Lateral line facts for kids
The lateral line is a special sense organ that most fish have. It helps them feel what's happening in the water around them. Think of it like a built-in radar system! This amazing organ helps fish detect movement, changes in water pressure, and even tiny vibrations. It's super important for how fish live and survive underwater.
This system is made of tiny, sensitive cells called hair cells. These cells are like tiny microphones. They pick up signals from the water. Then, they send these signals as electrical messages to the fish's brain. This way, the fish knows what's going on, even in dark or murky water.
Contents
What is the Lateral Line?
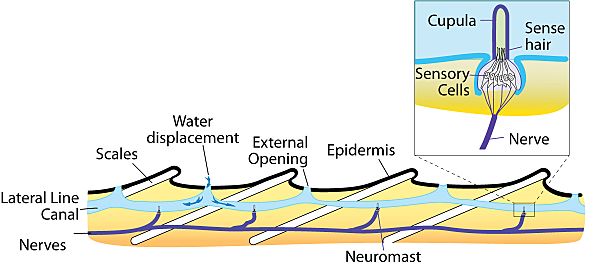
The lateral line looks like a faint line running along each side of a fish's body. It goes from just behind their gills all the way to the base of their tail. This line isn't just a mark. It's a row of tiny pores or openings. These openings lead to canals just under the skin. Inside these canals are the special hair cells.
These hair cells are covered by a jelly-like cap. When water moves or vibrates, it pushes on this cap. This movement bends the hair cells. When the hair cells bend, they create an electrical signal. This signal then travels to the fish's nervous system. This tells the fish about the movement.
Why is it Important for Fish?
The lateral line is vital for many things fish do every day.
Finding Food
Fish use their lateral line to find food. For example, if a small fish swims away quickly, it creates tiny swirls or "vortices" in the water. A predator fish can feel these swirls with its lateral line. This helps the predator follow and catch its prey, even if it can't see it.
Staying Safe
This sense also helps fish avoid danger. They can feel the approach of a larger predator. This gives them time to swim away quickly. It's like having eyes all over their body.
Swimming in Groups
Many fish swim together in large groups called schools. The lateral line helps them do this. Each fish can feel the movements of the fish next to it. This allows them to swim in perfect sync. They can turn and move as one big unit. This makes it harder for predators to catch them.
The lateral line also helps fish know where they are. It helps them sense currents and obstacles. This is especially useful in dark water or at night. It helps them navigate without bumping into things.
Electroreception: A Special Use
In some fish, the lateral line system has a special ability. It can detect tiny electrical impulses. These modified organs are called electroreceptors. Some fish, like sharks and rays, use these to find prey. Many animals give off small electrical fields. These fish can "feel" these fields. This helps them find prey hidden in the sand or mud.
Lateral Line in Amphibians
While land animals don't have a lateral line, some amphibians do. Young amphibians, like tadpoles, have a system similar to the lateral line. Some adult amphibians that live mostly in water also keep this sense. It helps them feel vibrations and movements in the water, just like fish.
Images for kids
-
Oblique view of a goldfish (Carassius auratus), showing pored scales of the lateral line system
-
The small holes on the head of this Northern pike (Esox lucius) contain neuromasts of the lateral line system.
-
Some scales of the lateral line (center) of a Rutilus rutilus.
-
A three-spined stickleback with stained neuromasts
See also
 In Spanish: Línea lateral para niños
In Spanish: Línea lateral para niños