Cytology facts for kids
Cytology is the exciting study of cells! Cells are the tiny building blocks that make up all living things, from plants and animals to humans. Cytology helps us understand what cells look like, how they are built, and how they interact with each other and their surroundings.
Scientists divide cells into two main groups:
- Prokaryotic cells: These are simpler cells. They do not have a clear, organized nucleus or other special compartments (called organelles) inside them. Their genetic material just floats freely. Bacteria are examples of prokaryotic cells.
- Eukaryotic cells: These cells are more complex. They have a clear nucleus that holds their genetic material, and many different organelles, each with a special job. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all made of eukaryotic cells.
Contents
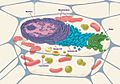
Inside a Eukaryotic Cell: Key Parts and Their Jobs
Eukaryotic cells have many tiny parts called organelles. Each organelle has a specific role to help the cell work properly. Here are some of the most important ones:
- Mitochondria: These are often called the "powerhouses" of the cell. They produce most of the energy the cell needs to do its work.
- Endoplasmic reticulum: This is like a busy factory inside the cell. It helps make and transport important substances like proteins and fats (lipids) that the cell needs.
- Golgi bodies: Imagine these as the cell's packaging and shipping center. They take proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum, process them, and then package them up to be sent to other parts of the cell or outside the cell.
- Plastids: You'll find these only in plant cells and some algae. The most famous type is the chloroplast, which contains a green chemical called chlorophyll. Chloroplasts are essential for photosynthesis, the process where plants use sunlight to make their own food.
- Nucleus: This is the control center of the cell. It contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and directs all the cell's activities, telling it what to do and when.
- Centrosomes: These organelles play a key role when a cell divides. They help organize the cell's internal structure and guide the chromosomes during mitosis (when a cell makes an exact copy of itself) and meiosis (when cells are made for reproduction).
Related Studies
- Cell biology: This field focuses on how cells work, including how they grow, divide, and interact with each other. It also looks at the tiny molecules inside cells.
- Histology: This is the study of tissues. Scientists use special techniques to prepare and look at tissues (groups of cells working together) under a microscope.
- Cytopathology: This is a medical field where doctors study cells under a microscope to find out if there are any diseases or problems.
Images for kids
-
Czech anatomist Jan Evangelista Purkyně is famous for discovering special nerve cells called Purkinje cells in 1837.
-
Theodor Schwann was a scientist who discovered Schwann cells, which are important for nerve function.
-
Yoshinori Ohsumi won the Nobel Prize for his important work on autophagy, a process where cells clean out damaged parts.
See also
 In Spanish: Biología celular para niños
In Spanish: Biología celular para niños
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |