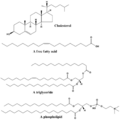Biochemistry facts for kids
Biochemistry is like a special science that looks at the amazing chemicals and reactions happening inside all living things, from tiny bacteria to big animals! It helps us understand how our bodies work, how cells grow, and how we get energy from food. Biochemists study important molecules like enzymes, DNA, sugars, proteins, and lipids (fats).
Many molecules in our bodies are huge chains called polymers. Biochemistry helps us understand how these tiny building blocks are made and how they create energy from the food we eat.
Contents
What are Macromolecules?
Our bodies are full of giant molecules called macromolecules. Think of them like super-long chains made of many smaller pieces linked together. These small pieces usually have only a few atoms, mostly carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Sometimes, they also have sulfur or phosphorus, which are very important for the molecules to work correctly.
There are four main types of these giant molecules that are essential for life:
Nucleic Acids: The Body's Instruction Manuals

Nucleic acids are long chain-like molecules. The two most famous types are DNA and RNA. Their small building blocks are called nucleotides.
DNA is found in almost every cell in your body. It's like the master instruction book for making everything your body needs, including all your proteins and other nucleic acids. DNA is famous for its unique "double helix" shape, which looks like a twisted ladder. It's the key to heredity, meaning it carries all the information that gets passed down from parents to children.
RNA helps carry out the instructions from DNA inside your cells. When your body needs to make a specific protein, the information from DNA is copied onto an RNA molecule. Then, another type of RNA molecule uses these instructions to build the protein. This special RNA, called a ribosome, acts like a tiny factory, speeding up the process of linking small amino acids together to form a protein.
Proteins: The Body's Workers and Builders
Proteins are long chains made from smaller units called amino acids. There are 20 different common types of amino acids.
Proteins have two main jobs:
- Building Blocks: Many parts of your body are made of proteins. For example, your muscles, hair, and skin are mostly protein. They give your body structure and strength.
- Speeding Up Reactions: Proteins also act as special helpers called enzymes. They make chemical reactions in your cells happen much, much faster – sometimes over a million times quicker! Your body constantly performs thousands of chemical reactions, called metabolism, to turn food into energy or create new molecules. Enzymes are vital for these reactions to occur at the right speed for life.
Carbohydrates: Your Body's Energy Source
Carbohydrates are molecules that include sugars and starches. They are a major source of energy for your body.
- Sugars: These are the simplest carbohydrates. "Single sugars" like glucose and fructose are called monosaccharides. When two single sugars join, they form a disaccharide, like table sugar (cane sugar) (which is made of glucose and fructose).
- Starches: These are "many sugars" (polysaccharides) joined together. Most starches are long chains of glucose. You find starch in foods like grains, potatoes, and bread. Starch is a great way for your body to store and get energy quickly.
- Cellulose: This is another type of polysaccharide made of many glucose units. Cellulose is the main material that gives plants their structure and strength. It's what makes up half of all wood!
The most important job of carbohydrates in your body is to provide quick energy for your cells. When your body breaks the chemical bonds in carbohydrates, it releases energy that your cells can use to do their work.
Lipids: Storing Energy and More
Lipids are a group of molecules that include fats and waxes.
- Saturated Lipids: These have only single bonds between their carbon atoms. They are usually solid at room temperature, like butter and lard.
- Unsaturated Lipids: These have one or more double bonds between their carbon atoms. They are often liquid at room temperature, like many oils.
Your human body stores lipids as a way to save energy for later. When your body needs a lot of energy, it can break down these lipid molecules to release that stored power. Lipids are also important for building cell membranes and for some hormones.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Gerty Cori and Carl Cori jointly won the Nobel Prize in 1947 for their discovery of the Cori cycle at RPMI.
-
Structures of some common lipids. At the top are cholesterol and oleic acid. The middle structure is a triglyceride composed of oleoyl, stearoyl, and palmitoyl chains attached to a glycerol backbone. At the bottom is the common phospholipid, phosphatidylcholine.
-
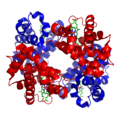
A schematic of hemoglobin. The red and blue ribbons represent the protein globin; the green structures are the heme groups.
-
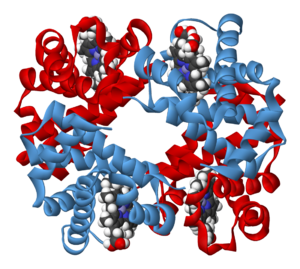
Examples of protein structures from the Protein Data Bank
-
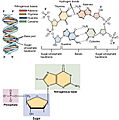
The structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the picture shows the monomers being put together.
See also
 In Spanish: Bioquímica para niños
In Spanish: Bioquímica para niños
 | DeHart Hubbard |
 | Wilma Rudolph |
 | Jesse Owens |
 | Jackie Joyner-Kersee |
 | Major Taylor |