Hokkaidō facts for kids
Hokkaidō (which means 北海道 in Japanese) is a large island in Japan. It is also sometimes called Ezo or Yezo. Hokkaidō is the most northern of Japan's four main islands. It is known for its many volcanoes.
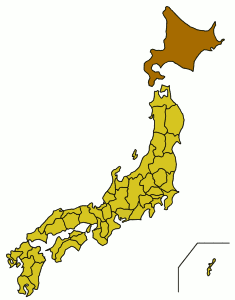
The entire island of Hokkaidō is also a prefecture, which is like a state or province in other countries. This means the island and the Hokkaidō Prefecture share the same name and borders.
Around 5.5 million people live on Hokkaidō. It is located north of Honshū, which is Japan's largest island. Hokkaidō itself is the second largest island in Japan. The island has a humid continental climate. This means it has very cold, snowy winters and warm to hot summers.
Farming is a very important part of Hokkaidō's economy. Many different crops are grown here.
Geography and Climate
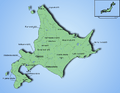
Hokkaidō is a big island with lots of nature. It has many mountains, forests, and beautiful lakes. Because it is so far north, Hokkaidō gets a lot of snow in winter. This makes it a popular place for winter sports like skiing and snowboarding.
In summer, the weather is warm and pleasant. This is a great time to explore the island's national parks and enjoy outdoor activities. The climate helps many different plants and animals to live here.
Life on Hokkaidō
Many people on Hokkaidō work in agriculture. They grow crops like potatoes, corn, and wheat. Dairy farming is also very important, and Hokkaidō is famous for its delicious milk and cheese. Fishing is another big industry, as the island is surrounded by rich waters.
Sapporo is the largest city on Hokkaidō. It is a modern city with many shops, restaurants, and cultural places. Other important cities include Hakodate and Asahikawa.
History of Hokkaidō
For a long time, Hokkaidō was mainly home to the Ainu people. They are the native people of Hokkaidō and have their own unique culture and language. Japanese settlers started moving to Hokkaidō more in the 17th century.
The island was officially named Hokkaidō in 1869. This was when the Japanese government started to develop the island more. Today, the Ainu culture is still an important part of Hokkaidō's history and identity.
Images for kids
-
The samurai and the Ainu, around 1775
-
Matsumae Takahiro, a Matsumae lord from the late Edo period (December 10, 1829 – June 9, 1866)
-
The Ainu, Hokkaidō's native people
-
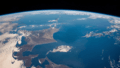
Hokkaido seen from the International Space Station
-
The Oyashio Current colliding with the Kuroshio Current off the coast of Hokkaido. When two currents meet, they create eddies. Tiny phytoplankton growing in the water become concentrated along the edges of these eddies, showing how the water moves.
See also
 In Spanish: Hokkaidō para niños
In Spanish: Hokkaidō para niños