Greater fairy armadillo facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Greater fairy armadillo |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Holotype published by Hermann Burmeister | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Cingulata |
| Family: | Chlamyphoridae |
| Subfamily: | Chlamyphorinae |
| Genus: | Calyptophractus Fitzinger, 1871 |
| Species: |
C. retusus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Calyptophractus retusus (Burmeister, 1863)
|
|
 |
|
| Greater fairy armadillo range | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The greater fairy armadillo (Calyptophractus retusus) is a unique type of armadillo. People also call it Burmeister's armadillo or the Chacoan fairy armadillo. This small animal lives in parts of Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay. It prefers dry areas like shrublands and grasslands. Sadly, its home is shrinking, and some people even harm it. This armadillo is the only species in its group, called Calyptophractus.
Contents
What Does It Look Like?
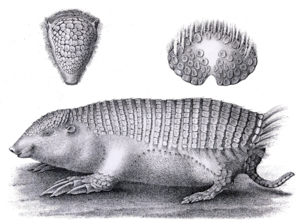
The greater fairy armadillo is a small animal. It grows to about 14 to 17.5 centimeters (5.5 to 7 inches) long. Its tail is about 3.5 centimeters (1.4 inches) long. It can weigh up to one kilogram (2.2 pounds).
Like other armadillos, it has hard plates that cover its back. These plates are like armor. But unlike most armadillos, its armor is soft. It is also attached to its hips and spine. The plates are connected by skin, which helps the armadillo move easily.
The armor stops suddenly at the back of its body. Its belly is covered in thick, soft hair. It also has some thin hairs on its back. Its front feet are shaped like scoops. They have curved claws for digging. Its back feet have sharp claws, also good for burrowing.
Where Does It Live?
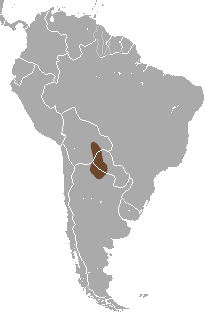
The greater fairy armadillo lives in the Gran Chaco region. This area includes northern Argentina, central and southeastern Bolivia, and western Paraguay. It likes dry, grassy places. You can only find it where the soil is light and sandy. This type of soil is perfect for digging its burrows.
How Does It Behave?
Scientists don't know much about the greater fairy armadillo's behavior. It is an amazing digger. It spends most of its time in shallow tunnels underground. You will rarely see it above ground during the day.
If something bothers it, the armadillo can quickly bury itself. It might even block the entrance to its burrow. It uses the plates on its rear end to do this. This armadillo eats many different things. It is an omnivore. Its diet includes worms, insect larvae, insects, snails, roots, and seeds.
Life Cycle and Reproduction
We don't know much about how these armadillos have babies. After mating, the fertilized egg might stay in the mother for months. It waits before it attaches to the uterus. Sometimes, one egg can split into up to four babies.
The babies probably grow inside the mother for about four months. This is similar to other armadillo species. When they are born, the young armadillos can move around quickly. Their body armor is soft at first. It takes a few weeks for it to get hard. They also stop drinking their mother's milk around this time. They can have their own babies when they are between six months and one year old.
What Is Its Status?
The greater fairy armadillo was once listed as "Near Threatened". This was because its home was disappearing. But in 2010, its status changed to "Data Deficient". This means we don't have enough information about the animal to know if it's truly in danger.
The places where it lives are spread out. In some areas, like where the Guarani live, people harm it. They believe it brings bad luck or is the spirit of a dead baby. However, this armadillo lives in some nature reserves and national parks. In these protected areas, humans should not bother them.
See also
 In Spanish: Pichiciego Grande para niños
In Spanish: Pichiciego Grande para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |


