Myocardial infarction facts for kids
A heart attack happens when a blood vessel in your heart suddenly gets blocked. Blood vessels carry blood and oxygen to your heart. If a blood vessel in the heart is blocked, a part of the heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen. This is called ischemia.
When the heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen, it can cause chest pain. This pain is called angina. If this goes on for too long, the heart muscle can die. This is what "myocardial infarction" means: "muscle death in the heart."
A heart attack is a serious medical emergency. Getting help quickly is very important for saving the person's life. Some damage from a heart attack can be fixed if treatment starts within the first hour.
Contents
What Causes a Heart Attack?
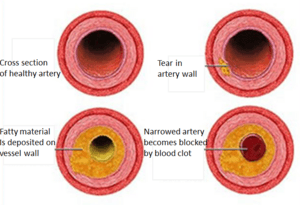
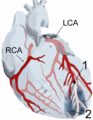
Most heart attacks happen because of coronary heart disease (CAD). In this disease, a waxy material called plaque builds up inside the heart's arteries. This buildup is called atherosclerosis.
Plaque is made of cholesterol and other cells. It slowly grows, making the blood vessels in the heart narrower. This means less blood can flow through them. Sometimes, platelets (which help blood clot) build up near the plaque. This can form a blood clot. If the clot gets stuck in a narrow part of the blood vessel, it can completely block the vessel. This stops blood from reaching part of the heart, causing a heart attack.
You can lower your chances of getting coronary artery disease. Eating healthy foods, exercising, not smoking, and not drinking too much alcohol can help.
Signs and Symptoms
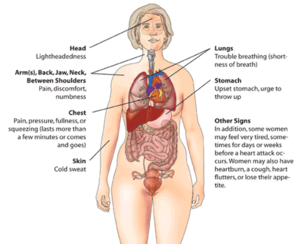
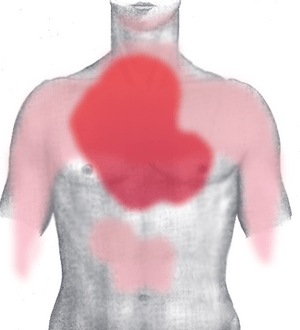
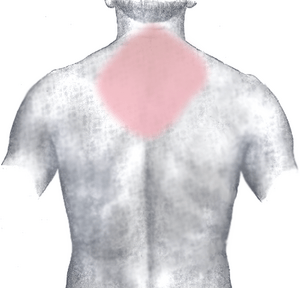
Signs of a heart attack usually appear over several minutes. They rarely happen all at once. Most people having a heart attack feel chest pain. Sometimes, the pain also spreads to the left arm, lower jaw, neck, right arm, back, or parts of the abdomen.
Many women have different symptoms than men. The most common symptoms for women include shortness of breath (trouble breathing), weakness, and feeling very tired. Some women might feel tired, not sleep well, and have shortness of breath for up to a month before a heart attack. Women may also feel nausea and have an upset stomach during a heart attack.
Sometimes, people have "silent heart attacks." These heart attacks do not cause any pain. They are more common in older people, women, and people with diabetes. For these people, suddenly feeling very tired or fainting might be the only sign of a heart attack.
Getting Treatment
A heart attack is a medical emergency that needs treatment as fast as possible. The main goal is to save as much heart muscle as you can. The longer someone waits, the more damage can happen to the heart.
Doctors or paramedics often start treatments as soon as they think someone is having a heart attack. These treatments include:
- Aspirin: Aspirin helps stop blood clots from forming. This can prevent more blockages in the blood vessels and heart.
- Nitroglycerin (nitro): Nitro helps widen the blood vessels in the heart. This makes it easier for blood to flow to the heart muscle.
- Oxygen: If the person has trouble breathing, oxygen can be given.
- Pain medicine: Medicine can be given for chest pain if needed.
Once doctors are sure someone is having a heart attack, there are two main treatments: "clot-busting medicines" and percutaneous coronary intervention.
Clot-Busting Medicines
"Clot-busting medicines" are also called thrombolytics. They can dissolve blood clots that are blocking the heart's blood vessels. This allows blood and oxygen to flow again to the part of the heart that was not getting enough. A common clot-busting medicine is called tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
These medicines work best if given within 30 minutes of arriving at the hospital. However, if a patient gets a clot-busting medicine within 12 hours of the heart attack starting, they have a better chance of surviving. These medicines do have some risks, like causing too much bleeding.
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Percutaneous coronary intervention is a way to open blocked heart arteries. "Percutaneous" means the procedure is done without a large cut, unlike surgery. This procedure is also called "coronary angioplasty."
During this procedure, a doctor inserts a thin, flexible tube into a blood vessel, usually in the upper thigh. The doctor guides this tube up to the blocked blood vessels in the heart. At the end of the tube is a small balloon. The doctor inflates the balloon, which pushes the plaque and blood clot against the side of the blocked blood vessel. This helps blood flow through the vessel again. Sometimes, a doctor might also place a small mesh tube called a stent into the blood vessel. The stent helps keep the blood vessel open so it doesn't get blocked again.
What to Do in an Emergency
If you think someone might be having signs of a heart attack, you should call emergency services right away. For example, in the US, you dial 911. In most of Europe, you dial 112. Many people wait about three hours before asking for help. Waiting too long can cause more serious damage to the heart. The American Heart Association says "time is muscle": the more time passes, the more heart muscle can die.
If the person is having trouble breathing, sitting straight up can help. The person should follow any instructions given by the emergency operator or their doctor.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Infarto agudo de miocardio para niños
In Spanish: Infarto agudo de miocardio para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |