Essex facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Essex
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Ceremonial Essex within England |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Constituent country | England | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Region | East | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Established | Ancient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (Greenwich Mean Time) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+01:00 (British Summer Time) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Members of Parliament | 18 Members of Parliament
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Police | Essex Police | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Largest city | Southend-on-Sea | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Essex is a county in the East of England. It is one of the "home counties," meaning it's close to London. Essex shares borders with Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, and the North Sea to the east. To the south, it's separated from Kent by the Thames Estuary. Greater London is to the southwest, and Hertfordshire to the west.
The biggest town in Essex is Southend-on-Sea, and the main county town is Chelmsford. The county covers about 3,670 square kilometers (1,417 sq mi) and has a population of over 1.8 million people. Besides Southend-on-Sea, other large towns include Colchester and Basildon. The southern part of Essex is very busy with lots of people, while the rest of the county, apart from Colchester and Chelmsford, is mostly countryside.
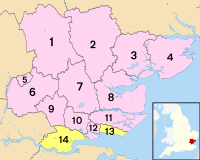
For local government, Essex has twelve districts and two special areas called unitary authorities: Thurrock and Southend-on-Sea. Chelmsford, Colchester, and Southend are also officially cities. Historically, parts of what is now north-east Greater London used to be part of Essex.
Essex is a mostly flat county with a long coastline. It has old forests like Epping Forest and shares the beautiful Dedham Vale area with Suffolk. Its coastline is one of the longest in England, stretching 562 miles (905 km). Many rivers flow into the sea here, creating large estuaries like the Stour, Colne, Blackwater, Crouch, and the Thames. Parts of the coast are wetlands and salt marshes, with big beaches too.
Long ago, during the Iron Age, the Trinovantes tribe lived in what is now Essex. They built a settlement at Colchester, which is Britain's oldest recorded town. The Romans later took over Colchester, but the Trinovantes rebelled and attacked it during the Boudican revolt. Later, in the Early Middle Ages, the Saxons invaded and formed the Kingdom of Essex. After them came the Vikings, who won the Battle of Maldon and made King Æthelred pay them a special tax called Danegeld.
After the Norman Conquest, much of Essex became a royal forest. In 1381, many people from Essex joined the Peasants' Revolt. In later centuries, Essex became more connected to London's economy. In the 1800s, railways helped coastal towns like Clacton-on-Sea grow, and the Port of London moved downriver to Tilbury. More recently, new towns like Basildon and Harlow were built, and the Harwich International Port and petroleum industry grew.
History of Essex
The name Essex comes from the Anglo-Saxon period, meaning "East Saxons." This was the eastern kingdom of the Saxons who settled in Britain. Other places like Middlesex and Sussex also get their names from Saxon groups. Essex was first mentioned in AD 527. It used to be much larger, including parts of what are now Middlesex and Hertfordshire. Later, its size was reduced to lands east of the River Lea.
Britain's Oldest Town
Colchester in north-east Essex is Britain's oldest recorded town. It existed even before the Romans arrived, when it was called Camulodunum and even had its own coin-making facility. In AD 824, the Saxon kingdoms of Essex, Sussex, and Kent joined the kingdom of the West Saxons, uniting much of England. After the Norman Conquest, Essex officially became a county.
Royal Forests and Administration
During the Middle Ages, large parts of Essex were designated as royal forests, meaning they were special hunting grounds for the king. Over time, these forest areas became smaller.
The Essex County Council was created in 1889 to manage the county. However, some large towns like West Ham, Southend-on-Sea, and East Ham had their own councils and were not controlled by the county council. Today, 12 smaller areas (boroughs and districts) handle local services like rubbish collection and planning.
Changing Borders
Over the years, some small parts of Essex were moved to other counties like Hertfordshire, Suffolk, and Cambridgeshire.
A big change happened in 1965 when many areas in south-west Essex, including East Ham, West Ham, Barking, and Ilford, became part of Greater London. This created new London boroughs like Barking and Dagenham, Havering, Newham, Redbridge, and Waltham Forest.
In 1998, Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock became "unitary authorities." This means they manage their own local services and are no longer under the main Essex County Council. However, the Essex Police force still covers all of Essex, including these two unitary authorities.
The main office for Essex County Council is County Hall in Chelmsford. Before 1938, the council often met in London because it was easier for people to travel there by train. County Hall is a historic building, mostly built in the 1930s, and has beautiful artworks.
Geography of Essex
Essex is mostly a low-lying county. Its highest point is Chrishall Common, which is about 482 feet (147 meters) high, near the border with Hertfordshire.
Borders and Landscape
Essex is bordered by the River Thames and its estuary to the south (shared with Kent). To the southwest is Greater London. The River Lea and the Stort river largely form the western border with Hertfordshire. To the northwest is Cambridgeshire, and to the north is Suffolk, with the River Stour forming much of that border. The North Sea is to the east.
The way people live in Essex varies a lot. The Metropolitan Green Belt is a protected area that stops London from spreading further into the county. However, Essex does have "new towns" like Basildon and Harlow. These towns were originally built after World War II to rehouse people from London whose homes were destroyed. Epping Forest also helps protect the area from London's growth.
Because Essex is so close to London, many towns and villages, especially those near train stations, are "dormitory towns." This means people live there and travel to London for work.


Parts of south-east Essex, including Basildon, Southend, and Thurrock, are part of the Thames Gateway project, which means they are planned for more development. Some areas in the southwest, like Buckhurst Hill and Chigwell, are so close to London that they are sometimes considered part of the Greater London area.
North of the green belt, away from big towns like Colchester and Chelmsford, Essex is mostly rural. It has many small towns and villages built with traditional materials like timber and brick. This northern part of Essex feels more like East Anglia.
Government and Politics
National Government
Essex is part of the East of England region. It is represented by 18 Members of Parliament (MPs) in the UK Parliament. Each MP represents a specific area, called a constituency.
After the 2024 general election, Essex has:
- 10 MPs from the Conservative Party
- 5 MPs from the Labour Party
- 2 MPs from Reform UK
- 1 MP from the Liberal Democrats
Historically, the Conservative Party has been very strong in Essex, winning almost all seats in previous elections. However, in the 2024 election, their support decreased, and other parties gained seats. For example, the Labour Party won seats in Thurrock, Harlow, Colchester, and Southend-on-Sea for the first time in a while. The Liberal Democrats also won in Chelmsford.
In the 2016 vote on whether the UK should leave the European Union, 62.3% of voters in Essex chose to leave. All 14 local council areas in Essex voted to leave the EU.
Local Government
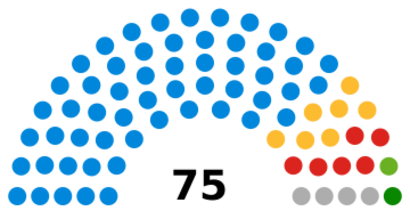
The Essex County Council manages the main part of Essex (not including Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock). It has 75 councillors who are elected from different areas. The council is currently controlled by the Conservative Party, who hold 52 of the 75 seats. The council meets at County Hall in Chelmsford.
The county council is responsible for big services like roads, libraries, most state education, social services, and public transport. Smaller local services, like housing, local planning, and rubbish collection, are handled by the 12 district and borough councils, and by the two unitary authorities (Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock).
Youth Councils
Essex County Council also has a Youth Assembly. This group has 75 members, aged 11 to 19, who represent young people across Essex. They decide what is important for young people and work to make changes. Some districts and unitary authorities also have their own youth councils. These young councillors are elected by their schools and work to improve services for young people in Essex.
Town and Parish Councils
Below the district level, there are nearly 300 town and parish councils in Essex. These councils vary in size and can help with local life in many ways. They might maintain parks, help with crime prevention, or provide sports facilities. They can also share their opinions with bigger councils about local needs and planning.
Economy of Essex
Many people in Essex, especially in the south, travel to London or other places for work. These jobs in London often pay well and add to the economy of Essex.
Most of the industry in Essex is in the south, while the rest of the county is mainly used for farming. Harlow is a hub for electronics, science, and medicine companies. Chelmsford has been important for electronics companies, like the Marconi Company, since the industry began. It also has many insurance and financial companies. Basildon is home to the European headquarters of New Holland Agriculture and the British headquarters of the Ford Motor Company. Debden, in Loughton, is where British and foreign banknotes are printed.
Other businesses in Essex include mechanical engineering, metalworking, glassmaking, plastics, and many service industries. Colchester is a military town, and the presence of the Army helps the local economy. Southend-on-Sea has the Adventure Island theme park and is a growing seaside resort, thanks to good train links to London.
However, some parts of eastern Essex face challenges. For example, Jaywick near Clacton-on-Sea has been identified as one of the most deprived areas in Southern England. In contrast, central, western, and south-western Essex are very wealthy areas, often called the London commuter belt. This area has many middle-class families and is known for its private schools.
