Chūgoku region facts for kids
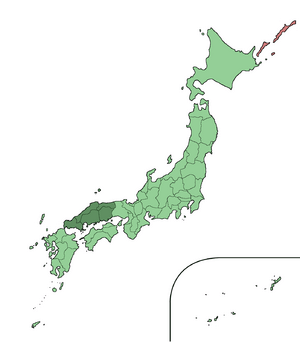
The Chūgoku region (中国地方 (Chūgoku-chihō)) is one of Japan's traditional areas. It is also known as the San'in-San'yō region (山陰山陽地方 (San'in san'yō-chihō)). Japan is divided into eight main regions for geography and history. These regions have been used since 1905 to describe and compare different parts of the country. They also help show cultural differences.
Japan's regions combine old historical divisions with modern needs. The Chūgoku region is important for its geography, culture, and how it is managed.
Contents
History of the Chūgoku Region
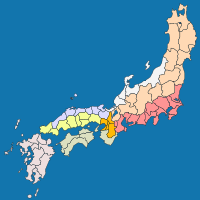
In the late 600s, two main administrative areas were created as part of Japan's Imperial system. These were called the San'indō and San'yōdō.
What is Gokishichidō?
Gokishichidō is an old system of names for different parts of Japan. It included the San'indō and San'yōdō. The Chūgoku region covers the western part of Honshū island. This area is roughly the same as the traditional San'indō and San'yōdō areas.
How Regions Were Formed in Modern Japan
During the Meiji period, Japan's modern regional system was officially created. Japan was divided into regions called chihō, and the Chūgoku region was one of them. Each region had a special council. The governor of the most powerful prefecture in that region led this council. Important leaders from central government ministries also joined the council.
Over time, the Chūgoku region developed its own special ways of speaking (dialects). It also has unique customs and a traditional culture that makes it stand out.
Images for kids
-
Chūgoku region and Shikoku seen from the International Space Station
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Región de Chūgoku para niños
In Spanish: Región de Chūgoku para niños