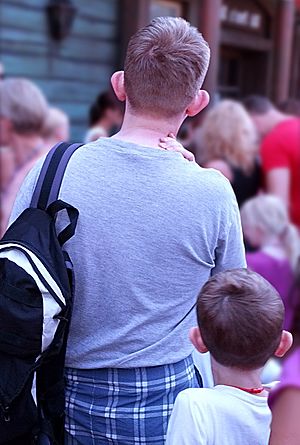Heredity facts for kids
Heredity is how living things pass on their special features, called traits, from parents to their children. These traits can be things like eye color, hair type, or even how tall someone might grow. In biology, the study of heredity is known as genetics.
When we talk about a trait that can be passed down, we say it is heritable. This means it's something you are born with or that is innate.
What is Heredity?
Heredity is the reason why family members often look alike or share similar characteristics. It's like a set of instructions passed from one generation to the next. These instructions are found in something called DNA, which is inside almost every cell in your body.
How Traits Are Passed Down
Traits are passed down through tiny units called genes. You get half of your genes from your mother and half from your father. These genes contain the information that tells your body how to grow and what traits to have. For example, a gene might carry the instruction for brown eyes, or for curly hair.
Sometimes, a trait might be very obvious, like your hair color. Other times, it might be something you can't see, like a tendency to be good at running or a certain blood type.
Studying Heredity
Scientists study heredity in different ways:
- Breeding experiments: For plants and animals, scientists often carefully choose which parents to breed together to see how traits are passed on. This usually happens in a laboratory.
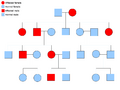
- Family trees: For humans, scientists look at family trees (also called pedigrees). This helps them track how traits appear across many generations in a family.
- Identical twins: Studying identical twins is also helpful because they start with almost the same genetic information. Comparing them can show what traits are mostly due to genes and what traits are more influenced by their environment.
- DNA analysis: Modern science allows us to look directly at DNA and study the entire set of genes, called the genome. This gives us many clues about how traits are inherited.
Images for kids
-
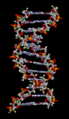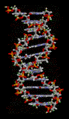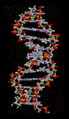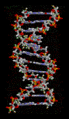
DNA structure. The parts called bases are in the middle, surrounded by phosphate–sugar chains in a double helix.
-
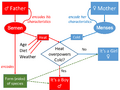
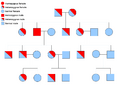
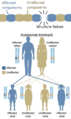
When there are problems with enzymes due to heredity, it's usually passed down in a recessive way. This is because we have two copies of most genes, and often one good copy is enough to prevent problems.
-
However, problems with structural proteins (like in osteogenesis imperfecta or Marfan's syndrome) are often passed down in a dominant way. This means even one faulty gene can cause issues because the whole structure might not work correctly.
See also
 In Spanish: Herencia genética para niños
In Spanish: Herencia genética para niños