Comparison of regions of Japan facts for kids
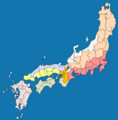
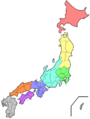
Japan is divided into different areas called regions. These regions are a mix of old historical areas and newer ways of organizing the country. They help us understand how Japan is set up and how it has changed over time.
Contents
Japan's Changing Map
Japan's geography and how its areas are divided have changed a lot throughout history. Since the late 600s, Japan's regions have been grouped based on where they are located.
During the Meiji period (a time of big changes in Japan), a modern system for regions was created. Japan was split into main regions called chihō. Each region had a special council led by the governor of the most important area (prefecture) in that group. This system showed how much people cared about their local areas.
Kansai Region
The Kansai region is a very important part of Japan. It's often used as a starting point when comparing different areas.
Kinai: The Old Capital's Heart
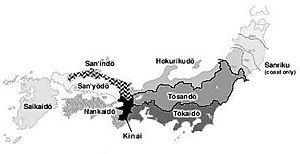
Since the late 600s, the Kinai region was known as the "Five Home Provinces." These provinces surrounded the old capital city of Kyoto. The Kinai region was created in 645 as part of the Taika Reform, which was a big change in how Japan was governed. Today, these lands are mostly part of the Kansai region.
Kantō Region
The Kantō region is another key area in Japan. It's where the modern capital, Tokyo, is located.
Tōkaidō: The Eastern Sea Road
Since the late 600s, the Tōkaidō region was called the "Eastern Sea Circuit." It included 15 old provinces along the Pacific Ocean. Famous places like Mount Fuji, Tokyo, and Yokohama are in this region. Tōkaidō also refers to an old road that connected the main cities in this area on Japan's largest island, Honshū.
Tōhoku Region
The Tōhoku region is in the northeastern part of Honshū. It's known for its beautiful nature and colder climate.
Tōsandō: The Eastern Mountain Road
Since the late 600s, the Tōsandō region was known as the "Eastern Mountain Circuit." It had 13 old provinces. Like Tōkaidō, Tōsandō also named a road that linked the main cities in this region on Honshū. After 711, Musashi Province became part of Tōsandō.
Chūbu Region
The Chūbu region is in the central part of Honshū. It's a diverse area with mountains and coastlines.
Hokurikudō: The Northern Land Road
Since the late 600s, the Hokurikudō region was called the "Northern-land Circuit." It included 7 old provinces along the Sea of Japan. Hokurikudō also named a road that connected the main cities in this region on Honshū.
Chūgoku Region
The Chūgoku region is in the western part of Honshū. It's divided by mountains into two main parts.
San'indō: The Mountain-Shade Road
Since the late 600s, the San'indō region was known as the "Mountain-shade Circuit." It had 8 old provinces along the Sea of Japan. San'indō also named a road that connected the main cities in this region on Honshū.
San'yōdō: The Mountain-Sun Road
Since the late 600s, the San'yōdō region was called the "Mountain-sun Circuit." It included provinces on the southern, "sunny" side of the mountains. San'yōdō also named a road that connected the 8 main cities in this region on Honshū.
Shikoku Region
The Shikoku region is Japan's smallest main island.
Nankaidō: The South Sea Road
Since the late 600s, the Nankaidō region was known as the "South-sea Circuit." It included 6 old provinces: the island of Awaji, the four provinces of Shikoku, and Kishiu on Honshū. Nankaidō also named a road that connected the main cities in this region.
Kyūshū Region
The Kyūshū region is Japan's third-largest island, located in the southwest.
Saikaidō: The West Sea Road
Since the late 600s, the Saikaidō region was called the "West-sea Circuit." It included the 9 old provinces of the Kyūshū region. Saikaidō also named a road that connected the main cities in this region. After 1878, the Ryukyu Islands (like Okinawa) were also included in this region.
Hokkaidō Region
The Hokkaidō region is Japan's second-largest island and its northernmost prefecture.
In the late 1800s, the Hokkaidō region, or "North Sea Circuit," was made up of 10 old provinces of Yezo. The Kurile Islands became an 11th northern province in 1875.
Images for kids
Related pages