Incense clock facts for kids

Quick facts for kids Incense clock |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 香钟 | ||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 香鐘 | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
An incense clock is a special device used to tell time. It came from China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279). These clocks then spread to nearby countries like Japan and Korea.
Incense clocks are like fancy holders for incense. They use incense sticks or powder that burn at a steady speed. This burning helps measure minutes, hours, or even days. Some clocks even had small bells or gongs. These would ring when a certain amount of time had passed. While other clocks like water clocks were known, incense clocks were very popular in homes and temples in ancient times.
Contents
History of Incense Clocks
Incense clocks were one of many ways people told time in ancient Asia. They were used alongside water clocks and mechanical clocks. The first incense clocks appeared in China around the 6th century. From there, they traveled to Japan. One very old incense clock still exists in Japan today.
Some early incense clocks found in China have carvings that look like they came from India. This made some historians wonder if the idea for incense clocks came from India first. However, no incense clocks have ever been found in India. So, many experts believe that while the carvings might have Indian roots, the Chinese were the ones who invented the clock part of the device.
Types of Incense Clocks
There were two main kinds of incense clocks. These were the stick incense clock and the powdered incense clock. Both types helped people keep track of time in different ways.
How Stick Incense Clocks Work
Stick incense clocks use special incense sticks. These sticks are made to burn at a known, steady speed. Many of these clocks were quite fancy. They sometimes had thin threads with small weights tied to them. These weights were placed at even spaces along the incense stick.
As the incense burned, the thread would break. This would make the weight drop onto a plate or a gong below. The sound would tell people that a certain amount of time had passed. Some clocks even used incense sticks with different smells. This way, a change in scent would mark a new hour.
Incense sticks could be straight or shaped like spirals. The spiral ones were much longer. They were used for measuring longer periods of time. Sometimes, these long spiral clocks hung from the ceilings of homes or temples. In ancient China, people who kept time would even mark incense sticks. They would draw lines on them to show how long they would burn. This helped them sell the sticks to others.
Incense clocks were also used in Traditional Chinese medicine. Doctors would make small breaks in an incense stick. Patients would take their medicine each time the incense burned down to one of these marks. In Japan, entertainers called geisha were paid based on how many "incense clocks" (senko-dokei) had burned while they were present. This practice continued until 1924.
Powdered Incense Clocks Explained
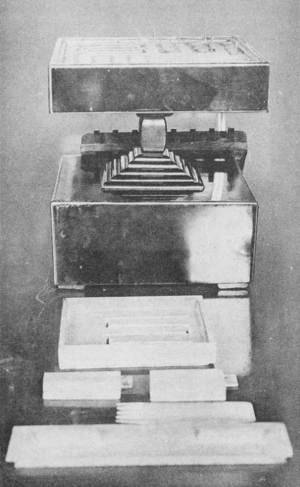
Powdered incense clocks are also called incense seal clocks. They are special containers that burn lines of powdered incense. These lines are shaped like a seal. They were used for similar events as the stick clocks. While often used for religious purposes, they were also popular at social gatherings. Chinese scholars and thinkers enjoyed using them too.
The "seal" was usually a disk made of wood or stone. It had grooves carved into it. People would carefully pour incense powder into these grooves.
These clocks were very common in China. However, fewer of them were made in Japan. To mark time, small pieces of fragrant wood or different scented incense could be placed along the powder trails. When the fire reached these pieces, it would release a new smell. The length of the incense trail was the main thing that decided how long the clock would last. Some could burn for 12 hours, while others could last for a whole month!
At first, incense seals were made of wood or stone. But during the Song dynasty, the Chinese started making them from metal. These metal seals were often made of a material called paktong. They looked like small, layered boxes with pretty patterns on top. Gold and silver powdered incense clocks are very rare today.
Metal seals made it easier for artists to create both large and small designs. They could also make the paths of the grooves different. This allowed the clocks to adjust for the changing length of days throughout the year. As smaller seals became available, these clocks grew even more popular in China. They were often given as gifts.
Today, powdered incense clocks are sought after by clock collectors. However, not many are left outside of museums or temples. Even though they are not used for telling time anymore, scholars and monks in the East still use them. They help create a calm mood and are beautiful to look at.
To set up an incense seal clock, you need to do some preparation. First, a thin layer of damp white wood ash is put into a small container. This ash is then smoothed and gently pressed down. If the seal was a metal stencil, it was placed on the ash. Then, incense powder was poured over it. After lightly pressing the powder, lifting the stencil would leave a long trail of incense powder on the ash. Other seals had a raised pattern. This would create a hollow shape in the ash. Incense powder was carefully spooned into this hollow and then pressed down again with the seal.
See also
- Incense in China
- History of timekeeping devices