Double helix facts for kids
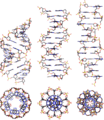
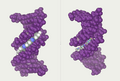
In science, a double helix is a special shape that looks like two spirals twisted around each other. Think of a twisted ladder! This shape is super important because it's how many nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, are built. DNA, which holds all our genetic instructions, is the most famous example of a double helix.
Contents
What is a Double Helix?
A double helix is a geometric shape made of two helices (spirals) that share the same central line. Imagine two corkscrews wrapped around the same invisible pole. These two spirals are slightly offset from each other as they go up or down the pole.
DNA: The Famous Double Helix
When most people hear "double helix," they think of DNA. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It's like the instruction manual for every living thing, telling cells how to grow, work, and reproduce. The double helix shape of DNA is perfect for its job. It helps DNA store a lot of information in a small space.
How DNA Forms a Double Helix
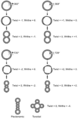
DNA is made of long chains of tiny building blocks called nucleotides. Each nucleotide has a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base. There are four types of bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C).
The two strands of the DNA double helix are held together by these bases. A always pairs with T, and G always pairs with C. These pairs are called base pairs. They act like the rungs of our twisted ladder. This specific pairing is called complementarity. It's why the two strands fit together perfectly.
Why the Double Helix is Important
The double helix structure is vital for life. It helps DNA do two main things:
- Store Information: The order of the base pairs along the DNA strands holds all the genetic instructions.
- Copy Itself: When a cell divides, the two strands of the double helix can separate. Each old strand then acts as a template to build a new, matching strand. This ensures that new cells get an exact copy of the DNA.
This amazing structure was discovered by James Watson, Francis Crick, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins in the 1950s. Their work changed our understanding of biology forever.
Images for kids
-
Two complementary regions of nucleic acid molecules will bind and form a double helical structure held together by base pairs.
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |