United States Senate facts for kids
Quick facts for kids United States Senate |
|
|---|---|
| 117th United States Congress | |

|
|

Flag of the U.S. Senate
|
|
| Type | |
| Type | |
|
Term limits
|
None |
| History | |
|
New session started
|
January 3, 2021 |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
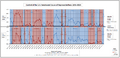
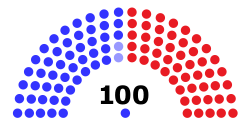
| Seats | 100 51 (or 50 plus the Vice President) for a majority |
 |
|
|
Political groups
|
Majority (50)
Minority (50)
|
|
Length of term
|
6 years |
| Elections | |
| Plurality voting in 46 states Varies in 4 states
|
|
|
Last election
|
November 3, 2020 (35 seats) |
|
Next election
|
November 8, 2022 (34 seats) |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
| Senate Chamber United States Capitol Washington, D.C. United States |
|
| Constitution | |
| United States Constitution | |
The United States Senate is one of two parts of the United States Congress. It is often called the "upper chamber." The other part is the House of Representatives, which is the "lower chamber." Together, these two groups form the national law-making body of the United States. This system, with two chambers, is called a bicameral legislature.
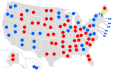
The rules for the Senate, including its members and powers, are set by Article One of the United States Constitution. Each of the 50 states in the U.S. has two senators. This means there are 100 senators in total. Senators serve for six years, but their terms are "staggered." This means not all senators are elected at the same time. The Vice President of the United States leads the Senate meetings. They only vote if there is a tie. If the Vice President is not there, a senator called the president pro tempore leads instead. This person is usually the longest-serving member of the party with the most senators.
The Senate has special powers that the House of Representatives does not. These include approving treaties (agreements with other countries). They also confirm (approve) important government officials. This includes people like Cabinet secretaries, federal judges (including Supreme Court justices), and ambassadors. If no one gets enough votes for Vice President in the Electoral College, the Senate chooses one. The Senate also holds trials for officials who have been impeached (accused of wrongdoing) by the House.
The Senate is often seen as a more serious and important group than the House. This is because senators serve longer terms and represent an entire state. Also, there are fewer senators (100) than House members (435). This often leads to more discussion and less disagreement between political parties.
How the Senate Has Changed
From 1789 to 1913, state legislatures chose senators. People did not vote for them directly. But in 1913, the Seventeenth Amendment was added to the Constitution. After this, people started voting for their senators directly. In the early 1920s, the main political parties in the Senate started choosing "floor leaders." These leaders help manage the Senate's work. The Senate majority leader is in charge of planning the Senate's law-making and other business.
Where the Senate Meets
The Senate meets in the Senate Chamber. This room is in the north wing of the Capitol Building in Washington, D.C..
See also
 In Spanish: Senado de los Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Senado de los Estados Unidos para niños
Images for kids
-
The Senate side of the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C.
-
Committee Room 226 in the Dirksen Senate Office Building is used for hearings by the Senate Judiciary Committee.
-
The Senate has the power to try impeachments; shown above is Theodore R. Davis's drawing of the impeachment trial of President Andrew Johnson, 1868