Sea of Japan facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sea of Japan |
|
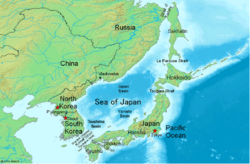
Sea of Japan map
|
The Sea of Japan (also known as the East Sea) is a large body of water. It is part of the western Pacific Ocean. This sea is surrounded by land. To its west is Korea. To its north is Russia. To its east and south is Japan.
South Korea calls this sea the East Sea. North Korea uses the name East Sea of Korea.
Contents
Exploring the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is located on the northwestern edge of the Pacific Ocean. It is separated from the main ocean by the Japanese Archipelago. These islands include Sakhalin, Hokkaidō, and Honshū. The sea is surrounded by these islands and the Eurasian Continent.
It covers a huge area of about 978,000 square kilometers. The average depth of the sea is 1,667 meters. At its deepest point, it goes down to 3,742 meters.
Connecting to Other Seas
The Sea of Japan connects to other seas through five (or sometimes six) narrow channels.
- The Strait of Tartary and La Pérouse Strait link it to the Sea of Okhotsk.
- The Tsugaru Strait connects it to the Pacific Ocean.
- The Kanmon Straits lead to the Seto Inland Sea.
- The Busan and Tsushima Strait connect it to the East China Sea.
Under the Sea
The Sea of Japan has a shallow area in its center. This area is called the Yamato Bank. It is less than 1,000 meters deep.
The sea floor also has three main deep areas, like huge flat plains.
- The Yamato Basin is in the southeast.
- The Japan Basin is in the north.
- The Tsushima Basin is in the southwest.
These three deep basins surround the Yamato Bank in a counterclockwise direction. These deep-sea features are very important for the water and living things found deep in the sea.
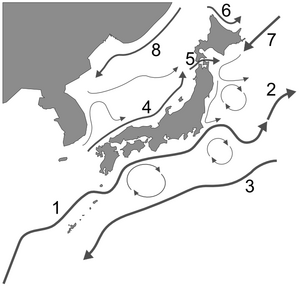
Ocean Currents
The water in the Sea of Japan can be thought of in two main layers. There is surface water, which is less than 300 meters deep. Below that is the deep-sea water.
The surface currents move in a counterclockwise circle.
- One important current is the Tsushima Current. This is a warm current. It flows from the Korean Straits northeast along the coast of Japan. It is a branch of the larger Kuroshio Current.
- The other main current is the Liman Current. This is a cold current. It flows southwest from the Strait of Tartary along the coast of Russia and Asia.
The deep-sea water is different. It does not mix much with water from other seas. This is because the channels connecting the Sea of Japan to other seas are narrow and shallow. The deep water in the Sea of Japan stays at the bottom for a long time. It is often called "the inherent water of the Sea of Japan." This special deep water makes up about 80% of all the water in the sea.
The Name Debate
The name of this sea has been a topic of discussion for many years.
In 1929, the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) decided to officially call this area the "Sea of Japan."
Since 1992, South Korea has asked countries around the world to use the names "East Sea" or "Sea of Korea" instead of "Sea of Japan." South Korea believes that this sea has been called "East Sea" for a very long time. They also think the name "East Sea" was removed from world maps in the early 1900s when South Korea was under Japanese rule.
However, Japan says that the name "Sea of Japan" was used more widely in Europe and America even before the 1700s. Japan also argues that the sea is named after Japan because of its location.
Today, most international maps and documents still use the name "Sea of Japan." But in some cases, the name "East Sea" is also included alongside "Sea of Japan."
Images for kids
-
The Tumen River flows into the Sea of Japan. The last 17 km of the river form the border between North Korea and Russia. This picture is of the Korea Russia Friendship Bridge that crosses the Tumen River.
-
The mouth of Partizanskaya River near Nakhodka. View from Sopka Sestra.
-
Sea lions on Moneron Island
See also
 In Spanish: Mar del Japón para niños
In Spanish: Mar del Japón para niños