Transport in Essex
Because much of Essex is in the London commuter belt, transport links to London are very important for the economy. There are also major ports and airports that add to the traffic on local roads and railways.
Railway Lines
Essex has several railway lines connecting it to London:
- The West Anglia Main Line goes from London Liverpool Street to Harlow, Stansted Airport, and further into Cambridgeshire.
- The London Underground Central line serves the southern part of the Epping Forest area.
- The Great Eastern Main Line goes from London Liverpool Street to Shenfield, Chelmsford, Colchester, and into East Anglia. It has branches to:
- Harwich and its port.
- The Sunshine Coast Line connecting Colchester to seaside towns like Clacton-on-Sea and Walton-on-the-Naze.
- Braintree.
- A branch from Marks Tey to Sudbury (Suffolk).
- A branch to Southend Victoria and other towns in south Essex. This branch also has the Crouch Valley Line to the Dengie Peninsula.
- The London, Tilbury & Southend Railway also serves Southend (Southend Central) and many towns in the south of the county. Its London station is Fenchurch Street.
Road Network

Essex has six main roads, most of which connect to London:
- The M25 is London's ring road, which includes the Dartford Road Crossings over the Thames Estuary, linking Essex to Kent.
- Four main roads lead into London:
- The M11 motorway, which also serves Stansted Airport.
- The A12, going to East Anglia through Chelmsford and Colchester. It also serves the ports of Harwich and Felixstowe.
- The A127, going to the Rochford Peninsula, including Southend and Southend Airport.
- The A13, also going to the Rochford Peninsula and serving the growing ports of Tilbury and London Gateway.
The A120 is another important road heading west from the ports of Harwich and Felixstowe.
Ports and Water Transport
The Port of Tilbury is one of Britain's three largest ports. The port of Harwich has passenger and freight services to the Hook of Holland. The UK's largest container terminal, London Gateway at Shell Haven in Thurrock, opened in 2013.
These ports have special railway lines for freight, which sometimes can cause delays for passenger trains. There is also a pedestrian ferry across the Thames from Tilbury to Gravesend, Kent during certain hours.
Airports

The main airport in Essex is Stansted Airport, which has flights to Europe, North Africa, and Asia. London Southend Airport, which used to be one of Britain's busiest, opened a new runway and terminal in 2012. It has its own train station with direct links to London. Southend Airport offers scheduled flights to Ireland, the Channel Islands, and many European destinations. Essex also has smaller airfields, some of which were military bases during World War I or II, now used for pleasure flights or flying lessons.
Culture and Community
Symbols of Essex

Both the Flag of Essex and the county's coat of arms feature three Saxon knives called "seaxes." They are white and point to the right, arranged one above another on a red background. This three-seax symbol is also the official logo of Essex County Council.
This emblem was first linked to the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Essex in the 1600s. An author named Richard Verstegan claimed that the first king of the East Saxons, Erkenwyne, used these knives as his symbol. However, there's no older proof of this, as heraldry (family symbols) only really started in the 12th century.
The cowslip flower is the official plant of Essex.
Patron Saint
The East Saxon royal family became Christian around AD 604, but later stopped practicing. In the mid-7th century, a new Christian king, Sigeberht the Good, asked monks from Lindisfarne to help spread Christianity again.
St Cedd, a monk from Northumbria, sailed south and built a chapel dedicated to St Peter at the old Roman fort of Othona (now Bradwell-on-Sea). This chapel still stands today. St Cedd became the Bishop of London, overseeing the East Saxons. His feast day, October 26, is also known as Essex Day.
Essex Dialect and Speech
Essex has its own special way of speaking, called the Essex dialect. However, this dialect is now mostly heard in the north of the county and among older residents. It has been partly replaced by Received Pronunciation (RP), which is a standard accent, and Cockney, an accent from East London.
The spread of Cockney, especially in southern Essex, happened because many people from East London moved to Essex after World War II. A mix of RP and Cockney is now common and is known as Estuary English.
Traditions
Essex is also home to the Dunmow Flitch Trials. This is a traditional ceremony that happens every four years. It tests how devoted a married couple is to each other. The story goes that it started in 1104 at the Little Dunmow Priory. A lord and his wife, pretending to be humble, asked for a blessing after being married for a year and a day. The prior was so impressed that he gave them a "flitch of bacon." The lord then gave land to the priory, saying that a flitch should be given to any couple who could prove similar devotion.
