Insomnia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Insomnia |
|
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Sleeplessness, trouble sleeping |
 |
|
| Depiction of insomnia from the 14th century medical manuscript Tacuinum Sanitatis | |
| Symptoms | Trouble sleeping, daytime sleepiness, low energy, irritability, depressed mood |
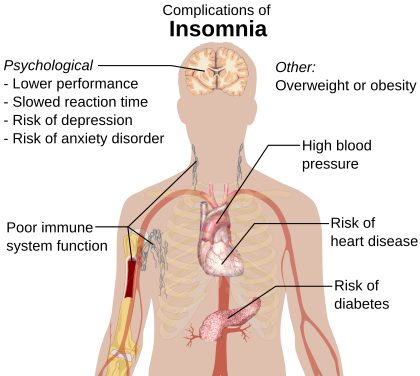
| Complications | Motor vehicle collisions |
| Causes | Unknown, psychological stress, chronic pain, heart failure, hyperthyroidism, heartburn, restless leg syndrome, others |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, sleep study |
| Similar conditions | Delayed sleep phase disorder, restless leg syndrome, sleep apnea, psychiatric disorder |
| Treatment | Sleep hygiene, cognitive behavioral therapy, sleeping pills |
| Frequency | ~20% |
Insomnia, also called sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people find it hard to sleep. This means they might struggle to fall asleep, or they wake up often and can't get back to sleep. When someone has insomnia, they often feel tired during the day, have low energy, get easily annoyed, or feel sad. It can also make it harder to focus and learn new things.
Insomnia can last for a short time, like a few days or weeks, or it can be a long-term problem, lasting more than a month. Sometimes, insomnia happens on its own, and other times, it's caused by another health issue or life event.
What is Insomnia?
Insomnia is more than just a bad night's sleep. It's a real problem where you don't get enough restful sleep, even when you have the chance to sleep. This lack of sleep then causes problems during the day.
Signs and Symptoms of Insomnia
If you have insomnia, you might notice some of these signs:
- Difficulty falling asleep when you go to bed.
- Waking up during the night and finding it hard to go back to sleep.
- Waking up too early in the morning.
- Feeling very sleepy during the day.
- Having low energy or feeling tired all the time.
- Finding it hard to concentrate or remember things.
- Feeling irritable, anxious, or sad.
- Having trouble focusing on schoolwork or daily tasks.
Sometimes, people have trouble falling asleep at the start of the night. This is called sleep onset insomnia. It can be a sign of anxiety. Other times, people wake up in the middle of the night and can't get back to sleep. This is also very common. Waking up much earlier than you want to and not being able to sleep again can be a sign of depression.
What Causes Insomnia?
Insomnia can happen for many reasons. Sometimes, there's no clear reason, and this is called Primary Insomnia. This type might start because of stress, but then it continues even after the stress is gone. This often happens because people get worried about not sleeping, and that worry keeps them awake.
Here are some common things that can cause or be linked to insomnia:
- Sleep breathing problems: Like sleep apnea, where you stop breathing for short times during sleep.
- Medications and substances: Some medicines, caffeine, or nicotine can make it hard to sleep.
- Pain: If you're in pain from an injury or illness, it can be hard to get comfortable and stay asleep.
- Hormone changes: For example, during menstruation or menopause.
- Life events: Things like stress, anxiety, worries about school or family, or losing a loved one can affect sleep.
- Stomach problems: Like heartburn or constipation.
- Mental health conditions: Conditions like clinical depression, anxiety, PTSD, or ADHD can often lead to sleep problems.
- Changes in your body clock: Working night shifts or experiencing jet lag can mess up your natural sleep rhythm.
- Other health conditions: Such as hyperthyroidism (an overactive thyroid gland).
- Poor sleep habits: Things like a noisy bedroom, drinking too much caffeine, or using phones/computers late at night.
- Too much blue light: Spending a lot of time looking at screens (phones, tablets, computers) before bed can make it harder to sleep because of the blue light they give off.
- Lack of exercise: While exercise is good, intense exercise right before bed can sometimes make it hard to fall asleep.
Scientists have found that people with insomnia often have higher levels of certain stress hormones in their bodies, even during the night. Their brains also seem to be more active. It's still being studied whether these changes cause insomnia or are a result of it.
How Can We Prevent Insomnia?
Preventing and treating insomnia often involves a mix of different approaches. These can include changing your habits, trying special types of therapy, and sometimes using medicines.
Here are some lifestyle habits that can help prevent insomnia:
- Stick to a schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps set your body's internal clock.
- Exercise regularly: Being active during the day can help you sleep better at night. Just avoid very intense exercise a few hours before bedtime.
- Watch what you eat and drink: Avoid large meals, sugary drinks, alcohol, and nicotine close to bedtime.
- Create a good sleep environment: Make your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool. Keep electronic devices like phones and TVs out of your bedroom.
- Relax before bed: Try calming activities like reading a book, taking a warm bath, or listening to quiet music.
- Limit naps: If you must nap, keep it short (20-30 minutes) and not too close to bedtime.
How is Insomnia Managed?
Before treating insomnia, doctors usually check for any other medical or mental health problems that might be causing it.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
This is often the first and best treatment for long-term insomnia. CBT-I helps you change the thoughts and behaviors that keep you from sleeping well. It teaches you how to improve your sleep habits and deal with worries about sleep. The good thing about CBT-I is that its positive effects can last a long time, even after you stop the therapy.
Sleep Hygiene
Sleep hygiene refers to all the good habits that help you get a healthy night's sleep. These habits create a strong foundation for sleep and can help prevent insomnia. Sleep hygiene tips are often part of CBT-I. They include things like reducing caffeine, having a regular sleep schedule, exercising, and making your bedroom a good place for sleep.
Medications
Sometimes, doctors might prescribe sleeping pills to help with short-term insomnia. However, these medicines are usually not recommended for long-term use. It's also important to treat any other health conditions, like depression or chronic pain, that might be making your insomnia worse.
Who Gets Insomnia?
Insomnia is very common. About 10% to 30% of adults experience insomnia at any given time. Up to half of all people will have insomnia at some point in a year. Around 6% of people have long-term insomnia that isn't caused by another health problem.
Older people (over 65) tend to have insomnia more often than younger people. Also, women are more likely to be affected by insomnia than men. In fact, it's about 40% more common in women. University students also report higher rates of insomnia compared to the general population.
Descriptions of insomnia have been found in writings from as far back as ancient Greece.
Images for kids
-
Depiction of insomnia from the 14th century medical manuscript Tacuinum Sanitatis
See also
 In Spanish: Insomnio para niños
In Spanish: Insomnio para niños
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |