Khoisan languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Khoisan |
|
|---|---|
| Khoesaan | |
| Geographic distribution: |
Kalahari Desert, central Tanzania |
| Linguistic classification: | (term of convenience) |
| Subdivisions: |
Khoe–Kwadi
Kxʼa
Tuu
Sandawe
Hadza
|
| ISO 639-2 and 639-5: | khi |
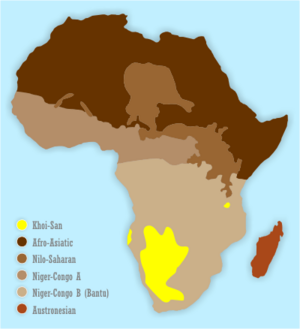 Map showing the ancestral distribution of the Khoisan languages (yellow)
|
|
The Khoisan languages (pronounced KOY-sahn) are a group of languages found in Africa. They were once thought to be part of one big language family. This idea was first suggested by a linguist named Joseph Greenberg.
What makes Khoisan languages special is that they all use unique sounds called click consonants. These sounds are made by clicking your tongue in different ways. However, experts now agree that these languages are not all related in the same way. Instead, they are made up of three different language families and two languages that stand alone.
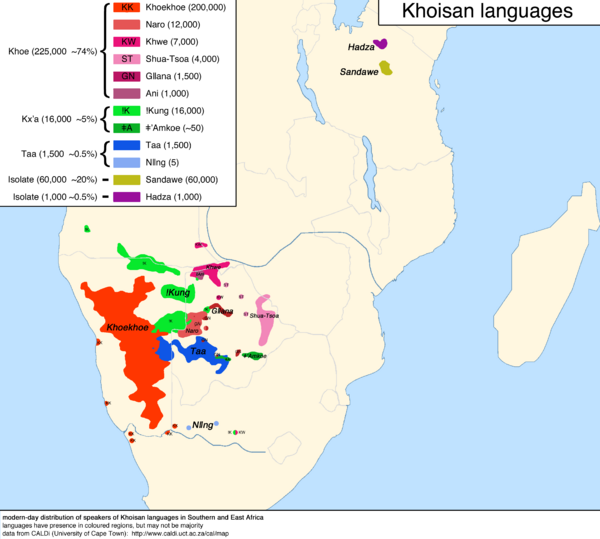
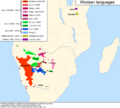
Most Khoisan languages come from southern Africa. They are spoken by people like the Khoikhoi and the San (also known as Bushmen). Two other languages, Sandawe and Hadza, are spoken in eastern Africa. Even though they have clicks, the people who speak them are not ethnically Khoikhoi or San.
Long ago, languages like Khoisan were probably spoken all over southern and eastern Africa. Today, you mostly find them in the Kalahari Desert. This area is mainly in Namibia and Botswana. You also find them in the Rift Valley in central Tanzania.
Many of these languages are in danger of disappearing. Some are spoken by very few people, and some have already died out. Most Khoisan languages were never written down. The most widely spoken Khoisan language is Khoekhoe. It has about 250,000 speakers in Namibia, Botswana, and South Africa. Sandawe in Tanzania is next, with about 40,000 to 80,000 speakers.
Khoisan languages are famous for their click sounds. These clicks are part of the words themselves. They are written with special symbols like ǃ and ǂ. Because clicks can be made in many ways, Khoisan languages often have a lot of different consonant sounds. For example, the Juǀʼhoan language has 48 click sounds!
Contents
Are Khoisan Languages a Single Family?
The idea of Khoisan as one big language family was first suggested in the mid-1900s. But many linguists who study these languages now disagree. They use the name "Khoisan" more as a convenient way to group them. It does not mean they are all related through a shared ancestor.
Experts like Bonny Sands and Anthony Traill have studied these languages closely. They found that there isn't enough proof to show that all Khoisan languages come from one common language. The main reason they were grouped together was because they all have click sounds. However, having clicks doesn't automatically mean they are related.
Today, most scholars believe that the three main southern groups are separate language families. They cannot be shown to be related to each other.
How Different Are Khoisan Languages?
Even though they all have clicks, Khoisan languages can be very different from each other. Linguist Anthony Traill showed this by comparing words from different Khoisan language groups.
