Helix facts for kids
In math, a helix is a special kind of curve that goes around in three dimensions. Think of it like a spiral that also moves upwards, like a spring or a screw. Every helix has a straight line in its center called its axis. The curve always stays at the same angle to this central line. You can find helices everywhere, from tiny DNA strands to huge roller coasters and even in nature!
Contents
Different Types of Helices
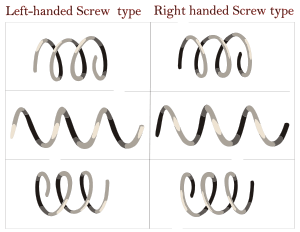
Helices can be either right-handed or left-handed. This is like telling your left hand from your right hand.
Right-Handed vs. Left-Handed Helices
Imagine you are looking straight down the middle (the axis) of a helix.
- If you turn it clockwise, and it moves away from you, it's a right-handed helix.
- If you turn it clockwise, and it moves towards you, it's a left-handed helix.
This "handedness" (also called chirality) is a true property of the helix itself. You can't just turn a right-handed helix to make it look left-handed. You would need to see it in a mirror!
Many common things are right-handed helices:
- Most screw threads on hardware are right-handed.
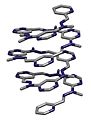
- The common forms of DNA (called A-DNA and B-DNA) are also right-handed.
- However, one type of DNA, called Z-DNA, is left-handed!
Understanding Helix Pitch
The pitch of a helix is how tall one full turn of the helix is. Imagine a spring: the pitch is the distance from one coil to the next, measured straight along the center axis.
What is a Double Helix?
A double helix is made of two helices that share the same central axis. They are usually exactly alike and just shifted a bit along the axis. The most famous example is the structure of DNA.
Other Helix Shapes
There are many other types of helices, each with special features:
- A conic helix spirals around a cone shape. An example is the path of a roller coaster that twists around a central point, like the Corkscrew ride at Cedar Point.
- A circular helix is one that has a constant radius, meaning it's always the same distance from its central axis. Think of a perfect Slinky toy.
- A general helix (or cylindrical helix) is a curve where its direction always makes the same angle with a fixed line in space.
Examples of Helices in Real Life
Helices show up in many unexpected places:
- In music, the way we understand different musical notes and how they relate to each other (like the circle of fifths) is often shown using helices. This helps explain how notes sound similar even when they are higher or lower in octave.
- Many things in nature, like the twisting stems of some climbing plants, grow in a helical shape.
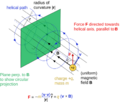
- In physics, tiny charged particles moving through a steady magnetic field often follow a helical path.
- The springs you find in pens or car suspensions are also great examples of helical coils.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hélice (geometría) para niños
In Spanish: Hélice (geometría) para niños