Bantu languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Bantu |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution: |
Subsaharan Africa, mostly Southern Hemisphere |
| Linguistic classification: | Niger–Congo
|
| Subdivisions: |
Northeast Bantu
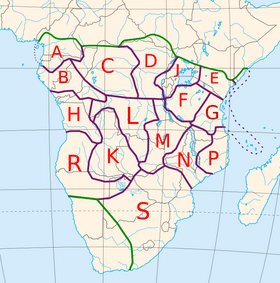
Zones A–S (geographic)
Central Bantu (in doubt)
Northwest Bantu (in doubt)
|
| ISO 639-2 and 639-5: | bnt |
| [[File:
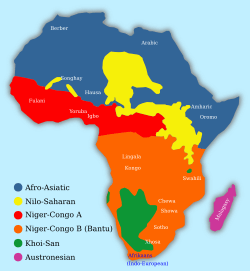
Map showing the approximate distribution of Bantu vs. other Niger-Congo languages.|300px]] |
|
The Bantu languages are a large group of languages spoken by millions of people in Africa. They are part of an even bigger language family called Niger-Congo languages. There are about 520 different Bantu languages! Most of these languages are spoken in central, eastern, and southern Africa.
The Bantu language with the most total speakers is Swahili. It is widely used in East Africa. The Bantu language with the most native speakers is Shona. About 13.8 million people speak Shona in countries like Zimbabwe and Mozambique. Zulu is another major Bantu language, with 10.3 million speakers.
Bantu languages first came from the area of eastern Nigeria or Cameroon. Around 2000 years ago, people who spoke Bantu languages began to move south and east. As they moved, they shared new ideas like farming and working with iron. This helped shape much of the African continent.
Bantu Words in Other Languages
Some words from Bantu languages have become popular in other languages, including English. Here are a few examples you might know:
- Kwanzaa
- Marimba (a musical instrument)
- Safari (meaning a journey or expedition)
- Samba (a type of dance and music)
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas bantúes para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas bantúes para niños