Nankaidō facts for kids
The Nankaidō (which means "southern sea road" in Japanese) was an important part of ancient Japan. It was both a special area of the country and the main road that ran through it.
Contents
History of Nankaidō
The Nankaidō was one of the main "circuits" (like big regions) in a system called the Gokishichidō. This system was first set up a very long time ago, during the Asuka period in Japan.
Over many centuries, the government's use of the Gokishichidō system became less important. However, the traditional eight regions, including Nankaidō, stayed important as cultural areas.
The Nankaidō road helped connect the main cities of the different provinces in this region.
Geography of Nankaidō
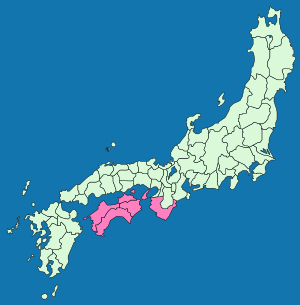
Nankaidō is the geographic region of Shikoku, which is one of Japan's main islands. Awaji Island was also part of this region.
The Nankaidō region included parts of six ancient provinces and one island. These were:
- Awa Province
- Iyo Province
- Kii Province
- Sanuki Province
- Tosa Province
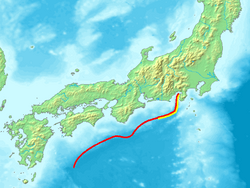
Some natural features, like the undersea Nankai Trough, were named after this region. A "trough" is a long, narrow dip in the ocean floor.
Nankaidō Earthquakes
Many big earthquakes in history have been named "Nankai" or "Nankaido." Major earthquakes are often named using the Japanese era name and the location, such as Nankaidō.
Timeline of Major Nankai Earthquakes
- 1498 (Meiō 7): A big earthquake called the Meiō Nankaidō earthquake happened. It was 7.5 on the Richter Scale.
- 1605 (Keichō 10): Another major earthquake, the Keichō Nankaidō earthquake, struck the region.
- 1854 (Ansei 1): The Ansei-Nankai earthquake caused damage in the area.
- 1944 (Shōwa 19): This year saw the Tōnankai earthquake.
- 1946 (Shōwa 21): The Nankaido earthquake was another significant event.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Nankaidō para niños
In Spanish: Nankaidō para niños