Heteroptera facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Heteroptera |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| A pair of pondskaters mating | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Suborder: |
Heteroptera
Latreille, 1810
|
The Heteroptera are a large and interesting group of insects, often known as "true bugs." There are about 40,000 different kinds of these bugs found all over the world! They are part of a bigger group of insects called Hemiptera.
The name "Heteroptera" comes from Greek words meaning "different wings." This is because most of these bugs have special front wings. The front part of these wings is tough and hardened, while the back part is thin and clear, like a membrane. These unique wings are called hemelytra.
In the world of science, Heteroptera is usually seen as a major group, or suborder, within the Hemiptera order.
Contents
Types of True Bugs
There are many different kinds of true bugs in the Heteroptera group. Here are some well-known families:
- Assassin bugs: These bugs are hunters! They use their strong beaks to catch and eat other insects.
- Broad-headed bugs
- Bedbugs and flower bugs: Bedbugs are tiny insects that feed on blood, usually at night.
- Plant bugs: Many of these bugs feed on plants.
- Leaf-footed bugs, squash bugs and sweetpotato bugs: These bugs can sometimes be pests in gardens.
- Seed bugs: As their name suggests, these bugs often feed on seeds.
- Stink bugs or shield bugs: These bugs are known for releasing a bad smell when they feel threatened.
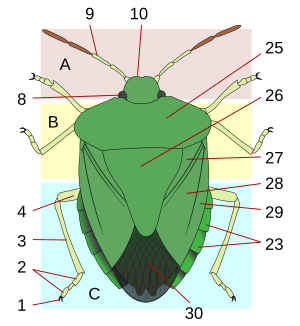
Body Parts of a True Bug
Like all insects, true bugs have bodies divided into three main parts:
- A: Head: This is where the bug's brain, eyes, and mouthparts are located.
- 8: Compound eye: True bugs have large eyes made up of many tiny lenses.
- 9: Antenna: These are like feelers that help the bug sense its surroundings.
- B: Thorax: This is the middle part of the body where the legs and wings are attached.
- 25: Pronotum: This is a shield-like plate on the top of the thorax.
- 26: Scutellum: This is a triangular plate found on the back of the thorax, often between the wings.
- 27: Clavus, 28: Corium, 29: Embolium, 30: Membrane: These are different parts of the special front wings (hemelytra).
- C: Abdomen: This is the last part of the body, which holds many of the bug's organs.
- 1: Claws, 2: Tarsus, 3: Tibia, 4: Femur: These are the different parts of the bug's legs, helping it walk and climb.
Amazing Water Bugs
"Waterbug" is a common name for many different kinds of aquatic insects. These true bugs have adapted to live in water, either on the surface or completely submerged.
Families of Water Bugs
Here are some interesting families of water bugs:
- Backswimmers (Notonectidae): These bugs swim upside down!
- Giant water bugs (Belostomatidae): These are some of the largest true bugs and are fierce predators.
- Water scorpions (Nepidae): Despite their name, they are not scorpions, but they do have a long "tail" used for breathing.
- Water boatmen (Corixidae): These bugs are good swimmers and often feed on algae.
- Pond skaters (Gerridae): These bugs are famous for being able to "skate" across the surface of the water.
- Smaller water strider (Veliidae): Similar to pond skaters, but usually smaller.
See also
 In Spanish: Heteroptera para niños
In Spanish: Heteroptera para niños