La Plata, Huila facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
La Plata, Huila
San Sebastian de la Plata
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Municipality and town
|
|||
 |
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
La Plata, Huila
|
|||
| Motto(s):
Huila Folk of Paradise
|
|||
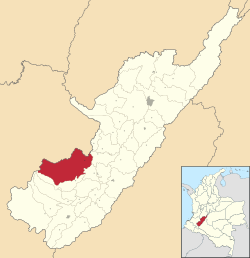
Location of the municipality and town of La Plata, Huila in the Huila Department of Colombia.
|
|||
| Country | |||
| Department | Huila Department | ||
| Area | |||
| • Municipality and town | 814.6 km2 (314.5 sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 3.47 km2 (1.34 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 1,050 m (3,440 ft) | ||
| Population
(2018 census)
|
|||
| • Municipality and town | 61,026 | ||
| • Density | 74.915/km2 (194.030/sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 25,791 | ||
| • Urban density | 7,433/km2 (19,250/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Colombia Standard Time) | ||
| Website | http://www.facebook.com/LaPlataHuilaColombia - http://www.laplata-huila.gov.co | ||
La Plata is a town and municipality in the Huila Department, Colombia. It is home to about 61,000 people, including those living in nearby rural areas (2018 census). The town is located at an altitude of 1,050 meters.
La Plata is about 122 km from Neiva, 147 km from Popayán, and 210 km from San Agustín. It sits in the southwestern part of the Huila region, at the foot of the Central Mountain Range.
The municipality shares its northern and western borders with the Cauca Department. To the south, it borders La Argentina, and to the east, it borders Paicol and Pital.
Contents
History of La Plata
La Plata was officially founded on June 5, 1651, by Captain Diego de Ospina y Maldonado. He also organized the local church, called the parish of San Sebastián de La Plata.
The town's name comes from the discovery of silver mines in the area. Spanish explorers were very interested in finding these valuable metals.
How La Plata was founded multiple times
La Plata has a unique history because it was founded three times!
- The first founding happened on October 22, 1553, due to a rebellion against the Spanish crown.
- The second was in early 1554, linked to the mining and trading of silver.
- The third time was on June 17, 1577, after the town was destroyed by local indigenous groups like the Paez, Andaquíes, and Yalcones.
La Plata is a very historic place. Even Simón Bolívar, a famous leader who helped South American countries gain independence, visited the town many times. He often stayed at nearby plantations. There is also a special religious site close to the city called 'la Quiebra Milagrosa'.
History of the San Sebastian Cathedral
The main church in La Plata is the Cathedral of San Sebastian. Several smaller churches were built before it. The impressive building we see today started being built in the early 1900s.
The first stone was laid on October 3, 1934. The church was officially blessed and opened on April 29, 1957. The San Sebastian Cathedral is known for its beauty and grand size. It has three main sections inside that fit together perfectly.
At the front, there are two tall towers, each 52 meters high. At the back, there is a large, round dome with many windows. A huge statue of San Sebastian, 5.40 meters tall, stands at the top of the central part of the church. Inside, the church is 60 meters long and 30 meters wide. It is filled with light and beautiful decorations.
La Plata's Culture
La Plata has a rich history and strong traditions. Its location makes it a busy meeting point for people from different areas. This helps the town grow and change while still keeping its old customs alive.
Places to Visit
La Plata offers many interesting places for visitors to explore.
- National Park Puracé
- Moscopan monolithic statues
- Aguabonita statues
- Laguna de San Rafael (San Rafael Lake)
- San Andres lagoon (San Andres Lake)
- The River of Silver
- Custodio García Rovira Park
- Pola Park
- The Sulfur Waterfall
- The Candelaria Waterfall
- The Monkey Waterfall
- San Nicolas and Bedon Waterfalls
- San Sebastian hot springs
- San Sebastian Cathedral
- The temple in San Andres Piedra
Nature and Wildlife
La Plata is home to a rich variety of plants and animals. Its ecosystems are very important for wildlife.
- You can find many types of birds here.
- Some animals include antelopes, spectacled bears, and smaller wild cats like ocelots.
- There are also different kinds of snakes, such as jackets and coral snakes.
The area near the Nevado del Huila Natural Park is very important. It has a lot of different plants and provides a lot of water. San Isidro is a large area of forest, about 412.5 hectares. It has trees like black cedar, butter trees, and apple trees. You can also find animals like the Pava Guiche bird, tigrillos (small wild cats), foxes, and squirrels.
Tourism in La Plata
La Plata has many natural attractions that draw visitors.
- Azufrada Dos Aguas Archaeological Zone: This area is located in San Vicente and is important for its history.
- Thermal Cascada San Sebastian de la Mona: This waterfall gets its name from the hot spring that forms it.
- Private Reserve Meremberg: This reserve means "sea of mountains." It is the biggest source of water for the municipality. It has natural forests with cedar and oak trees, along with lagoons and swamps.
- Cascada de La Candelaria: This stunning waterfall drops over 150 meters high.
Economy
The economy of La Plata is mainly based on farming and raising livestock.
Livestock Farming
Livestock farming happens in two main areas:
- Warm areas (460 to 1,200 meters above sea level)
- Cold areas (1,800 to 2,500 meters above sea level)
These areas cover about 56,460 hectares. Farmers mostly raise cattle for both meat and milk. They also raise pigs and do some fish farming.
Agriculture
Agriculture is a very important part of La Plata's economy. The main crops grown here include:
- Rice
- Coffee (often grown with bananas)
- Bananas
- Cacao (also grown with bananas)
- Corn
- Sugarcane
- Beans
- Potatoes
Farmers also grow various fruits like lulos, tree tomatoes, and blackberries.
Education
La Plata offers many educational opportunities for its young people.
Schools
- Departmental Marillac Educational Institution
- Educational Institution San Sebastian
- Agricultural Technical Educational Institution
- Educational Institution Luis Carlos Trujillo Polanco
- Educational Institution Misael Pastrana Borrero
- Business School of the Andes
- Creative World School
- School Evita Roso de Palacios
- Modern Lyceum Plateño
- José Celestino Mutis Institute
Higher Education
For students who want to continue their studies after high school, La Plata has several options:
- SENA
- Universidad Surcolombiana
- UNAD Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia
- Universidad Minuto de Dios
- Corporación Universitaria Remington
Climate
| Climate data for La Plata (Esc Agr La Plata), elevation 1,070 m (3,510 ft), (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 28.2 (82.8) |
29.0 (84.2) |
28.6 (83.5) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.4 (83.1) |
28.2 (82.8) |
27.9 (82.2) |
28.7 (83.7) |
29.6 (85.3) |
29.1 (84.4) |
28.0 (82.4) |
28.1 (82.6) |
28.5 (83.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 22.1 (71.8) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.4 (72.3) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.3 (72.1) |
21.8 (71.2) |
21.7 (71.1) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.2 (72.0) |
22.1 (71.8) |
22.2 (72.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 17.6 (63.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
18.0 (64.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
18.0 (64.4) |
17.4 (63.3) |
16.8 (62.2) |
16.6 (61.9) |
16.8 (62.2) |
17.6 (63.7) |
18.1 (64.6) |
17.8 (64.0) |
17.6 (63.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 144.3 (5.68) |
149.8 (5.90) |
169.4 (6.67) |
168.8 (6.65) |
139.8 (5.50) |
84.7 (3.33) |
67.9 (2.67) |
46.0 (1.81) |
71.4 (2.81) |
155.4 (6.12) |
164.5 (6.48) |
151.2 (5.95) |
1,513.2 (59.57) |
| Average precipitation days | 16 | 17 | 21 | 21 | 22 | 19 | 18 | 14 | 14 | 19 | 21 | 19 | 213 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83 | 81 | 82 | 83 | 83 | 82 | 79 | 75 | 73 | 78 | 83 | 84 | 80 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 151.9 | 127.0 | 114.7 | 111.0 | 124.0 | 117.0 | 120.9 | 127.1 | 126.0 | 133.3 | 129.0 | 148.8 | 1,530.7 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 4.9 | 4.5 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.8 | 4.2 |
| Source: Instituto de Hidrologia Meteorologia y Estudios Ambientales | |||||||||||||
See also
 In Spanish: La Plata (Huila) para niños
In Spanish: La Plata (Huila) para niños