Municipal Borough of Ilford facts for kids
| Ilford | |
| Motto: In unity progress | |
 Ilford (now Redbridge) Town Hall |
|
 Ilford within Essex in 1961 |
|
| Geography | |
| Status | Civil parish (1888—1965) Local board (1890—1894) Urban district (1894—1926) Municipal borough (1926—1965) |
| 1911 area | 8,496 acres (34.38 km2) |
| 1931 area | 8,493 acres (34.37 km2) |
| 1961 area | 8,404 acres (34.01 km2) |
| HQ | Ilford |
| History | |
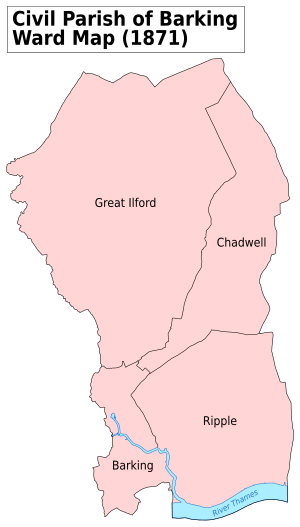
| Origin | Chadwell and Ilford wards of Barking parish |
| Created | 1888 |
| Abolished | 1965 |
| Succeeded by | London Borough of Redbridge |
Quick facts for kids Demography |
|
|---|---|
| 1911 population - 1911 density |
78,188 9.2/acre |
| 1931 population - 1931 density |
131,061 15.4/acre |
| 1961 population - 1961 density |
178,024 21.2/acre |
 Achievement of arms of the Borough Council |
|
Ilford was once a special area in south west Essex, England. It had its own local government from 1888 to 1965. This area covered the town of Ilford. During this time, many more people moved to Ilford. This was because the city of London was growing bigger and bigger. Ilford became one of the most populated areas of its kind in England. Today, most of the old Ilford area is part of the London Borough of Redbridge in Greater London.
Contents
How Ilford's Government Started
Long ago, Ilford was just a part of a bigger area called the Parish of Barking. But in 1888, Ilford and another part called Chadwell Ward became their own separate area for local government. Think of it like a new school district being created.
Since 1840, the police in Ilford were part of the Metropolitan Police District. This is the main police force for London and its surrounding areas.
In 1890, a "local board" was set up for Ilford. This board helped manage things like public health. Then, in 1894, Ilford became an "urban district." This meant it had more power to run its own local services, thanks to a law called the Local Government Act 1894.
Ilford as a District and Borough
At first, the Urban District Council met in small rooms above a shop. Later, they rented a schoolroom. In 1901, they started building the Ilford Town Hall. It cost about £30,000, which was a lot of money back then! The building was designed in a fancy Renaissance style. It was made bigger in 1927 and again in 1933.
Over the years, the council got more powers. They used these powers to improve life for people in Ilford. They built sewers, public baths, a special hospital for sick people, and a fire station. They also set up electricity and a tram system. Many public parks were created, including Valentines Park, which opened in 1898. In 1904, the council also took over running the local schools.
In 1926, Ilford became a "municipal borough." This gave it even more independence and power. The borough ran its own tram services. But in 1933, these trams became part of a bigger transport system for London.
There was an idea in 1929 to join Ilford with Barking and Dagenham. These three areas all had parts of a large housing estate called Becontree. However, this idea never happened.
Ilford tried five times to become a "county borough." This would have made it completely independent from the Essex County Council. The last try was in 1954. At that time, Ilford had about 184,000 people. It was bigger than nearby East Ham and was the second-largest "non-county borough" in England.
In 1914, the church area of Barking (which included Ilford) changed from one church region to a new one. This change happened because more people were moving to the east of London.
Population Growth
The number of people living in Ilford grew a lot. This was partly because of the Becontree housing estate, which started being built in 1921. Also, the Central Line of the London Underground started running in 1947. The population of Ilford reached its highest point in 1951.
| Year | 1891 | 1901 | 1911 | 1921 | 1931 | 1951 | 1961 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 10,913 | 41,234 | 78,188 | 85,194 | 131,061 | 184,706 | 178,024 |
End of Ilford's Borough Status
Ilford was considered part of the "Greater London Conurbation." This is a big area where many towns and cities have grown together around London. In 1965, a new law called the London Government Act 1963 changed how local government worked in London.
Because of this law, the Municipal Borough of Ilford was ended. Its area became part of Greater London. It joined with the areas of Municipal Borough of Wanstead and Woodford and parts of Municipal Borough of Dagenham and Chigwell Urban District. Together, these areas formed the new London Borough of Redbridge.
Freedom of the Borough
Some special people and military groups were given the "Freedom of the Borough" of Ilford. This is a special honor.
Individuals Honored
- George, Duke of York: He received this honor in 1929. He later became King George VI.
Military Units Honored
- The Essex Regiment: This army group received the honor on June 14, 1947.
- The 3rd East Anglian Regiment (16th/44th Foot): This army group was honored on September 9, 1958.
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |