Mitochondrial DNA facts for kids
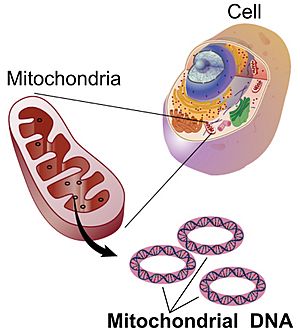
Mitochondrial DNA (often called mtDNA or mDNA) is a special type of DNA found inside tiny parts of your cells called mitochondria. Mitochondria are like the "powerhouses" of your cells. They turn the energy from the food you eat into a form your body can use.
What's really interesting about mtDNA is that you almost always get it only from your mother! It's passed down through the egg cell. While most of your DNA is found in the main control center of your cell, the cell nucleus, mtDNA is a small, separate part.
What are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are tiny structures inside nearly all eukaryotic cells. Think of them as mini-factories within your cells. Their main job is to convert chemical energy from food into a usable form called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is like the energy currency that your cells use to do everything, from moving muscles to thinking.
Most of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell is found in the cell nucleus. This nuclear DNA is organized into long strands called chromosomes. Mitochondrial DNA is much smaller and shaped like a circle. In plants, there are also other parts of the cell called chloroplasts that have their own DNA.
How is mtDNA Different?
In humans, mitochondrial DNA contains 37 genes. These genes are arranged in a circular shape with about 16,600 base pairs. A base pair is like a single step on a ladder of DNA. Scientists first mapped out the entire human mitochondrial DNA sequence a long time ago.
Compared to the DNA in the nucleus, mtDNA is much smaller. For example, the DNA in the nucleus has billions of base pairs. In plants, the mtDNA can be much larger than in humans. For instance, a plant called Arabidopsis has mtDNA that is about 367,000 base pairs long.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Genoma mitocondrial para niños
In Spanish: Genoma mitocondrial para niños
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |