a bill, it goes back to the legislature. They can then vote again to try and overrule the veto. This needs a special majority vote.
Since 1930, the governor has had a "line-item veto" power. This is a special type of veto. It lets the governor remove parts of spending bills without rejecting the whole bill. Governors can even remove words, numbers, or whole sentences from these bills. The legislature can still try to overrule these partial vetoes.
This strong veto power led to the term "Frankenstein veto". It describes how a governor can change a bill so much that it becomes something new. In 2023, Governor Tony Evers used this power. He changed a part of the state budget that funded schools until the "2024-2025" school year. He changed it to "2425," which meant funding for over 400 years! On April 18, 2025, the Wisconsin Supreme Court said this was allowed by his constitutional powers.
Other Important Powers
The governor is the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces, called the militia. If needed, the governor can call special meetings of the state legislature. They can even hold these meetings anywhere in the state. This might happen if Madison, the state capital, is not safe due to an invasion or a serious illness spreading.
The governor can also pardon people, which means releasing them from punishment. They can also reduce sentences or delay them. This cannot be done for cases of treason or impeachment. The governor must tell the Wisconsin State Legislature about these actions every year. They also have to explain why they did them. For treason cases, the governor can delay the punishment until the legislature meets. Then, the legislature votes on whether to grant a pardon or carry out the sentence.
The governor also has to tell the legislature about the "condition of the state" at every meeting. This is often called the "state of the state" speech. They can also suggest new ideas for the legislature to think about.
Managing State Agencies and Money
As the head of the executive branch, the governor also manages state agencies. These agencies are created by the Wisconsin legislature. Since 1965, governors have used executive orders more often. These orders help set rules for how state agencies work. However, since 2011, the Wisconsin Legislature has tried to limit the power of these agencies.
The governor also chooses the leaders of many state agencies. This power is not directly written in the Wisconsin Constitution. Instead, laws passed by the legislature give the governor this power. For example, the governor made 307 executive appointments between 2017 and 2018.
However, the governor of Wisconsin has fewer appointment powers than some other leaders, like the President of the United States. For instance, supreme court judges in Wisconsin are elected by the people, not chosen by the governor. Other important state jobs, like Secretary of State of Wisconsin and Superintendent of Public Instruction of Wisconsin, are also elected directly. This means the governor cannot choose who holds these positions.
Some appointments, like those to the Wisconsin Natural Resources Board, are "staggered." This means that the terms of board members end at different times. This can sometimes lead to agencies having different goals than the governor. In some cases, if the Wisconsin Senate does not approve the governor's choices, the old leaders have stayed in their jobs. This can extend the influence of the previous governor.
State law also requires the governor to create a budget plan for the state. This helps the governor guide what laws and projects the state will focus on.
How Governors Are Chosen and How Long They Serve
The governor of Wisconsin is chosen by a direct vote. This means the person with the most votes becomes governor. If two candidates get the same number of votes, and it's the highest number, the state legislature votes to decide between them.
Governors now serve for four years. This change happened after the 1970 election. Before that, they served for two years. There is no limit to how many terms a governor can serve.
The governor who served the longest was Tommy Thompson. He was governor for over 14 years, from January 5, 1987, to February 1, 2001. The shortest-serving governor was Arthur MacArthur Sr.. He was governor for only 5 days in March 1856.
To be a candidate for governor, a person must be a U.S. citizen. They must also be a qualified voter in Wisconsin.
Leaving the Governor's Office
A governor usually leaves office when their term ends and they are not re-elected. But there are other ways a governor can leave their job. For example, a governor might resign. Four governors have resigned:
- William Barstow left due to accusations of fraud.
- Robert La Follette Sr. resigned to become a U.S. Senator.
- Patrick Joseph Lucey resigned to become the Ambassador to Mexico.
- Tommy Thompson resigned to become the United States Secretary of Health and Human Services.
Two governors, Louis Harvey and Walter Samuel Goodland, died while they were in office. Also, Orland Steen Loomis, who was elected governor, died before he could even start the job.
A governor can also be removed through an impeachment trial or a recall election. An impeachment trial happens if most members of the Wisconsin State Assembly agree to it. No governor in Wisconsin's history has been removed by impeachment. However, Arthur MacArthur Sr. became acting governor in 1856. He was removed after the Wisconsin Supreme Court decided that Coles Bashford, Barstow's opponent, was the real winner of the election.
Recall elections were not common in Wisconsin until the 2000s. In 2012, Scott Walker became the only governor in Wisconsin history to face a recall election. He was also the first governor in American history to keep his job after such an election.
History of Elections
In the 2022 election for governor, over 2.6 million people voted. This was the highest number of votes ever for a governor's election in Wisconsin. It was even more than the 2012 recall election.
Wisconsin has had 44 different governors. One governor, Philip La Follette, served terms that were not back-to-back. Four main political parties have had their candidates elected as governor: the Democratic Party, the Whig Party, the Republican Party, and the Progressive Party.
Who Takes Over if the Governor Can't Serve?
The lieutenant governor of Wisconsin is chosen to take over if the governor cannot serve. Since 1979, the Wisconsin Constitution says that the lieutenant governor becomes governor for the rest of the term if the governor dies, resigns, or is removed.
However, if the governor is impeached, unable to do their job, or just away, the lieutenant governor only acts as governor. They serve until the governor can return to their duties. If the lieutenant governor also cannot serve, the secretary of state is next in line.
Since 1967, the Wisconsin Constitution has required the governor and lieutenant governor to be elected together. Before this rule, there were nine times when the elected governor and lieutenant governor were from different political parties.
Timeline of Wisconsin Governors
| Timeline of Wisconsin governors |
 |


