Computational chemistry facts for kids
Computational chemistry is a special part of chemistry that uses computer science to help solve problems about chemicals. It uses computers to figure out how molecules and solids are built and what they are like. This field often works with real-life experiments to understand things better.
Computers can even guess what might happen in chemistry before anyone sees it in a lab. This is very helpful for making new drugs and different kinds of materials.
Contents
What Computational Chemistry Can Do
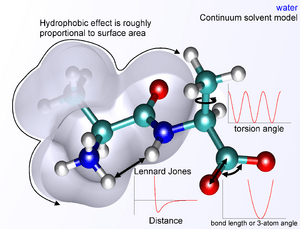
Computational chemistry can guess many things about molecules. It can predict where a molecule's atoms are located. It also figures out how much energy molecules have, both alone and when they interact.
Computers can show how electrons are spread out in a molecule. They can also find out how molecules vibrate, which helps scientists understand them. This field helps predict how chemicals will react with each other. It can even guess how molecules might bump into other tiny particles.
How Computers Study Molecules
Computational chemistry looks at molecules in two ways:
- Static systems: This means looking at molecules when they are still. It helps understand their fixed shapes and properties.
- Dynamic systems: This looks at how molecules move and change over time. It's like watching a tiny movie of their actions.
When scientists study bigger groups of molecules, the computer needs more time and power. This is because there are more things to calculate. The system can be just one molecule, a group of molecules, or even a solid material.
Related Areas of Study
- Bioinformatics: This field uses computers to understand biology.
- Statistical mechanics: This uses math to study how many tiny particles act together.
- Theoretical chemistry: This uses math and physics to explain chemical ideas.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Química computacional para niños
In Spanish: Química computacional para niños