Navajo Mine and Railroad facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Navajo Mine and Railroad |
|
|---|---|
Navajo Mine and Railroad, mining status as of 2016
|
|
| Overview | |
| Status | Operating |
| Locale | San Juan County, New Mexico |
| Termini | South Terminals: coal load outs in the Navajo Mine North Terminal: Four Corners Generating Station |
| Service | |
| Type | Freight railroad for sub-bituminous coal |
| History | |
| Opened | 1974 |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 13.3 miles (21.4 km) |
| Track length | 17.8 miles (28.6 km) |
| Number of tracks | 1 |
| Character | single track main line two branches |
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) |
| Electrification | No, formerly 25 kV 60 Hz (AC) overhead catenary |
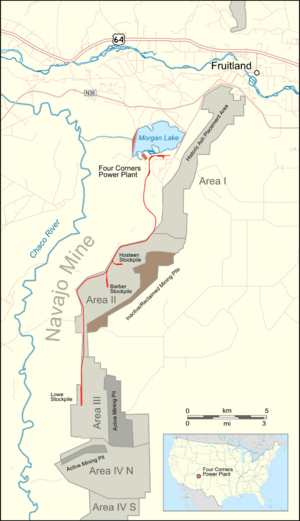
The Navajo Mine is a large coal mine in New Mexico, United States. It is owned and run by the Navajo Transitional Energy Company (NTEC). This mine is located on the land of the Navajo Nation. It is about 20.5 miles southwest of Farmington, New Mexico. The Navajo Mine Railroad is a special train line. It has 13.8 miles of track. This railroad connects the mine to the Four Corners Generating Station.
Contents
The Navajo Mine got permission to dig for coal in 1957. Mining operations started in 1963. Back then, it was run by a company called Utah International. The Navajo Mine is the only place that supplies coal to the nearby Four Corners Power Plant. In 1977, General Electric bought the mine. Later, in 1984, another company called BHP took over the Navajo Mine.
In 2013, the Navajo Nation Council created the Navajo Transitional Energy Company (NTEC). By the end of that year, NTEC bought the Navajo Mine. NTEC also got permission to keep the mine and power plant running for 25 more years. This was a big step for the Navajo Nation.
In 2016, NTEC hired North American Coal Corporation to help run the mine. They formed a new company called Bisti Fuels Company, LLC. Two years later, in 2018, NTEC bought a small part of the Four Corners Power Plant. This made NTEC the only Native American tribal company to own part of a coal power plant.
NTEC grew even more by buying other coal mines in Wyoming and Montana. These mines included Antelope, Cordero Rojo Mine, and Spring Creek. This made NTEC one of the biggest coal producers in the United States. On October 1, 2021, NTEC took full control of running the Navajo Mine. This was a historic moment. It made NTEC the first tribal company to operate a coal mine on tribal land. The Navajo Mine employs about 370 people. A large number, 86%, are members of the Navajo Nation.
Railroad Development
A 7-mile long train track was built in 1974. It connected the power plant to a coal storage area. The track was made longer in 1983, reaching its current length of 14 miles. Since the railroad was not connected to other train lines, special diesel trains and coal cars had to be brought in by large trucks. At first, only one train ran at a time. The diesel trains had problems with coal dust clogging their air filters. This issue was fixed with new filter types.
In 1984, the railroad switched to electric trains. This was because electric power was cheaper than diesel fuel. More coal cars were bought, allowing two trains to run at once. Each train had 18 cars. However, in 2017, the railroad went back to using diesel trains. They bought new GE ET44AC diesel locomotives. This change happened because the electric trains were difficult to maintain.
When the Kayenta Mine closed, its coal cars were moved to the Navajo Mine. NTEC has also started looking into other energy sources. They are investing in solar power. They also bought a company that finds and sells helium. This company has helium wells on the Navajo Nation.
The Navajo Mine Railroad runs from the Navajo Mine. It goes north-northwest to the Four Corners Generating Station. This power plant is located about 25 miles west of Farmington, New Mexico. The railroad does not connect to any other train lines.
How the Railroad Operates
In the past, when the railroad used electricity, trains had two types of locomotives. An electric GE E60 locomotive was on the north end. A diesel-electric ALCO Century 425 locomotive was on the south end. The diesel locomotive was mostly used as a control room for the electric train. This happened when the empty train returned to the mine. The diesel engine could also provide power if the electricity went out.
There were enough trains and cars for three full trains. But usually, only two trains ran. Each train had 21 coal cars. Each train typically made 12 round trips every 24 hours. Only one crew member worked at a time. This person would take an empty train to get loaded with coal. Then, they would switch to the loaded train and take it to the power plant. While this train was moving, the other train would be loaded.
The electric power lines above the track had a voltage of 25,000 volts. The parts on top of the electric trains that collect power were very high. This was because the power lines were unusually high. Special filters were added to the trains to keep the air clean from coal dust.
At the coal loading areas, large front-end loaders put coal into the train cars. Each car could hold between 100 and 125 tons of coal.
In 2020, Arizona Public Service (APS) announced plans to close the Four Corners Generating Station. If this happens, both the Navajo Mine and its railroad would no longer be needed.
Besides the Navajo Mine, NTEC also owns three other mines. These mines are located in Montana and Wyoming.
Train Engines (Motive Power)
- ALCO Century 425 locomotives: These trains have road numbers LOD7, LOD8, and LOD9. They used to belong to the Norfolk & Western (N&W) railroad. They were rebuilt to work on the Navajo Mine Railroad.
- Two General Electric ET44AC locomotives: These new diesel trains were delivered in 2017. Their road numbers are 2026 and 2027.
Past Train Engines
- General Electric E60 locomotives: These electric trains had road numbers LOE20, LOE21, and LOE23. They were first built for Amtrak. Most were sold directly to the Navajo Mine Railroad. These trains were taken apart in 2003. They were replaced by other E60s that used to run in Mexico.
See also
- Mine railway
- Black Mesa and Lake Powell Railroad – another electric freight railroad on Navajo land, now closed
- Deseret Power Railroad – another electric freight railroad

