Little Boy facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Little Boy |
|
|---|---|
|
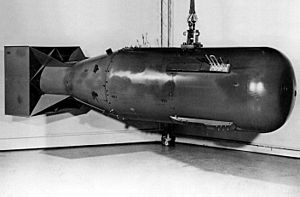
A post-war Little Boy model
|
|
| Type | Nuclear weapon |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Los Alamos Laboratory |
| Manufacturer | Los Alamos |
| Produced | 1945 |
| No. built | only 26 were ever made |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 9,700 pounds (4,400 kg) |
| Length | 10 feet (3.0 m) |
| Width | About 1 foot |
| Height | About 1 foot |
| Diameter | 28 inches (71 cm) |
|
|
|
| Filling | Uranium-235 |
| Filling weight | 64 kg |
| Blast yield | 15 kilotons of TNT (63 TJ) |
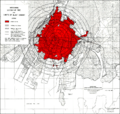
The Little Boy was the secret name for the first atomic bomb ever used in war. It was dropped on the city of Hiroshima, Japan, on August 6, 1945. This happened during World War II.
The bomb was carried by a special airplane called the Boeing B-29 Superfortress Enola Gay. Colonel Paul Tibbets was the pilot. When the bomb exploded, it released a huge amount of energy. It caused a lot of damage and destruction in Hiroshima. This event was only the second time a nuclear explosion created by humans had happened. The first was a test called the Trinity test.
Scientists at the Manhattan Project's Los Alamos Laboratory developed the Little Boy. This was during World War II. They based it on an earlier design that didn't work. The Little Boy was a "gun-type" bomb. This means it used a special method to create an explosion. It got its power from splitting atoms of uranium-235. The bomb contained about 64 kilograms (141 pounds) of enriched uranium. But less than one kilogram actually split to create the explosion. Parts of the bomb were made in different factories. This was to keep the full design a secret.
After World War II ended, people thought the Little Boy design wouldn't be needed again. Many plans for it were destroyed. However, by 1946, a problem with reactors made plutonium scarce. So, six more Little Boy bombs were built. The Navy also made 25 more in 1947. These were for special aircraft that could launch from aircraft carriers. All Little Boy bombs were taken out of service by early 1951.
How the Little Boy Bomb Was Designed
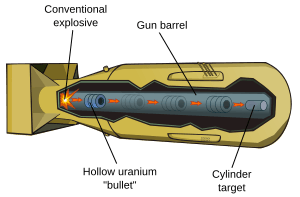
The Little Boy bomb was about 3 meters (10 feet) long. It was 71 centimeters (28 inches) wide. It weighed around 4,400 kilograms (9,700 pounds). The design used a "gun method" to make it explode.
Here's how it worked:
- Inside the bomb, there were two pieces of enriched uranium.
- One piece was a hollow cylinder, like a thick pipe. This was called the "projectile."
- The other piece was a solid cylinder, called the "target."
- When the bomb was set off, a special powder pushed the hollow "projectile" very fast.
- The "projectile" shot down a barrel, like a gun.
- It then slammed into the solid "target" piece.
- When the two pieces of uranium came together, they formed a "super-critical mass." This means there was enough uranium in one place to start a nuclear chain reaction.
- This chain reaction caused the huge atomic explosion.
The uranium pieces were surrounded by heavy materials. These materials helped to make the explosion more powerful. Special devices called neutron initiators were also activated by the impact. They helped start the chain reaction.
Images for kids
-
As part of Project Alberta, Commander A. Francis Birch (left) assembles the bomb while physicist Norman Ramsey watches. This is one of the rare photos where the inside of the bomb can be seen.
-
Arming plugs for a Little Boy type atomic bomb on display at the National Air and Space Museum's Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center.
-
Little Boy in the bomb pit on Tinian island, before being loaded into Enola Gay's bomb bay. A section of the bomb bay door is visible on the top right.
-
The mushroom cloud over Hiroshima after the dropping of Little Boy
-
One of five casings built for the Little Boy bomb used on Hiroshima on display at the Imperial War Museum in London during 2015
See also
 In Spanish: Little Boy para niños
In Spanish: Little Boy para niños