Kalinga (India) facts for kids
Kalinga is an ancient region in India that has a long and interesting history. It's mostly found along the eastern coast of India, between two big rivers called the Mahanadi and the Godavari. Today, this area covers a large part of Odisha and the northern part of Andhra Pradesh. Sometimes, when Kalinga was at its biggest, it even included parts of modern-day Chhattisgarh.
The people of Kalinga, known as the Kalingas, were mentioned as an important group in the famous ancient Indian story, the Mahabharata.
Contents
Kalinga's History
The Mauryan Empire and the Kalinga War
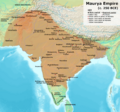
Around 3rd century BCE, Kalinga became part of the powerful Maurya Empire. This happened after a very famous and fierce battle known as the Kalinga War. This war was fought by Emperor Ashoka, who was a Mauryan ruler. After seeing the terrible destruction and loss of life in the Kalinga War, Emperor Ashoka felt very sad and decided to stop fighting wars. He then became a follower of Buddhism and spread its message of peace.
Rulers of Kalinga
Over time, Kalinga was ruled by many different local families, or dynasties. The rulers of these dynasties often used a special title: Kalingadhipati, which means "Lord of Kalinga."
Some of the important dynasties that ruled Kalinga included:
- Mahameghavahana
- Vasishtha
- Mathara
- Pitrbhakta
- Shailodbhava
- Somavamsi
- Eastern Ganga
There was also another important dynasty called the Bhauma-Karas. Even though they were powerful in the region, they didn't call their kingdom Kalinga.
Kalinga Becomes Part of Larger Empires
At different times, the Kalinga region also became a part of bigger empires that covered much larger areas of India. After the Eastern Ganga dynasty, Kalinga slowly started to lose its unique political identity. This means it became less of a separate kingdom and more integrated into the larger empires around it.
Images for kids
-
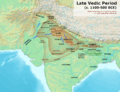
Kalinga located in eastern Indian coast, in Vedic Period in c.1100 BCE
-
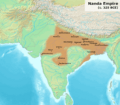
Possible extent of the Nanda Empire under its last ruler Dhana Nanda
-
Gupta Empire on its zenith in 350 CE, under Samudragupta
See also
 In Spanish: Kalinga para niños
In Spanish: Kalinga para niños