By the 1300s, the Dunmow Flitch Trials were well-known, even mentioned in a book by author William Langland.
Media
Essex is served by BBC East and ITV Anglia for television, but southern parts also get BBC London and ITV London. Local radio stations include BBC Essex, Heart Essex, and Radio Essex.
Sports in Essex
Essex has many sports teams and has been home to famous athletes.
Football and Rugby
While West Ham United's stadium is in historical Essex, the ceremonial county has two professional football teams: Southend United and Colchester United. Other local teams include Braintree Town and Chelmsford City. Essex teams have also won national trophies for non-league teams, like the FA Trophy and the FA Vase.
The county also has amateur rugby league teams, the Eastern Rhinos and Brentwood Eels.
Other Sports
Essex has basketball teams like the Essex Leopards and a national league volleyball club, Team Essex Volleyball Club, based in Chelmsford.
Essex County Cricket Club became a top-level cricket county in 1894. They have won the County Championship league title eight times, with many wins between 1979 and 1992, and more recently in 2017 and 2019.
Racing and Olympics
Essex has had speedway teams like the Lakeside Hammers. During the 2012 London Olympics, Hadleigh Farm in Essex hosted the mountain bike races.
Essex has one horse racing track, Chelmsford City Racecourse. There is also a greyhound racing track at Harlow Stadium.
Famous Sports People
Many famous sports stars have come from or trained in Essex. These include swimmers like Mark Foster; cricket players such as Nasser Hussain and Alastair Cook; footballers like Peter Taylor; tennis stars John Lloyd; Olympic Gold-winning gymnast Max Whitlock; and world champion boxers like Nigel Benn and Frank Bruno.
Education in Essex
Education in Essex is mainly provided by three authorities: Essex County Council and the two unitary authorities, Southend-on-Sea and Thurrock. There are about 90 state secondary schools, most of which are comprehensive schools (meaning they accept students of all abilities). However, some areas like Uttlesford, Chelmsford, Colchester, and Southend-on-Sea have selective grammar schools, which require an entrance exam. There are also many private schools, especially in the countryside and western parts of the county.
The University of Essex, founded in 1963, is located near Colchester, with other campuses in Loughton and Southend-on-Sea. Anglia Ruskin University has a campus in Chelmsford. Writtle University College, near Chelmsford, offers higher education in subjects related to land management.
Landmarks and Places to Visit
Essex has over 14,000 buildings with "listed status," meaning they are historically important. About 1,000 of these are considered very important. These buildings include the 7th-century Saxon church of St Peter-on-the-Wall and the clubhouse of the Royal Corinthian Yacht Club. Southend Pier is famous for being the longest pleasure pier in the world!
Here are some other interesting places in Essex:
- Abberton Reservoir (a large reservoir)
- Audley End House and Gardens, Saffron Walden (a grand country house)
- Brentwood Cathedral
- Clacton-on-Sea (a popular seaside town)
- Chelmsford Cathedral
- Colchester Castle (a historic castle and museum)
- Colchester Zoo (a large zoo)
- Epping Forest (a large ancient woodland)
- Greensted Church (an ancient wooden church)
- Hadleigh Castle (castle ruins)
- Harlow New Town (a planned town)
- Hedingham Castle (a well-preserved Norman castle)
- Ingatestone Hall (a Tudor manor house)
- Kelvedon Hatch Secret Nuclear Bunker (a Cold War bunker)
- Lakeside Shopping Centre (a large shopping mall)
- Maldon (a historic market town)
- Mersea Island (an island known for birdwatching)
- Mountfitchet Castle (a re-created Norman castle and village)
- Royal Gunpowder Mills in Waltham Abbey (historic gunpowder factory)
- Saffron Walden (a charming market town)
- Southend Pier (the world's longest pleasure pier)
- Tilbury Fort (a historic fort on the Thames)
- Thaxted (a picturesque village)
- University of Essex (a university campus)
- Waltham Abbey Church (a historic abbey church)
Notable People
Many famous people have come from Essex or have lived there.
Sister Counties and Regions
Essex has partnerships with other regions around the world:
 Jiangsu, China
Jiangsu, China Picardy, France
Picardy, France Thuringia, Germany
Thuringia, Germany Henrico County, Virginia, United States
Henrico County, Virginia, United States Accra, Ghana
Accra, Ghana
See also
 In Spanish: Essex para niños
In Spanish: Essex para niños