Nuclear fallout facts for kids
Nuclear fallout is the leftover radioactive material from a nuclear explosion or a nuclear accident. When a nuclear explosion happens, this material first forms a radioactive cloud. Then, it "falls out" of the cloud as winds carry it through the air. This can happen minutes, hours, or even days after the explosion.
How much fallout there is and where it spreads depends on several things. These include the power of the weapon, how much of it uses nuclear fission, how high in the air it explodes, and the weather.
Some nuclear weapons use a lot of fissionable fuel, like uranium or plutonium. Their fallout mainly consists of fission products and some fuel that didn't split. Other types of nuclear weapons create fallout when neutrons make nearby materials radioactive.
Fallout can also come from nuclear accidents. These include problems at nuclear reactors or with nuclear waste. In these cases, radioactive materials usually spread into the air or water.
Fallout can cause serious health problems, both right away and over a long time. It can also lead to radioactive contamination far from where the explosion or accident happened. Many countries stopped testing nuclear weapons in the atmosphere and underwater after the 1963 Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty. Underground testing, which sometimes caused fallout, mostly stopped after the 1996 Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty.
Contents
Understanding Nuclear Fallout
Fallout is generally split into two main kinds. This depends on how high the explosion happens.
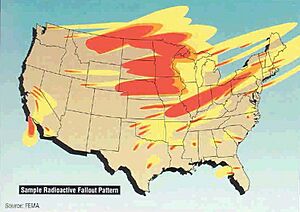
Global Fallout: Spreading Far and Wide
If a nuclear weapon explodes high enough in the air, its fireball doesn't mix much with dirt from the ground. The radioactive materials stay high up for a longer time. This extra time allows the most dangerous, short-lived radioactive elements to decay before they reach the ground. This makes the fallout less intense when it finally settles. It also spreads the radioactive cloud over a much larger area. This type is called "global fallout." It causes a small increase in background radiation over huge parts of the world.
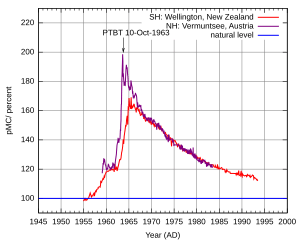
After a high-altitude explosion, tiny radioactive particles, about 10 nanometers to 20 micrometers wide, are lifted into the stratosphere. These particles can take months or even years to settle back to Earth. They can land anywhere in the world. This type of fallout slightly increases the risk of health issues like cancer. For example, after widespread nuclear weapons testing in the 1950s, there was a measurable increase in atmospheric radioactivity.
Radioactive fallout has been found all over the world. People have been exposed to substances like iodine-131 from atmospheric nuclear tests. Fallout can land on plants, fruits, and vegetables. Exposure can happen if people are outside, depending on the weather, or if they eat contaminated food.
A major example of widespread fallout happened after the 1986 Chernobyl disaster. This accident contaminated over 20,000 square kilometers (about 7,700 square miles) of land in Ukraine and Belarus. Some people became very ill and sadly passed away. Even though residents were moved away quickly, many showed signs of radiation sickness. In the long term, there was an increase in thyroid cancer cases, especially among children. Fallout from Chernobyl spread across Europe, affecting areas like Northern Scandinavia and even some sheep farms in the United Kingdom.
Local Fallout: Close to the Blast
When a nuclear device explodes at ground level, or in shallow water, it's called a surface burst. The intense heat turns large amounts of earth or water into vapor. This material is then sucked up into the mushroom cloud. It becomes radioactive by mixing with fission products or by being hit by neutrons.
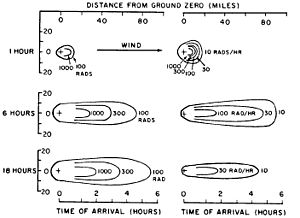
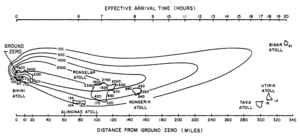
A surface burst creates many particles, from very tiny to several millimeters in size. The larger particles fall out of the cloud quickly, often within an hour, near the explosion site. More than half of all the radioactive debris lands within about 24 hours as local fallout. The type of elements in the fallout affects how fast they settle.
Severe local fallout can spread far beyond the immediate blast and heat effects. The path of fallout depends on the weather at the time of the explosion. Stronger winds carry fallout faster and spread it over a larger area, making it less concentrated. However, thunderstorms can bring down radioactive particles more quickly if they mix with the nuclear cloud.
If people stay in a contaminated area, they face immediate external radiation exposure. They also risk internal exposure from breathing in or eating radioactive materials. For example, iodine-131 can build up in the thyroid gland.
What Affects Fallout Spread?
Explosion Location
The location of an explosion matters a lot. There are two main things to consider: how high it explodes and what the surface is made of.
An air burst, where a nuclear weapon explodes high in the air, creates less fallout than an explosion near the ground. This is because an air burst doesn't pull up much soil or other materials into the cloud.
If an explosion happens on or near water, the particles tend to be lighter and smaller. This creates less local fallout but spreads it over a wider area. These particles often contain sea salt and water, which can cause local rain that brings down more fallout.
Underwater explosions can also make parts of the seabed radioactive. After the Castle Bravo test, white dust, which was radioactive calcium oxide from crushed corals, fell for hours. This caused burns and radiation exposure to people on nearby islands and a fishing boat crew. They called it Bikini snow.
For explosions underground, there's a special cloud called a "base surge." This cloud rolls outward from the bottom of the main cloud. It's made of a lot of dust or water droplets. Even though it usually contains only about 10% of the total radioactive debris, it can cause higher radiation doses than regular fallout nearby. This is because it arrives sooner, before much of the radioactivity has decayed.
Weather Conditions
Weather plays a huge role in how fallout spreads, especially local fallout. Winds can carry fallout over very large distances. For example, after the 15-megaton Castle Bravo test in 1954, a cigar-shaped area of the Pacific Ocean over 500 kilometers (310 miles) long was heavily contaminated.
Snow and rain can also speed up local fallout, especially if they come from high altitudes. Under certain weather conditions, like a local rain shower above a radioactive cloud, small areas of very heavy contamination can form downwind from a nuclear blast.
Health and Environmental Effects
Radiation can cause many changes in living things. These range from quick death after very high doses to long-term health problems that appear years later.
Immediate Effects

A high dose of radiation can make people very sick, a condition called radiation poisoning. Symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, and extreme tiredness. The amount of radiation that could be very harmful to many people is often discussed. For gamma rays, a dose of about 3.5 Gy was considered very dangerous in the 1950s. Developing babies are very sensitive to radiation.
The good news is that radiation levels from nuclear fallout drop very quickly after an explosion. The radiation is reduced by 50% in the first hour and by 80% within the first day. This means that quickly removing contaminated clothing can be very helpful. Most areas become much safer for travel and cleanup after three to five weeks.
Long-Term Effects
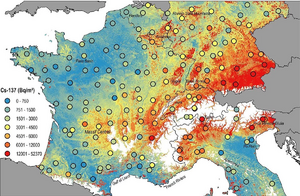
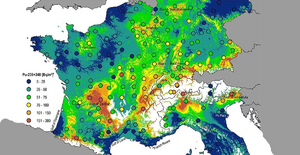
Long-term effects of radiation can appear months or years after exposure. These can include serious health issues like cancer, eye problems (cataracts), skin problems, and other lasting effects.
One study, called the Baby Tooth Survey, looked for strontium-90 in children's teeth. Strontium-90 is a radioactive substance from atomic tests that can cause cancer. It gets into bones and teeth because it's similar to calcium. The survey found that children born after 1963 had much higher levels of strontium-90 in their baby teeth. These findings helped convince leaders to sign the Partial Nuclear Test Ban Treaty, which stopped most atmospheric nuclear weapons testing. This was seen as a positive step to reduce global fallout.
Effects on the Environment
A large-scale nuclear event would have severe effects on the environment. In areas directly hit, everything would be destroyed. Cities would lose water systems. Suburban areas would have highly contaminated water supplies. All surface water in fallout zones would become contaminated.
In the first few months, dust, smoke, and radioactive particles would fall hundreds of kilometers away. This would pollute surface water. Iodine-131 would be a main concern early on, followed by strontium-90 in later months. These would contaminate rivers, lakes, and soil.
Groundwater supplies, like aquifers, would be safer at first. But over time, they could become contaminated and stay that way for over 10 years. Eventually, cesium-137 and strontium-90 would be the main radionuclides affecting fresh water.
Nuclear fallout also affects the food chain. Animals would eat contaminated plants and soil, and then humans could consume contaminated meat, milk, fish, and vegetables. This would lead to radioactive substances building up in human organs.
Scientists have studied how nuclear fallout affects the environment from past nuclear weapons tests. When explosions happened near the ground, they irradiated tons of soil. Radioactive dust was carried by winds, contaminating surrounding areas. If a radiation cloud met rainfall, the fallout would contaminate areas downwind.
Plants absorb contaminated material, and animals eat it. This can make livestock sick or kill them. If humans eat these animals, the radioactive material passes to them.
Different species react differently to nuclear radiation. Mammals are very sensitive, followed by birds, plants, fish, and insects.
Some scientists, like climatologist Alan Robock, have modeled what a small nuclear war might look like. They suggest that fires from such a war could release enough soot into the atmosphere to block sunlight. This could lower global temperatures and lead to widespread food shortages, sometimes called "nuclear famine." It could also disrupt rainfall and damage the Earth's ozone layer, affecting plant growth and human health.
Radiation from fallout would stay in soil, plants, and food chains for years. Marine food chains are especially vulnerable. Studies in Alaska showed that fallout affected the lichen-caribou-Eskimo food chain, causing thyroid problems in humans. Fallout severely harms human survival and the natural world.
Protecting Against Fallout
During the Cold War, governments tried to teach people how to survive a nuclear attack. This was called Civil Defense. The main goal was to reduce exposure to fallout.
Fallout protection mostly means protecting yourself from radiation. Fallout gives off alpha, beta, and gamma radiation. Regular clothes can block alpha and beta radiation. But most protection efforts focus on blocking gamma radiation, which is much more powerful.
Many materials have a "halving thickness." This is how much of the material is needed to cut gamma radiation exposure by half. For example, 1 centimeter (0.4 inches) of lead, 6 centimeters (2.4 inches) of concrete, or 9 centimeters (3.6 inches) of packed earth can halve gamma radiation. If you build a shield with ten halving thicknesses, like 90 centimeters (36 inches) of packed earth, it can reduce gamma radiation exposure by about 1024 times. A shelter built for this purpose is called a fallout shelter.
Personal Protection
Scientists are always looking for ways to protect people from high-energy radiation. The most immediate risk is Acute radiation syndrome (ARS) from high doses. While a thick fallout shelter is the best protection, it's not always possible.
For people who need to move around, like medical or security teams, full-body shielding is too heavy. So, scientists are researching "partial body protection." This idea is to shield areas with lots of bone marrow, like the pelvis. Protecting these areas could allow the body to regrow healthy blood cells, helping people survive.
The Seven-Ten Rule
The danger from fallout radiation decreases quickly over time. This is because radioactive materials decay. A helpful rule of thumb is the "seven-ten rule." It says that for the first few days after an explosion, the radiation dose rate goes down by a factor of ten for every seven-fold increase in hours. For example, it takes about seven times longer for the radiation to drop from 1000 units per hour to 10 units per hour (48 hours) than it does to drop from 1000 units per hour to 100 units per hour (7 hours). This is a general guide, not an exact scientific law.
Government Guides for Fallout Protection
In the 1960s, the U.S. government provided guides on how to survive nuclear fallout. These booklets explained how to build fallout shelters and what to do if you were unprepared.
The main idea was that dense materials like concrete, soil, and sand are needed to block radiation. Regular clothing cannot block fallout radiation because it would need to be too thick. However, protective clothing can keep radioactive particles off your body.
These guides suggested that fallout shelters should have enough supplies for up to two weeks. Community shelters were often preferred. If you had a basement, it was best to build a shelter in a corner, using the basement walls and adding cinder blocks filled with sand or soil for the other walls. A strong roof, like concrete blocks, was also important. Shelters needed water, food, tools, and a way to handle waste.
If a shelter wasn't built beforehand, people were advised to get underground if possible. If not, a tall apartment building far from the blast was suggested. People should stay in the center of the building, away from the top and ground floors.
Schools were often seen as good places for community shelters because they were spread out and had existing organization. The government suggested making schools stronger with thicker walls and roofs, better electrical systems, and protected water and ventilation.
Today, agencies like the U.S. Department of Homeland Security and the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) continue to develop guidance for responding to nuclear events.
Nuclear Reactor Accidents and Fallout
Fallout can also happen from nuclear accidents. However, a nuclear reactor does not explode like a nuclear weapon. The radioactive materials released from a reactor accident are different from those from a bomb.
The main differences are how easily the materials turn into gas (volatility) and how long they stay radioactive (half-life).
Half-life: How Long Radiation Lasts
A half life is the time it takes for the radiation from a specific substance to decrease to half its original level. Nuclear bomb fallout contains many short-lived radioactive materials. In a power reactor, these short-lived materials are also created, but most of them decay before they can be released in an accident. This means reactor fallout often has different types of radioactive materials that might last longer.
Preventing Accidents
Because nuclear reactors are a potential source of fallout, many steps are taken to control risks. In the 1950s and 60s, the United States Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) started creating safety rules for civilian nuclear reactors. They wanted to be very proactive because fallout can spread widely and last a long time.
One important step was the Price-Anderson Act in 1957. This law helped protect companies building nuclear reactors, ensuring the industry could continue to develop. Engineers worked hard to imagine every possible accident and the fallout it could cause. They focused on preventing a "Maximum Credible Accident" (MCA), which involved a major release of radioactive materials after a reactor meltdown.
To prevent such accidents, both "static" and "active" safety systems were developed. Static systems, like strong containment buildings, work without power or human input. Active systems, like cooling water pumps, need power and sensors. The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) was formed to set regulations based on research, moving towards a more mathematical approach to weigh the risks of potential radiation leaks. Today, the NRC continues to be a leading group for nuclear reactor safety.
Measuring Nuclear Events
The International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) is used to describe the seriousness of nuclear or radiological events to the public. Developed in 1990, it helps categorize accidents based on their potential impact.
- Defence-in-Depth: These are minor events that don't directly harm people or the environment but help improve safety.
- Radiological Barriers and Control: These events involve damage within facilities but no direct harm to people or the environment.
- People and the Environment: These are more serious accidents that could spread radiation to people nearby or involve a widespread release of radioactive material.
The INES scale has seven levels, from minor issues to major accidents needing immediate action.
Chernobyl Disaster
The 1986 nuclear reactor explosion at Chernobyl was a Level 7 accident, the highest on the INES scale. This was due to its widespread environmental and health effects. The explosion and fires released a significant amount of radioactive material into the atmosphere. Two plant workers died immediately, and 28 more passed away in the following weeks from severe radiation poisoning. Young children and teenagers in the most affected areas saw an increased risk of thyroid cancer. The accident also heavily contaminated the environment, including crops and urban areas.
Three Mile Island Accident
The nuclear meltdown at Three Mile Island in 1979 was a Level 5 accident. This was due to severe damage to the reactor core and a radiation leak. It was the most serious accident in U.S. commercial nuclear power history. However, its effects were different from Chernobyl. Studies showed that people living near the plant received only a very small average radiation dose. Unlike Chernobyl, there was no significant increase in thyroid cancer among those exposed.
Fukushima Disaster
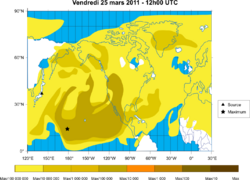
The incident at Fukushima in 2011 was initially a Level 5 accident. A tsunami caused power and cooling systems to fail, leading to meltdowns in three reactors. Later, it was upgraded to a Level 7 accident because of the combined events at all three reactors. People up to 30 kilometers (18 miles) away were advised to evacuate. Dealing with contaminated water was a huge challenge. However, the fallout from Fukushima had a minimal impact on the surrounding population. Most residents received very low external radiation doses. Screening campaigns for children showed no significant difference in the risk of thyroid cancer compared to other parts of the country.
Global Nuclear Safety
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) was founded in 1974 to set global standards for nuclear reactor safety. However, without a strong way to enforce these rules, they were sometimes overlooked. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster showed that nuclear safety is a global concern, as "A radiation cloud doesn't know international boundaries."
After Chernobyl, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) worked with the Soviets to improve safety. In 1989, the World Association of Nuclear Operators (WANO) was formed. WANO works with the IAEA to ensure high safety standards for all nuclear reactors worldwide. Efforts in the 1990s and 2000s aimed to bring all nuclear reactors up to international safety levels.
See also
 In Spanish: Lluvia radiactiva para niños
In Spanish: Lluvia radiactiva para niños
- Debris fallout
- Dirty bomb
- Fallout: An American Nuclear Tragedy
- Fallout Protection—U.S. government booklet
- Effects of nuclear explosions
- Fallout from the Trinity nuclear test
- Fallout (RTÉ drama)—Irish drama exploring scenarios following a nuclear accident at Sellafield.
- Fallout (series)
- Fallout shelter
- Fission product
- Hot particle
- Human radiation experiments
- List of nuclear accidents
- Lists of nuclear disasters and radioactive incidents
- Neutron bomb
- Mutation breeding#Radiation breeding
- Nuclear fallout effects on an ecosystem
- Nuclear terrorism
- Nuclear War Survival Skills by Cresson Kearny
- Nuclear weapon design
- Potassium iodide
- Project GABRIEL
- Protect and Survive, a series of booklets and a public information film series produced for the British government in the 1970s and 1980s.
- Radioactive contamination
- Radiation poisoning
- Radiation biology
- Radioactive waste
- Radiological weapon
- Joseph Rotblat
- Salted bomb
- Survival Under Atomic Attack, an official U.S. government booklet regarding the effects of a nuclear attack.
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |