Matamoros, Coahuila facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
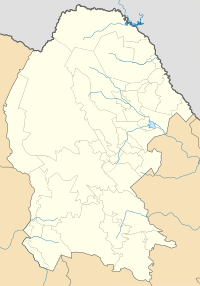
Matamoros, Coahuila
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Municipal seat
|
||
 |
||
|
||
| Country | ||
| State | Coahuila | |
| Municipality | Matamoros | |
| Population
(2005)
|
||
| • Total | 48,511 | |
Matamoros is a city in the southwestern part of Coahuila, a state in Mexico. It's the main city of the Matamoros area, also called a municipality.
It's just east of the bigger city of Torreón. Matamoros is part of a large city area called the Comarca Lagunera. This area includes Torreón in Coahuila, and Gómez Palacio and Lerdo in the nearby state of Durango. In 2010, about 52,599 people lived in the city. The whole Matamoros area (municipality) had about 107,007 people.
Contents
History of Matamoros
In 1839, a group of people settled in an area called "la Vega de Marrufo." But they had to leave later because of big floods.
How Matamoros Became a Village
In 1864, during a time when France was involved in Mexico, President Benito Juárez gave an important job to Don Juan de la Cruz Borrego. He was from a place now called "Congregation Hidalgo." Don Juan and his group were asked to protect eleven carts full of important documents. These papers were very valuable for the Liberal Party and for President Juárez's cause. They hid these documents in a place called "the Bat Cave," which is now known as "the Tobacco Cave."
On September 5, 1864, President Benito Juárez declared Matamoros a "Villa" (a type of village or town). A little earlier, on August 28 of the same year, President Juárez made a rule. This rule gave farmers the right to own the land lots that would make up the new town.
Much later, on February 27, 1927, when Plutarco Elías Calles was president, Matamoros was officially given the title of a "city."
Natural Resources
Matamoros has important natural resources. One main resource is sandy banks, which are used a lot by the construction industry. The clay from this region is especially good for making bricks.
Another natural resource found here is mesquite charcoal. People also use mesquite firewood in their homes and in bakeries in Matamoros.
People of Matamoros
According to a count done by the National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI), Matamoros has 59,762 people. This includes 29,256 men and 30,506 women.
On average, people in Matamoros have about 9.73 years of schooling. The birth rate is about 2.21 children per woman.
Religion
Catholic Church in Matamoros
Matamoros is part of the Diocese of Torreón. Every year on July 4, there is a fair for La Virgen del Refugio. She is the patron saint of the city. This fair includes fun rides, grape harvests, and concerts with religious music.
Getting Around
Roads and Transportation
You can reach Matamoros by land using Federal Highway 40, which connects Torreón and Saltillo. This highway goes across the entire state of Coahuila. Matamoros is also only about 30 minutes away from the Torreón Bus Station. If you travel by air, the Torreón International Airport is also about 30 minutes away.
Fun Things to Do
Many people visit places like the Plaza de Armas (main square), the Tobacco Cave, and the Home Run park. The main church, the Historic Center, and the Municipal Gymnasium are also popular spots.
The city government also organizes events like dances, plays, and folk music concerts. These often happen in the open area in front of the municipal presidency building. Matamoros is also home to the popular Wet Laguna water park, where you can have a lot of fun!
See also
 In Spanish: Matamoros (Coahuila) para niños
In Spanish: Matamoros (Coahuila) para niños