Manuscript facts for kids
A manuscript is any document that is written by hand. It is not printed or made in any other way. Before printing presses were invented, all books and documents were manuscripts. They tell us a lot about history and how people wrote long ago. Early printing methods even used many ideas that came from making manuscripts.
Contents
What is a Manuscript?
A manuscript is simply a text written by hand. The word "manuscript" comes from Latin. "Manus" means hand, and "scriptus" means written. So, it literally means "handwritten."
Why are Manuscripts Important?
Manuscripts are very important because they are often the only way we know about ancient texts. They show us how people wrote and drew in the past. They also help us understand how stories, laws, and knowledge were passed down.
How Were Manuscripts Made?
Making a manuscript was a long and careful process. Before paper was common, people used other materials.
Materials Used for Writing
- Papyrus: This was an early writing material made from a plant. It was used in ancient Egypt, Greece, and Rome.
- Parchment: This material was made from animal skin. It was very strong and could last a long time. Parchment was popular in Europe during the Middle Ages.
- Vellum: A very fine type of parchment, usually made from calfskin. It was often used for important or beautiful books.
- Paper: Paper was invented in China. It slowly spread to other parts of the world. Paper became more common for manuscripts after the 12th century.
The Scribes and Illuminators
Most manuscripts were created by people called scribes. Scribes were trained to write neatly and accurately. They copied texts word for word.
- Copying Text: Scribes would sit for hours copying books. This was often done in monasteries. They used pens made from reeds or quills.
- Illustrations and Decorations: Many manuscripts were decorated with beautiful pictures. These were called "illuminations." The artists who added these pictures were called illuminators. They used bright colors, gold, and silver.
- Binding: Once the pages were written and decorated, they were put together. They were then bound into a book. Covers were often made of wood and covered with leather. Sometimes, they were even decorated with jewels.
Types of Manuscripts
Manuscripts come in many forms. They include everything from ancient scrolls to medieval books.
- Scrolls: In ancient times, many texts were written on long rolls of papyrus or parchment. These were called scrolls.
- Codices: A codex is a book made of folded sheets. These sheets are bound together along one edge. This is the same form as modern books. Codices became popular around the 1st century AD.
- Illuminated Manuscripts: These are manuscripts that have been decorated. They often feature colorful designs, borders, and miniature pictures. Many religious texts were illuminated.
- Literary Manuscripts: These include copies of famous stories, poems, and plays.
- Scientific and Medical Manuscripts: These contain knowledge about science, medicine, and mathematics. They often have diagrams and drawings.
Manuscripts and Printing
The invention of the printing press in the 15th century changed everything. Before this, every book had to be copied by hand. This made books rare and expensive.
- Before Printing: Manuscripts were the only way to share written information widely. This meant that books were very valuable. Only wealthy people or institutions like churches owned many books.
- After Printing: Printing made it possible to make many copies of a book quickly. This made books much cheaper and more available. It helped spread knowledge and ideas faster than ever before. Even after printing, manuscripts were still made for special purposes. These included personal letters or unique artworks.
Images for kids
-
Manuscript, Codex Manesse. Most manuscripts were ruled with horizontal lines that served as the baselines on which the text was entered.
-
10th-century minuscule manuscript of Thucydides's History of the Peloponnesian War
-
First page of Satie's Sports et divertissements (published as a facsimile in 1923)
-
The Isha Upanishad manuscript
-
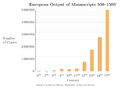
After plummeting in the Early Middle Ages, the high and late medieval period witnessed a sharp increase of manuscript production.
-
The Pentecost, from an illuminated Catholic liturgical manuscript, c.1310–1320
See also
 In Spanish: Manuscrito para niños
In Spanish: Manuscrito para niños