History of the London Underground facts for kids
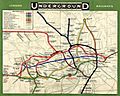
The London Underground, often called the "Tube," has a super interesting history that goes back over 150 years! It's one of the oldest underground railway systems in the world and has changed a lot since it first started. Let's explore some of the most important moments in its journey.
Contents
How the Tube Began
The idea of an underground railway was quite new when the Tube started. People needed a way to travel easily across London.
Early Tunnels and Trains
- 1843
The amazing Thames Tunnel was built by Sir Marc Brunel and his son Isambard Kingdom Brunel. This was an early step towards underground travel.
- 1863
A really big day! On January 10, the Metropolitan Railway opened. This was the world's first underground railway! It ran between Paddington (then called Bishop's Road) and Farringdon Street. Imagine riding a train underground for the very first time!
- 1868
More lines started to open. The Metropolitan District Railway opened its first part, connecting South Kensington to Westminster. Today, this is part of the District and Circle lines.
- 1869
Steam trains began using the Brunels' Thames Tunnel.
- 1880
The first "Tube" tunnel opened, running from the Tower of London to Bermondsey. This was a deeper tunnel, giving the railway its famous nickname.
- 1884
The Circle line was finished, making it easier to travel around central London.
Electric Trains Arrive
Early underground trains used steam, which made a lot of smoke. Electric trains were a big improvement!
- 1890
On December 18, the City and South London Railway opened. This was the world's first deep-level electric railway! It went from King William Street, under the River Thames, to Stockwell. No more smoke underground!
- 1900
The Prince of Wales opened the Central London Railway, also known as the "Twopenny Tube" because of its cheap fare. It ran from Shepherd's Bush to Bank and is now part of the Central line.
- 1902
Many different railway companies joined together to form the Underground Electric Railway Company of London, often called the Underground Group. This helped make the system more organized.
- 1905
The District and Circle lines became electric. This was a big step towards a cleaner, faster Tube.
- 1906
More electric lines opened: the Baker Street & Waterloo Railway (now part of the Bakerloo line) and the Great Northern, Piccadilly & Brompton Railway (now part of the Piccadilly line).
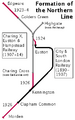
- 1907
The Charing Cross, Euston & Hampstead Railway (now part of the Northern line) opened. This year, Albert Stanley, who later became Lord Ashfield, took charge of the Underground Group.
Growing and Changing
The Tube kept growing and adding new features to make travel better.
- 1908
The word "Underground" started appearing in stations. Also, the famous roundel symbol, which you still see today, was first used!
- 1911
London's first escalators were put in at Earl's Court station. This made it much easier for people to get to and from the platforms.
- 1929
Tube trains got new air-operated doors, replacing the old doors that had to be opened by hand.
- 1933
A very important year! The Underground Group and the Metropolitan Railway joined to form the London Passenger Transport Board. This new group took control of all of London's public transport. Also, Harry Beck created his famous diagram of the Underground map. It's still used today because it's so clear and easy to understand!
The Tube During Wartime
The Tube played a vital role during difficult times, especially during World War II.
- 1940
From September 1940 to May 1945, during World War II, many Tube station platforms were used as air raid shelters. People would go underground to stay safe from bombs. Some parts of the Tube were even closed to store valuable items, like treasures from the British Museum!
Modernizing the Tube
After the war, the Tube continued to change and improve.
- 1948
The London Passenger Transport Board became the London Transport Executive, now owned by the government.
- 1952
The first train made of aluminium started running on the District line. Aluminium trains are lighter and more energy-efficient.
- 1961
Steam trains stopped running on the London Transport passenger lines for good.
- 1969
The Queen opened the Victoria line. This was a very modern line for its time, with automatic trains.
- 1971
The Victoria line was extended to Brixton, making it even more useful for commuters.
- 1975
An accident occurred on the Northern line at Moorgate. After this, new safety measures were put in place to make sure passengers were safer.
- 1977
The Queen opened Heathrow Central station (Terminals 1 2 3) on the Piccadilly line. This made it easy for people to get to the airport by Tube.
- 1979
The Prince of Wales opened the Jubilee line.
- 1980
A museum about the history of underground transport, called the Brunel Engine House, opened to the public.
- 1983
New dot matrix screens were introduced on platforms to show train destinations.
- 1987
A fire occurred at King's Cross station. Following this, new safety and fire regulations were introduced to prevent future incidents and keep everyone safe.
- 1992
The London Underground Customer Charter was launched, focusing on improving service for passengers.
- 1999
The extended Jubilee line opened, offering direct services from Stanmore to Stratford. This was a major expansion!
- 2003
The Oyster card was introduced. This made paying for journeys much easier and faster, as you just tap your card.
- 2005
Bomb attacks occurred on three Tube trains and a bus on July 7. This was a very sad day, and it led to increased security measures across the network.
- 2007
For the first time ever, the Tube carried over one billion passengers in a single year! This shows how important it is to London.
- 2010
The first air-conditioned, walk-through Underground train started running on the Metropolitan line. These new trains are much more comfortable for passengers.
- 2011
A whole new fleet of trains started running on the Victoria Line. Also, Green Park station became "step-free," making it easier for everyone, including those with buggies or wheelchairs, to use the station.
The London Underground continues to be a vital part of London life, always adapting and improving to serve millions of people every day!
Images for kids
-
The Central line opened as the "Twopenny Tube" in 1900. Here, a Northern line train leaves a tunnel mouth near Hendon Central station.
-
Russell Square station is a great example of the design used for many early Underground stations by Leslie Green.
See also
 In Spanish: Historia del Metro de Londres para niños
In Spanish: Historia del Metro de Londres para niños
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |