Negative feedback facts for kids
Negative feedback is a super important idea in how things work and stay balanced. It's used in engineering to build machines and in physiology to understand how our bodies work. In biology, negative feedback is often called homeostasis.
Imagine you have a system, like a central heating system in a house. Negative feedback happens when the system's output (like the heat) works against any changes to its input (like the temperature setting). This helps to keep things steady and within certain limits.
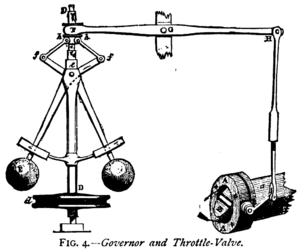
A great example is a home thermostat. When the room gets too cold, the heater turns on. When the room reaches the temperature you set, the thermostat senses this and turns the heater off. This "turning off" action is the negative feedback. It stops the temperature from getting too hot, keeping it just right.
Contents
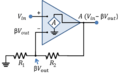
How Negative Feedback Works
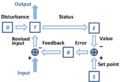
Negative feedback helps a system stay stable. It's like a balancing act. If something starts to change too much in one direction, negative feedback pushes it back in the other direction. This keeps the system from going out of control.
Think of it like riding a bicycle. If you start to lean too much to the left, your body automatically shifts a little to the right to correct it. This small correction is a form of negative feedback, helping you stay upright.
Homeostasis: Keeping Your Body Balanced
Homeostasis is the special name for negative feedback in living things. It's how your body keeps its internal environment stable and constant. This is super important for staying healthy!
Almost everything inside your body uses homeostasis. If these systems stop working correctly, you can get sick.
Here are some examples of what your body keeps balanced using homeostasis:
- Blood pressure: Your body works to keep your blood pressure at a healthy level.
- Blood glucose (sugar) level: After you eat, your blood sugar goes up. Your body uses hormones like insulin to bring it back down. If it gets too low, other hormones bring it back up.
- Body temperature: If you get too hot, you sweat to cool down. If you get too cold, you shiver to warm up.
- Water balance: Your body makes sure you have the right amount of water.
Scientists Claude Bernard and Walter Bradford Cannon helped us understand homeostasis. Bernard first talked about the idea of an "internal environment" in 1865. Cannon later used the term "homeostasis" to describe how living systems keep this internal environment stable.
When a system has overall negative feedback, it tends to be very stable. This means it can handle small changes and disturbances without breaking down.
Images for kids
-
Blood glucose levels are maintained at a constant level in the body by a negative feedback mechanism. When the blood glucose level is too high, the pancreas secretes insulin and when the level is too low, the pancreas then secretes glucagon. The flat line shown represents the homeostatic set point. The sinusoidal line represents the blood glucose level.
See also
 In Spanish: Realimentación negativa para niños
In Spanish: Realimentación negativa para niños