Chūbu region facts for kids
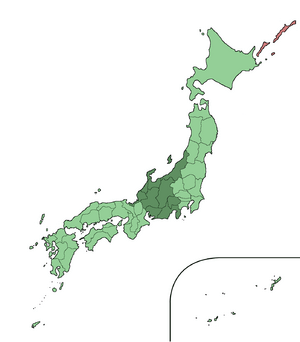
The Chūbu region (中部地方 (Chūbu-chihō)) is a big and important area in Japan. It's located on Honshū, Japan's largest island. Japan is traditionally divided into eight main regions, and Chūbu is one of them. These regions help people understand Japan's geography, culture, and how the government works. They have been used for a long time to describe different parts of the country.
Contents
History of the Chūbu Region
How Regions Were First Organized
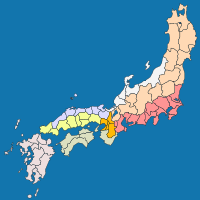
In the late 600s, Japan had an old system for dividing the country. One of the main areas was called the Hokuridō. This was part of a bigger system known as Gokishichidō. The Chūbu region today covers much of the same central area on Honshū island. This includes the traditional areas known as Hokuriku, Kōshin'etsu, and Tōkai.
Modern Regional System
Later, during the Meiji period (which started in 1868), Japan created a new, modern system for its regions. The country was divided into different chihō (regions). The Chūbu region was part of this new system. Each region had a special council. This council was led by the governor of the most powerful prefecture in that group. Important government officials from the central ministries also joined these councils.
Over many years, the Chūbu region has developed its own special ways. This includes unique local dialects, customs, and traditional culture.
Geography of Chūbu
The Chūbu region covers a large part of Honshū island. It has several smaller traditional areas within it. These include the Hokuriku, Kōshin'etsu, Shin'etsu, and Tōkai areas. Each of these sub-regions has its own distinct features and landscapes.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Mount Fuji is the Chūbu region's most famous landmark.
-
Tsu City (Kinki region)
See also
 In Spanish: Región de Chūbu para niños
In Spanish: Región de Chūbu para niños
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |