Great Recession facts for kids
The Great Recession was a big worldwide economic slowdown. It happened from the late 2000s into the early 2010s. Think of it like a time when many countries' economies got sick.
This economic problem caused many difficulties. Some countries, like Italy and Greece, felt its effects for a very long time. The Great Recession was the worst global economic downturn since World War II.
It affected different countries in different ways. Some nations, like China, India, South Korea, Poland, and Australia, managed to avoid a recession during this time. But for many others, it led to problems like families owing a lot of money, low pay, and many people losing their jobs.
Contents
What Was the Great Recession?
The Great Recession was a period when the world's economy slowed down a lot. A "recession" means that a country's economy stops growing and starts to shrink. This can lead to businesses closing and people losing their jobs.
This particular recession was called "Great" because it was so widespread and severe. It impacted almost every part of the world.
When Did It Happen?
The Great Recession began around 2007 and lasted until about 2009. However, its effects were felt for many years after that. Some countries took a long time to recover fully.
How Did It Start?
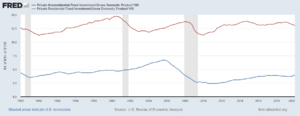
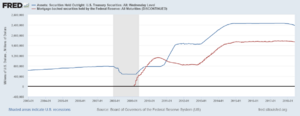
The Great Recession had many causes, but a big one was problems in the housing market. In some countries, like the United States, house prices had gone up very quickly. Many people borrowed a lot of money to buy homes.
When house prices started to fall, people found themselves owing more money than their homes were worth. This led to many people being unable to pay back their loans.
The Housing Bubble and Banks
Banks had lent a lot of money for these homes. They also bought and sold complex financial products related to these loans. When people couldn't pay, banks started to lose a lot of money.
This made banks nervous about lending money to each other. It also made them nervous about lending money to businesses and people. This lack of lending made the economic problems even worse.
What Were the Effects?
The Great Recession had many serious effects around the world.
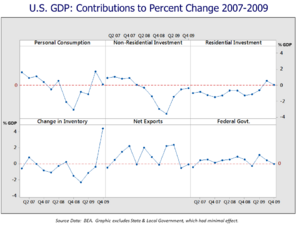
Job Losses and Unemployment
One of the biggest impacts was on jobs. Many businesses had to cut back or close down. This led to high levels of unemployment, meaning many people could not find work.
When people don't have jobs, they have less money to spend. This further slows down the economy.
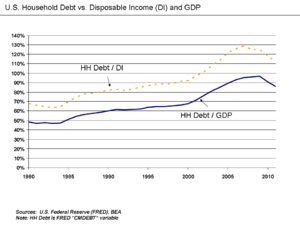
Household Debt and Wages
Families found themselves with a lot of "household debt." This means they owed a lot of money on things like mortgages, credit cards, and car loans.
At the same time, wages (the money people earn from their jobs) often stayed low. This made it harder for families to pay off their debts.
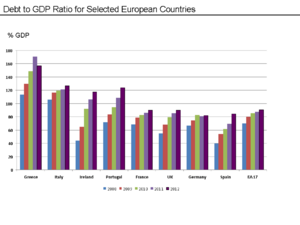
Impact on Different Countries
The recession hit some countries much harder than others.
- The United States experienced a severe downturn.
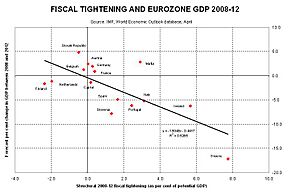
- Countries in Southern Europe, like Greece and Italy, faced very difficult economic times.
- However, some countries, such as Australia, managed to keep their economies strong.
How Did Countries Respond?
Governments and central banks around the world took action to try and fix the economy. They tried different ways to help banks and encourage spending.
For example, central banks lowered interest rates. This made it cheaper for people and businesses to borrow money. Governments also spent money on projects to create jobs.
Recovery and Long-Term Effects
The world economy slowly started to recover after 2009. However, the Great Recession left lasting effects. Many countries still faced challenges like high debt and slow economic growth years later.
The recession also changed how governments and banks manage money. They put new rules in place to try and prevent a similar crisis from happening again.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Gran Recesión para niños
In Spanish: Gran Recesión para niños
 | James B. Knighten |
 | Azellia White |
 | Willa Brown |