Molecular biology facts for kids
Molecular biology is a super cool science that looks at life at a tiny, tiny level – the molecular level! Imagine zooming in on living things until you can see the individual parts that make them work.
This field mixes ideas from other exciting science areas. These include cell biology (which studies cells), genetics (how traits are passed on), and biochemistry (the chemistry of living things).
Mostly, molecular biology tries to understand how tiny parts inside a cell work together. This includes how DNA (our genetic blueprint), RNA, and protein biosynthesis (making proteins) all connect. It also explores how these amazing processes are controlled.
Contents
What Molecular Biology Studies
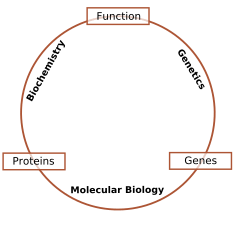
Scientists in molecular biology use special tools and ideas. They often combine them with techniques from genetics and biochemistry. These science areas are very closely linked!
Here's a simple way to think about how they relate:
- Biochemistry is about the chemical substances and important processes happening inside living organisms. It's like studying the ingredients and recipes of life.
- Genetics is the study of inheritance. This means how traits are passed from parents to children. It also looks at how small differences in our genes affect us.
- Molecular biology focuses on the structure and function of all the carbon-based macromolecules in living things. These are the big molecules that make up life. This includes the whole journey from a gene to a protein. This journey involves copying DNA, transcribing DNA into RNA, and translating RNA into protein.
- Cytology is the study of cells themselves. It looks at what cells and their parts look like. It also uses microscopes and special stains to see different parts of a cell.
DNA: The Blueprint of Life
One of the most important things in molecular biology is DNA. DNA is like a detailed instruction manual for building and running every living thing. It holds all the genetic information that makes you, you!
Scientists study how DNA copies itself (this is called DNA replication). They also look at how its instructions are read to make RNA (this is transcription). Then, how RNA's message is used to build proteins (this is translation). Proteins do most of the work in cells and are needed for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs.
Genes and Genomes
- A gene is a small part of DNA that carries instructions for a specific trait or protein. Think of it as a single recipe in the big instruction manual.
- A genome is the complete set of all the DNA in an organism. It's like having the entire cookbook for a living thing! Studying genomes is a big part of molecular biology today.
Related Topics
- Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things.
- Cell biology is the study of cells, their structure, and how they work.
- Cytology looks at the appearance of cells and their parts.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Biología molecular para niños
In Spanish: Biología molecular para niños