List of the prehistoric life of Alabama facts for kids
Alabama is a state in the southeastern United States. It has a rich history of ancient life, with many amazing fossils found there. These fossils tell us about the plants and animals that lived in Alabama millions of years ago, long before humans existed. Scientists study these fossils to understand how life on Earth has changed over time. This list explores some of the incredible prehistoric creatures whose remains have been discovered in Alabama.
Contents
Ancient Life from the Paleozoic Era
The Paleozoic Era was a very long time ago, lasting from about 541 to 252 million years ago. During this era, life mostly lived in the oceans, but plants and animals also started to move onto land. Alabama has many fossils from this period, showing us what these early life forms looked like.
Plants of the Paleozoic Era
Some of the most common plant fossils found in Alabama from the Paleozoic Era are from ancient ferns and tree-like plants.
- Alethopteris: This was a type of ancient seed fern. Its fronds (leaves) looked a bit like modern ferns.
- Calamites: These were giant relatives of modern horsetails. They grew tall like trees and had segmented stems.

- Lepidodendron: Often called "scale trees," these were huge club mosses that could grow very tall. Their trunks had a unique scale-like pattern.

- Sigillaria: Another type of giant club moss, similar to Lepidodendron. They also had tall, scarred trunks.

- Sphenopteris: This was another group of ancient seed ferns with delicate, fern-like leaves.
Animals of the Paleozoic Era
Many different types of animals lived in Alabama during the Paleozoic Era, especially in the ancient seas.
- Ctenacanthus: This was an ancient shark that lived during the Carboniferous period. Fossils of its spines and teeth have been found.
- Paladin: Trilobites were ancient marine creatures with hard, segmented bodies. They are related to modern crabs and insects.
- Pentremites: These were small, star-shaped marine animals related to starfish and sea urchins. They lived on the seafloor.
Amazing Creatures of the Mesozoic Era
The Mesozoic Era, often called the "Age of Dinosaurs," lasted from about 252 to 66 million years ago. During this time, dinosaurs roamed the land, and huge marine reptiles swam in the seas. Alabama has important fossils from this era, especially from the Late Cretaceous period.
Dinosaurs and Other Land Animals
While Alabama is not famous for many dinosaur fossils, some important discoveries have been made.
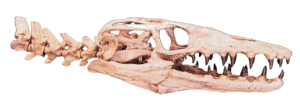
- Appalachiosaurus: This was a primitive tyrannosaur, a meat-eating dinosaur, that lived in what is now eastern North America. Its fossils were first found in Alabama.
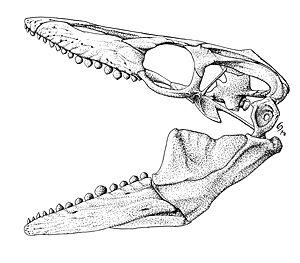
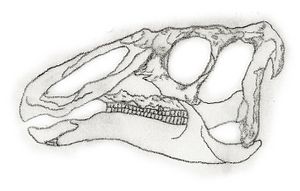
- Eotrachodon: This was an early type of duck-billed dinosaur (hadrosaur). Its discovery in Alabama helped scientists understand how duck-billed dinosaurs evolved.
- Lophorhothon: Another duck-billed dinosaur, Lophorhothon was one of the first dinosaurs found in eastern North America. Its skull had a small crest.
Marine Reptiles and Fish
The ancient seas covering Alabama during the Mesozoic Era were home to many large and fearsome marine animals.
- Baculites: These were straight-shelled ammonites, a type of ancient cephalopod related to modern squid and octopuses. Their shells grew in a straight line instead of a coil.
- Belonostomus: This was a long, slender bony fish that lived in the seas. It had a pointed snout.
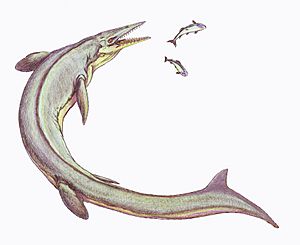
- Clidastes: A type of mosasaur, which were large, powerful marine reptiles. Clidastes was a fast swimmer with a long, snake-like body.
- Cretoxyrhina: Also known as the "Ginsu shark," this was a huge and powerful shark, similar in size to a modern great white shark. Its teeth were very sharp.
- Globidens: This mosasaur had unique, globe-shaped teeth, perfect for crushing the shells of clams and other hard-shelled prey. Its fossils were first found in Alabama.
- Pachyrhizodus: A large, predatory bony fish with sharp teeth. It was a fast swimmer in the ancient oceans.
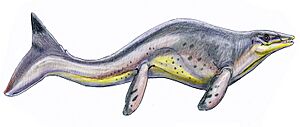
- Polycotylus: This was a type of plesiosaur, a marine reptile with a short neck and large flippers. It was a powerful swimmer.
- Protostega: One of the largest sea turtles that ever lived. It could grow up to 10 feet long.
- Saurodon: Another large, predatory bony fish from the Late Cretaceous. It had a long, pointed snout and sharp teeth.
- Selmasaurus: This was another type of mosasaur, first discovered in Alabama. It was a medium-sized marine reptile.
- Squalicorax: Known as the "crow shark," this shark was a scavenger and predator. Its serrated teeth are commonly found as fossils.
- Toxochelys: A common sea turtle from the Late Cretaceous period. It was smaller than Protostega.
- Tylosaurus: One of the largest and most powerful mosasaurs. It was a top predator in the Late Cretaceous seas.
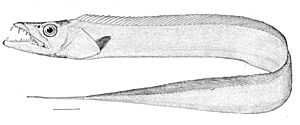
- Xiphactinus: A giant, predatory bony fish that could grow up to 17 feet long. It was known for eating other large fish.
Life in the Cenozoic Era
The Cenozoic Era began about 66 million years ago and continues to the present day. This is often called the "Age of Mammals" because mammals became very large and diverse during this time. Alabama has many fossils from this era, including ancient whales, giant sloths, and early horses.
Ancient Mammals
Many fascinating mammals lived in Alabama during the Cenozoic Era.
- Arctodus: This was the short-faced bear, one of the largest land predators in North America during the Ice Age.
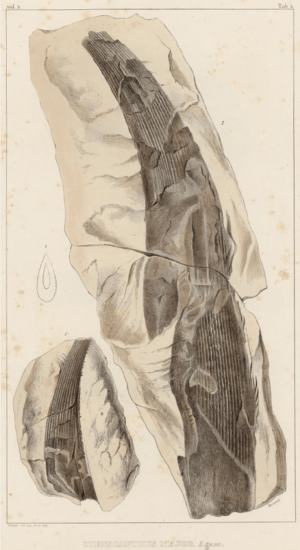
- Basilosaurus: An ancient whale that lived in the Eocene epoch. Despite its name, which means "king lizard," it was a mammal. It had a long, snake-like body.

- Castoroides: This was a giant beaver that lived during the Ice Age. It was much larger than modern beavers, growing up to 8 feet long.
- Coryphodon: A large, plant-eating mammal that lived in the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. It looked a bit like a hippopotamus.
- Cynthiacetus: Another ancient whale from the Eocene, similar to Basilosaurus but smaller.

- Dasypus: This genus includes modern armadillos. Ancient armadillos also lived in Alabama.
- Dinohyus: A huge, pig-like mammal from the Miocene epoch, sometimes called a "hell pig."
- Georgiacetus: An early whale that lived in the Eocene. Its fossils help us understand how whales evolved from land animals.
- Mammut: This genus includes the American mastodon, a large, elephant-like mammal that lived during the Ice Age.

- Mammuthus: This genus includes mammoths, another type of elephant-like mammal from the Ice Age.
- Megalonyx: This was a giant ground sloth, a huge, slow-moving mammal that lived during the Ice Age.
- Mylohyus: This was a type of peccary, a pig-like animal, that lived during the Pliocene and Holocene epochs.
- Nannippus: A small, three-toed horse that lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs.
- Neohipparion: Another ancient horse, similar to Nannippus, with three toes.
- Protohippus: An early horse from the Miocene epoch, also with three toes.
- Rangifer: This genus includes modern reindeer or caribou. Their fossils have been found in Alabama from the Ice Age.

- Smilodon: This is the famous saber-toothed cat, a powerful predator with long, sharp canine teeth that lived during the Ice Age.

- Synthetoceras: A unique mammal from the Miocene with three horns on its head.
- Tapirus: This genus includes modern tapirs. Ancient tapirs also lived in Alabama.
- Teleoceras: A rhinoceros that lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs. It was short-legged and barrel-bodied, similar to a hippopotamus.
- Ursus: This genus includes modern bears, like the American black bear, whose ancient relatives lived in Alabama.
- Zygorhiza: Another type of ancient whale from the Eocene, related to Basilosaurus.
Birds, Reptiles, and Fish
Alabama's Cenozoic fossils also include many birds, reptiles, and fish.
- Accipiter: This genus includes modern hawks, like the sharp-shinned hawk.

- Alopias: This genus includes modern thresher sharks, known for their long tails.
- Branta: This genus includes modern geese, like the Canada goose.

- Ectopistes: This genus includes the passenger pigeon, a bird that was once very common but is now extinct.

- Galeocerdo: This genus includes the modern tiger shark, a large and powerful predator.
- Grus: This genus includes modern cranes, like the whooping crane.

- Heterodontus: This genus includes modern bullhead sharks.
- Lampropeltis: This genus includes modern kingsnakes.

- Meleagris: This genus includes modern turkeys.

- Odocoileus: This genus includes modern deer, like the white-tailed deer.

- Palaeophis: An ancient sea snake that lived during the Cretaceous and Eocene periods.
- Plethodon: This genus includes modern salamanders, like the slimy salamander.

- Striatolamia: An ancient sand shark from the Paleocene and Miocene epochs. Its teeth are commonly found.

- Trichiurus: This genus includes modern cutlassfish, which are long, thin fish.
- Turdus: This genus includes modern thrushes, like the American robin.