Here is a table showing some words from different Khoisan languages:
| Sandawe | Hadza | Khoe | Ju | ǃXóõ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'person' | ǀnomese | ʼúnù | khoe | ʒú | tâa |
| 'man' | ǀnomese | ɬeme | kʼákhoe | ǃhõá | tâa á̰a |
| 'child' | ǁnoό | waʼa | ǀūá | dama | ʘàa |
| 'ear' | kéké | ɦatʃʼapitʃʼi | ǂée | ǀhúí | ǂnùhã |
| 'eye' | ǀgweé | ʼákhwa | ǂxái | ǀgàʼá | ǃʼûĩ |
| 'ostrich' | saʼútà | kénàngu | ǀgáro | dsùú | qûje |
| 'giraffe' | tsʼámasu | tsʼókwàna | ǃnábe | ǂoah | ǁqhūũ |
| 'buffalo' | ǀeu | nákʼóma | ǀâo | ǀàò | ǀqhái |
| 'to hear' | khéʼé | ǁnáʼe | kúm | tsʼàʼá | tá̰a |
| 'to drink' | tsʼee | fá | kxʼâa | tʃìi | kxʼāhã |
The Different Khoisan Language Families
The groups of languages once called "Khoisan" are now seen as separate families. This is because we cannot prove they are related using standard language comparison methods.
Hadza Language
The Hadza language is spoken by about 800 people in Tanzania. It is no longer considered a Khoisan language. It seems to be unrelated to any other language family. The Hadza people are also not related to the Khoisan people of Southern Africa.
Sandawe Language
Sandawe is spoken by about 40,000 people in Tanzania. There are some signs that it might be related to the Khoe family. For example, they have similar pronoun systems. However, there is not enough evidence to fully prove this link. Sandawe is not related to Hadza, even though they are spoken close to each other.
Khoe Language Family
The Khoe family is the largest and most diverse group of Khoisan languages. It has seven living languages and over 250,000 speakers.
- ?Khoe–Kwadi
- Kwadi (This language is now extinct.)
- Khoe
- Khoekhoe
- Nama (This includes dialects like ǂAakhoe and Haiǁom.)
- Eini (This language is now extinct.)
- South Khoekhoe
- Khoekhoe
*Korana (Very few speakers left.) *Xiri (Very few speakers left; it's a group of dialects.)
-
-
- Tshu–Khwe (Also called Kalahari) Many of these languages have lost some of their click sounds.
- East Tshu–Khwe (East Kalahari)
- Tshu–Khwe (Also called Kalahari) Many of these languages have lost some of their click sounds.
-
*Shua (A group of dialects like Deti, Tsʼixa, ǀXaise, and Ganádi.) *Tsoa (A group of dialects like Cire Cire and Kua.)
-
-
-
- West Tshu–Khwe (West Kalahari)
-
-
*Kxoe (A group of dialects like ǁAni and Buga.) *Naro (A group of dialects, including ǂHaba.) *Gǁana–Gǀwi (A group of dialects like Gǁana and Gǀwi.)
The Haiǁom people used to speak a Ju dialect, similar to ǃKung. But now they speak a different dialect of Nama. So, their language is sometimes said to be extinct or to have 18,000 speakers, depending on how you look at it.
Tuu Language Family
The Tuu family has two main groups of languages. They are similar to the Kxʼa languages (see below). However, it has not been proven that they are related by ancestry. The similarities might be because they are spoken in the same area.
- Tuu
- Taa
- ǃXoon (4,200 speakers. It's a group of dialects.)
- Lower Nossob (Two dialects, ǀʼAuni and ǀHaasi. Both are extinct.)
- ǃKwi
- Nǁng (Only 1 speaker left. It's a group of dialects.)
- ǀXam (A group of dialects. Extinct.)
- ǂUngkue (A group of dialects. Extinct.)
- ǁXegwi (Extinct.)
- Taa
Kxʼa Language Family
The Kxʼa family is a group of languages that were shown to be related in 2010.
- Kxʼa
- ǂʼAmkoe (200 speakers in Botswana. It's dying out. It includes dialects like Nǃaqriaxe, (Eastern) ǂHoan, and Sasi.)
- ǃKung (Also called ǃXun or Ju). This is a group of dialects with about 45,000 speakers. Juǀʼhoan is the most well-known dialect.
Other Languages with Clicks
Not all languages that use clicks are considered Khoisan. Many other languages that use clicks are neighboring Bantu languages in southern Africa. These include languages like Xhosa, Zulu, and Sotho.
These Bantu languages likely adopted clicks from Khoisan people they lived near. This often happened through marriage or when groups mixed. There is also the South Cushitic language Dahalo in Kenya, which has a few click sounds. It's thought that Dahalo speakers kept clicks from an older language they spoke before.
Images for kids