Lake Vermont facts for kids
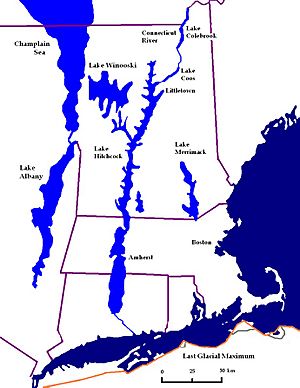
Lake Vermont, also known as Glacial Lake Vermont, was a huge, temporary lake. It formed at the end of the last ice age as giant glaciers melted and moved back. This ancient lake covered parts of what is now Quebec in Canada. It also stretched into the American states of Vermont and New York.
Lake Vermont was like an older version of today's Lake Champlain. As the glacier kept moving north, Lake Vermont eventually drained. Its water flowed into another ancient lake called Glacial Lake Candona. This lake later became the St. Lawrence River.
Contents
Where Was Lake Vermont?
At its largest, Lake Vermont stretched very far south. It reached almost to where the city of Albany, New York is today. The surface of this massive lake was about 500 feet (150 m) higher than Lake Champlain is now. In some places, Lake Vermont was incredibly deep, up to 900 feet (270 m)!
What Was the Lake Like?
The water in Lake Vermont was very muddy. This was because it carried a lot of fine dirt and rock from the melting glaciers. The bottom of the lake collected layers of this mud. These layers are called varves.
Varves are like natural calendars. Each year, a new layer formed. During the warmer summer months, silt settled down. In the colder winter, when the water moved less, finer clay settled. Scientists can study these layers to learn about the ancient climate.
How Lake Vermont Formed and Disappeared
Lake Vermont began to form around 13,500 years ago. This was when the huge Laurentide Ice Sheet started to melt and move north. The ice sheet had blocked the water at the northern end of the lake. This created a natural dam.
The Great Flood
About 12,000 years ago, something dramatic happened. The ice dam, located near what is now Warwick, Quebec, broke apart. This caused a huge, sudden flood. The lake's water level dropped by about 300 feet (91 m)! This massive drop happened incredibly fast, within just hours or a few days.
From Fresh to Saltwater
As the glacier continued to retreat further north, the landscape changed again. Saltwater from the ocean swept in. This saltwater replaced the freshwater of Lake Vermont. This is how the smaller, saltwater Champlain Sea was formed. The Champlain Sea was a temporary sea that existed after Lake Vermont.