Mars Climate Orbiter facts for kids

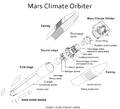
Artist's conception of the Mars Climate Orbiter
|
|
| Mission type | Mars orbiter |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA / JPL |
| Mission duration | 286 days Mission failure |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Martin |
| Launch mass | 338 kilograms (745 lb) |
| Power | 500 watts |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 11 December 1998, 18:45:51 UTC |
| Rocket | Delta II 7425 |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17A |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | 23 September 1999 09:06:00 UTC |
| Decay date | 23 September 1999 Unintentionally deorbited |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Areocentric |
| Epoch | Planned |
The Mars Climate Orbiter was a space probe sent by NASA to study the planet Mars. It was launched on December 11, 1998. Its main job was to learn about Mars' weather and air. Sadly, on September 23, 1999, NASA lost contact with the spacecraft. This happened just as it was about to enter orbit around Mars.
Contents
What Was the Mission?
The Mars Climate Orbiter was part of a bigger plan to explore Mars. Its goal was to watch Mars' atmosphere and surface for a whole Martian year. This would help scientists understand how water and dust move around the planet. It also carried special cameras to take daily pictures of the Martian weather.
Why Did the Mission Fail?
The mission failed because of a simple but critical mistake. One part of the team used imperial units (like feet and pounds) for their calculations. Another part of the team used metric units (like meters and kilograms).
- The software that controlled the spacecraft's path used imperial units.
- But the team on Earth sent commands using metric units.
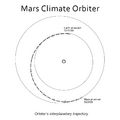
This mix-up meant the spacecraft thought it was higher above Mars than it actually was. When it tried to enter orbit, it flew too close to the planet.
What Happened to the Spacecraft?
Because the orbiter flew too low, it likely entered the Martian atmosphere. The friction from the atmosphere would have caused it to heat up very quickly. Scientists believe one of two things happened:
- The spacecraft burned up and broke apart in the atmosphere.
- It might have bounced off the atmosphere and then flown past Mars, ending up in an orbit around the Sun.
Even though the mission failed, it taught NASA a very important lesson. All teams working on space missions must use the same system of measurement. This helps prevent similar mistakes in the future.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Launch of Mars Climate Orbiter by NASA on a Delta II 7425 launch vehicle
See also
 In Spanish: Mars Climate Orbiter para niños
In Spanish: Mars Climate Orbiter para niños
 | May Edward Chinn |
 | Rebecca Cole |
 | Alexa Canady |
 | Dorothy Lavinia Brown |