Reform UK facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Reform UK
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Leader | Nigel Farage |
| Chairman | Richard Tice |
| Co-Deputy Leaders | David Bull Ben Habib |
| Founders |
|
| Founded | 23 November 2018 as the Brexit Party |
| Headquarters | 83 Victoria Street London SW1 0HW |
| Devolved branches | Reform UK Scotland Reform UK Wales |
| Membership | |
| Ideology | Right-wing populism Euroscepticism |
| Political position | Right-wing |
| Affiliates | Reform Derby Bolton for Change |
| Northern Irish affiliation | Reform UK–TUV alliance |
| Colours | Turquoise and white |
| Slogan | Britain Needs Reform |
| House of Commons | Parliament dissolved |
| London Assembly |
1 / 25
|
| Local government |
10 / 18,725
|
Reform UK is a political party in the United Kingdom. It was started in November 2018 as the Brexit Party. Its main goal then was for the UK to leave the European Union without a special deal.
The party won the most votes in the UK during the 2019 European Parliament election. However, it did not win any seats in the UK Parliament in the 2019 general election. The UK left the European Union in January 2020.
A year later, in January 2021, the party changed its name to Reform UK. During the time of the COVID-19 pandemic, the party spoke out against strict lockdowns. Since 2022, Reform UK has focused on other issues. These include opposing immigration and the government's plan to reach Net Zero carbon emissions.
Nigel Farage was the leader of a similar party called UKIP before. He returned to politics to lead the Brexit Party. This happened during the long process of Brexit after the 2016 vote. The Brexit Party wanted a "no-deal Brexit." Some politicians from the Conservative Party even joined it.
Farage offered a deal to Boris Johnson, who became the leader of the Conservative Party. This deal was for the 2019 general election. Johnson said no. But the Brexit Party still decided not to run candidates against Conservative politicians who were already in Parliament. They did not win any seats in that election.
After the UK left the EU, the party decided to focus on changing British democracy. They suggested changing the name from Brexit Party to Reform Party. When the COVID-19 pandemic started, the government put in place many lockdowns. Farage renamed the party Reform UK and focused on protesting against these lockdowns.
Farage stepped down as leader in March 2021. Richard Tice took over. In March 2024, Lee Anderson, a Conservative MP, joined Reform UK. This made him the party's first and only Member of Parliament. On June 3, 2024, Richard Tice announced that Nigel Farage would become leader again. Tice would continue as the party's Chairman.
History
Brexit Party
The Brexit Party officially started in November 2018. Catherine Blaiklock was its first leader. On February 5, 2019, it was registered to run in elections across the UK.
Nigel Farage said the party was Blaiklock's idea, and he fully supported it. Blaiklock said she would not lead the party without Farage. She saw herself as someone who would help him. Farage later said he would run as a candidate for the party in the European Parliament elections. Other politicians who had left UKIP also said they would join.
Blaiklock faced criticism for comments she made online. She resigned as leader on March 20, 2019. Farage then took over as leader. He said Blaiklock was never meant to be the long-term leader. He also said the party was mostly online at that time.
The Brexit Party shared its plans for the 2019 UK general election. These plans covered many areas like taxes, politics, and the environment. The party received two percent of all votes in the election. None of its 273 candidates won a seat.
Transition into Reform UK
Before the 2019 general election, Nigel Farage said the party would change its name to "Reform Party" after Brexit. He said it would then work to change the UK's voting system.
In November 2020, Farage and Tice announced they wanted to rename the Brexit Party to 'Reform UK'. They said the party would campaign against more COVID-19 lockdowns. They also wanted to change parts of how the UK government works, like the BBC and the House of Lords.
Some groups worried about the name change. But on January 4, 2021, the name change to Reform UK was approved.
In 2021, Reform UK gained a member in the Scottish Parliament. This was Michelle Ballantyne, who had been a Conservative and then an independent. She became Reform UK's leader in Scotland. However, she lost her seat in the 2021 Scottish Parliament election. She then left her role as leader in February 2022.
Farage stepped down as leader in March 2021. Richard Tice became the new leader. David Bull was made deputy leader. Nathan Gill became the leader of Reform UK Wales.
In 2021, Reform UK planned to have candidates in many elections. These included elections for the Senedd (Welsh Parliament), Scottish Parliament, and London Assembly. However, the party did not win any seats in these elections. They also lost their deposit in a special election in Hartlepool.
In October 2022, Reform UK and another party, the Social Democratic Party (SDP), announced they would work together. Richard Tice has said Reform plans to have candidates in most areas across England, Scotland, and Wales.
In December 2022, two Conservative local councillors joined Reform UK. This brought more attention to the party. Some polls showed a small increase in support for Reform UK. News outlets started to see the party as a challenge to the Conservative government.
In October 2023, Reform UK held a big meeting in London. Richard Tice confirmed that Reform UK would run candidates in areas where Conservatives usually win. By January 2024, the party was getting about 10% of the votes in polls. Some thought Reform UK could take votes away from the Conservatives.
In March 2024, the party made a deal with a party in Northern Ireland called the Traditional Unionist Voice (TUV). They would agree on candidates to support each other.
In May 2024, Alex Wilson became Reform's first member in the London Assembly. He was elected through a special voting system.
On June 3, 2024, Nigel Farage became the leader of the party again, replacing Richard Tice.
Representation
House of Commons
Reform UK has not won any elections to the UK Parliament on its own. However, Lee Anderson was elected as a Conservative MP in 2019. He then joined Reform UK in March 2024. This gave the party its first Member of Parliament.
European Parliament
In February 2019, nine Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) joined the Brexit Party. They had left UKIP because they disagreed with its leader. By April 2019, 14 MEPs had joined. They were part of a group in the European Parliament called Europe of Freedom and Direct Democracy.

Only three of these MEPs – Farage, Gill, and Bullock – ran for the Brexit Party in the 2019 European election. This election took place on May 23, 2019. The Brexit Party won 29 MEPs in total. This included Richard Tice and former Conservative MP Ann Widdecombe. Nigel Farage, Nathan Gill, and Jonathan Bullock kept their seats. The BBC said the Brexit Party was the clear winner in the UK's European elections. They got 31.6% of the votes in the UK.
When Brexit happened on January 31, 2020, all UK MEP positions ended.
London Assembly
Reform UK's Alex Wilson ran for the London Assembly in 2024. He won one seat for Reform UK in the London-wide assembly.
Senedd (Welsh Parliament)
In May 2019, four members of the Senedd (Welsh Parliament) joined the Brexit Party. They had originally been elected for UKIP. Mark Reckless became the leader of their group. In May 2020, Reckless said the party would campaign to get rid of the current Welsh government system. This caused some members to leave the group.
The party ran in the 2021 Senedd election. They wanted to end lockdowns and invest in the NHS. They also wanted to give parents more control over education. However, they did not win any seats.
Scottish Parliament
On January 11, 2021, Michelle Ballantyne, a member of the Scottish Parliament, joined Reform UK. She had been a Conservative but left over disagreements about COVID-19 lockdowns. She became Reform UK's leader in Scotland. She lost her seat in the 2021 Scottish Parliament election. She then resigned as the party's leader in Scotland in February 2022.
Ideology and platform
The party's main goal was for the UK to leave the European Union. Then, Britain would trade with other countries under World Trade Organization rules. In April 2019, Farage said the Brexit Party and UKIP had similar policies but different people. He said the party wanted to attract support from many different voters.
In May 2019, Farage said he admired how Italy's Five Star Movement grew from a protest group into a big political party. He saw the Brexit Party doing something similar. He said they were like a "company, not a political party."
Experts have described the party as "national populist" and "right-wing populist." Some media outlets have debated how to describe the party. Reform UK itself says it rejects certain labels and has threatened legal action against media using them.
2019 platform as the Brexit Party
The party's rules, published in May 2019, said it wanted to help people improve their lives. It also aimed to reduce the government's role and lower taxes.
The party's first policy not related to Brexit was about British Steel. They suggested making it partly owned by its workers. The party also supported cutting foreign aid and stopping the HS2 train project. They wanted to offer free WiFi on public transport. They also promised to remove interest on student loans and get rid of inheritance tax.
In July 2019, the Brexit Party joined other parties in calling for a fairer voting system for UK Parliament elections.
2019 UK general election platform as the Brexit Party
On November 22, 2019, the Brexit Party shared its plans for the 2019 UK general election. Key policies included:
- No extra time for the Brexit transition period.
- No selling off the NHS to private companies.
- Reducing immigration.
- Cutting tax on home energy bills.
- Stopping the UK from sending its waste abroad.
- Providing free internet in poor areas.
- Getting rid of the TV licence fee.
- Ending inheritance tax.
- Stopping the High Speed 2 (HS2) train project.
- Removing interest on student loans.
- Changing planning rules to help build more homes.
- Changing the Supreme Court.
- Making the voting system fairer.
- Getting rid of the House of Lords.
- Allowing people to vote out MPs who switch parties.
- Changing postal voting rules to prevent fraud.
- Allowing people to call for public votes (referendums) if enough people sign a petition.
2020–2024 as Reform UK
After the UK left the European Union, Farage wanted Reform UK to focus on new issues. The party started to oppose COVID-19 restrictions. This was similar to other right-wing groups in other countries.
In October 2021, leader Richard Tice said the Conservative Party was a "high tax" party. He promised Reform UK would offer lower taxes. He said they would raise the income tax starting point to £20,000. They would also remove company tax for the smallest businesses. Tice also said that the plan to reach "net zero" emissions was "absurdity." He believes it will harm the country financially. He also said energy companies should be owned by the government or British pension funds.
2024 UK general election platform as Reform UK
Reform UK wants to restart fracking and coal mining in the UK. They also want to produce more oil and gas from the North Sea. They say "net zero" is financially harmful. The party plans to cut NHS waiting times within two years. They would do this by using private healthcare services more.
The party is against high immigration. It supports low taxes and changing planning rules for housing. It also supports public ownership of important services like utilities. They want to get rid of the House of Lords. They also support changing the voting system to be more fair.
The party uses the slogan "Make Britain Great." This is similar to a slogan used by Donald Trump. Reform UK leaders have shown support for Trump.
Funding and structure
In its early days, the Brexit Party had very few official members. Instead, people signed up as "registered supporters." The party was criticized because these supporters had no voting power. Farage kept a lot of control over decisions. Since 2021, the party has allowed people to become full members.
Farage said the party would get most of its money from small donations. He said they raised £750,000 in small online donations in their first ten days. The party also accepts large donations.
In 2019, Christopher Harborne gave £6.4 million to the party. Jeremy Hosking, a former Conservative Party donor, gave £200,000. In 2023, the party received £200,000 from a company linked to Terence Mordaunt.
Two days before the 2019 European election, Farage accused the Electoral Commission of "interfering." This was after the watchdog visited the party's office to check its funding. Rules say donations of £500 or more must come from a "permissible donor." This means someone on the British electoral roll or a UK-registered business. Farage said the party only accepted British pounds.
In May 2024, The Guardian reported that 80% of the party's money came from Richard Tice. Tice said the Conservatives spend much more money each year than Reform.
After Farage became leader again on June 3, 2024, the party's membership increased by 50%.
Leaders
Reform UK has had three leaders. Catherine Blaiklock was the first leader. She served from January 20, 2019, to March 20, 2019. She resigned due to controversial comments she had made online. Richard Tice took over after Nigel Farage resigned. On June 3, 2024, Tice asked Farage to return as leader, and Farage accepted.
| No. | Leader (Birth) |
Portrait | Took office | Left office | Tenure length | Deputy Leader(s) | Chair |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Catherine Blaiklock (born 1963) |
20 January 2019 | 20 March 2019 | 60 days | vacant | Richard Tice | |
| 2 | Nigel Farage (born 1964) |
 |
22 March 2019 | 6 March 2021 | 1 year and 350 days | ||
| 3 | Richard Tice (born 1964) |
 |
6 March 2021 | 3 June 2024 | 4 years and 356 days | David Bull (2021–incumbent) Ben Habib (2023–incumbent) |
|
| (2) | Nigel Farage (born 1964) |
 |
3 June 2024 | Incumbent |
Timeline
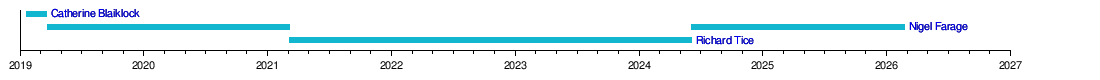
Elections
2019 European Parliament election as the Brexit Party
The Brexit Party ran candidates in Great Britain for the 2019 European Parliament election. This included well-known figures like former Conservative MP Ann Widdecombe. The party was not registered in Northern Ireland, so it did not have candidates there.
Many Conservative local councillors said they planned to vote for the Brexit Party. Some other politicians also announced their support.
Polls in May 2019 predicted the party would come first in the European elections. The party had 14 seats from politicians who had joined it before the election. They gained 15 more seats in the election. They won five more seats than UKIP had in the previous election.
The party won 29 seats in the election. This made it the biggest single party in the European Parliament.
When Brexit happened on January 31, 2020, all UK MEP positions ended.
| Year | Leader | Share of votes | Seats | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | Nigel Farage | 30.52% |
29 / 73
|
1st |
2019 general election
Farage said the party would have candidates in the 2019 general election. He promised not to run candidates against Conservative MPs who supported Brexit. In a special election in Peterborough in June, the Brexit Party came second.
After Boris Johnson became Prime Minister, Farage announced 635 candidates for the Brexit Party. He suggested a deal with the Conservative Party. This deal would help Brexit-supporting MPs win more seats. Johnson rejected this idea.
However, on November 11, Farage said his party would not run in any of the 317 seats the Conservatives won in the last election. The Conservative Party welcomed this. Both parties said they had not made a deal. Some Brexit Party supporters and candidates were unhappy with this decision.
The Brexit Party did not win any seats in the general election. They came second in some areas, like Barnsley Central and Barnsley East.
| Election | Leader | Votes | Seats | Outcome | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Share | Seats won | ± | |||
| 2019 | Nigel Farage | 642,303 | 2.0% |
0 / 650
|
New | No seats |
2024 general election
On June 3, 2024, Nigel Farage became the leader of Reform UK again. This happened before the 2024 United Kingdom general election. After this, polls showed an increase in support for the party. Some polls showed them very close to the Conservative Party. A BBC analyst said the change in leadership helped the party in the polls.
Farage said his goal was to make Reform the main opposition party in Parliament. Reform will have candidates in most areas across Great Britain.
A poll after a TV debate on June 7 found Farage to be the winner. He had 25% support from viewers. The debate covered topics like D-Day, war veterans, immigration, and the NHS.
Local government
The party first ran in local elections in Gloucester in July 2019. They did not win.
A local councillor in Rochdale joined the party in July 2019. This was the first councillor for the party. Soon after, other councillors from different parties also joined. All 12 UKIP councillors in Rotherham joined the Brexit Party in July 2019. The five UKIP councillors in Derby also joined. In September 2019, ten independent councillors in Hartlepool joined the Brexit Party.
The Hartlepool council group left the party in 2020. The Rotherham group formed a new party. Reform UK won two seats in the 2021 local elections. Both were in Derby. These were the first council seats the party won through an election. This gave them eight councillors in total.
In December 2021, a local councillor in North Shropshire joined the party from the Conservatives.
In the 2022 local elections, Reform UK candidates campaigned for fracking and North Sea oil exploration. They held two seats in Derby but lost one in Redbridge. They did not gain any new seats.
In December 2022, two more Conservative councillors joined the party. Another Conservative councillor joined in January 2023.
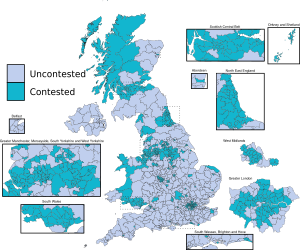
In the 2023 local elections, Reform UK won six seats out of over 8,500 available. They got about 6% of the vote where they ran candidates.
In March 2024, a councillor in East Riding of Yorkshire joined the party from the Conservatives.
In the 2024 English local elections, Reform UK got about 11% of the vote where they ran candidates. They won two seats on Havant Borough Council and one on the London Assembly. Richard Tice said his party was becoming the main opposition to the Labour Party.
Senedd (Welsh Parliament) elections
| Year | Regional vote | Constituency vote | Overall seats | Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 11,730 votes | 1.1% |
0 / 20
|
17,405 votes | 1.6% |
0 / 40
|
0 / 60
|
New Party |
Scottish Parliament elections
| Year | Regional vote | Constituency vote | Overall seats | Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 5,793 votes | 0.2% |
0 / 56
|
– | – |
0 / 73
|
0 / 129
|
New Party |
London Assembly elections
| Year | Regional vote | Constituency vote | Overall seats | ± | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 25,009 votes | 1.0% |
0 / 11
|
62,263 votes | 2.4% |
0 / 14
|
0 / 25
|
New Party |
| 2024 | 145,409 votes | 5.9% |
1 / 11
|
188,420 votes | 7.4% |
0 / 14
|
1 / 25
|
|
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Reform UK para niños
In Spanish: Reform UK para niños
- Euroscepticism in the United Kingdom
- Brexit Party election results
- Opinion polling for 2019 European Parliament election in the UK
- Opinion polling for the 2019 United Kingdom general election
- Reform Party of Canada
 | Toni Morrison |
 | Barack Obama |
 | Martin Luther King Jr. |
 | Ralph Bunche |