Gokishichidō facts for kids
Gokishichidō (pronounced Go-kee-shee-chee-doh) was a way ancient Japan was divided into different areas. It means "five provinces and seven circuits." This system started a long time ago, during the Asuka period (around 538 to 710 AD). The old Japanese government used these regions to organize the country.
Contents
What Were the Gokishichidō?
The Gokishichidō system had two main parts:
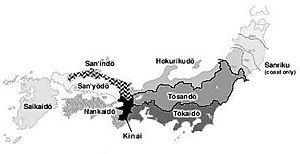
- Five Provinces (Goki): These were five special provinces located around the capital city. This area was called the Kinai.
- Seven Circuits (Shichidō): These were seven large regions, each with several smaller provinces.
This way of organizing the country came from China in the 600s. Even though the government stopped using this system for daily tasks over time, the names of the seven circuits stayed important for culture and geography.
The Core: Five Provinces
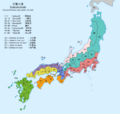
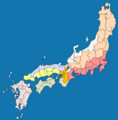
The central part of the Gokishichidō system was a special area called the Kinai. This area is now part of the Kansai region. It included five important provinces:
- Izumi Province: Today, this is the southern part of Osaka Prefecture.
- Kawachi Province: This is now the southeastern part of Osaka Prefecture.
- Settsu Province: This area includes the northern part of Osaka Prefecture (like the city of Osaka) and parts of Hyōgo Prefecture.
- Yamato Province: This is now Nara Prefecture.
- Yamashiro Province: This is the southern part of Kyoto Prefecture, including the city of Kyōto.
The Seven Circuits
Under the Gokishichidō system, there were seven main "roads" or routes that connected the capital city to all the other provinces. The land around each of these roads was named after the road itself. These seven circuits were:
- Hokurikudō: This circuit ran northeast along the coast of the Sea of Japan.
- Nankaidō: This circuit covered the southern side of the Seto Inland Sea.
- Saikaidō: This circuit included the southern islands of Japan.
- San'indō: This circuit followed the west coast of the Sea of Japan.
- San'yōdō: This circuit was on the northern side of the Seto Inland Sea.
- Tōkaidō: This circuit went along the east coast of the Pacific Ocean.
- Tōsandō: This circuit traveled northeast through the Japanese Alps.
See also
 In Spanish: Gokishichidō para niños
In Spanish: Gokishichidō para niños
Images for kids
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |