OpenAI facts for kids
 |
|
| Private | |
| Industry | Artificial intelligence |
| Founded | December 8, 2015 |
| Founders |
|
| Headquarters | 1455 3rd Street, San Francisco, California, U.S. |
|
Key people
|
|
| Products | |
| Revenue | |
|
Number of employees
|
2,000+ (2024) |
OpenAI is an American company that works on artificial intelligence, or AI. It was started in December 2015 in San Francisco, California. Its main goal is to create "safe and helpful" AI for everyone.
The company is trying to build something called artificial general intelligence (AGI). AGI would be a type of AI that is smart enough to do most jobs better than humans.
OpenAI is famous for creating popular AI tools. These include the ChatGPT chatbot, the DALL-E image creator, and the Sora video maker. When ChatGPT was released in 2022, it made people all over the world very interested in AI.
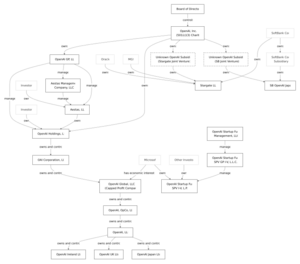
The company has a special structure. It started as a non-profit organization but now has a for-profit part to help pay for its research. Microsoft is a major partner, investing billions of dollars and providing powerful computers for OpenAI's work.
In recent years, some authors and companies have raised concerns that their work was used to train OpenAI's AI without their permission. The company also had a major leadership change in late 2023, but the original CEO, Sam Altman, quickly returned.
History
2015: How OpenAI Started
OpenAI was founded in 2015 as a non-profit organization. This means its goal was not to make money, but to do research for the good of humanity. The founders included well-known tech leaders like Sam Altman and Elon Musk.
They wanted to make sure that as AI became more powerful, it would be safe and helpful. They worried that a super-smart AI could be harmful if it wasn't built carefully. Their plan was to share their research openly with the world.
2016–2018: Early Years of Research
In its first few years, OpenAI focused on research. They released "OpenAI Gym," a toolkit for programmers to practice training AI. They also trained AI to play complex video games like Dota 2. This required a lot of computer power.
In 2018, Elon Musk left the board. He wanted to avoid any conflicts with his work on AI for self-driving cars at his company, Tesla.
In 2019, OpenAI announced GPT-2, a language model that was very good at writing human-like text.
2019: A New Structure and a Big Partner
In 2019, OpenAI changed its structure. It created a new "capped-profit" company called OpenAI Global, LLC. This allowed OpenAI to raise money from investors, which was needed for its very expensive research. The original non-profit organization still oversees the company to make sure it stays true to its mission.
Soon after, Microsoft invested $1 billion in OpenAI. Microsoft also provided its Azure cloud computing platform, giving OpenAI access to powerful supercomputers to train its AI models.
2020–2023: World-Famous Creations

In 2020, OpenAI released GPT-3, an even more powerful language model. It could answer questions, translate languages, and write all kinds of text.
In 2021, the company introduced DALL-E. This AI could create unique images just from a short text description.
The biggest event came in November 2022 with the launch of ChatGPT. It was a free and easy-to-use chatbot based on an improved version of GPT-3. It became incredibly popular, reaching over a million users in just five days. This success led Microsoft to invest another $10 billion in 2023.
In November 2023, there was a major leadership change. The board removed Sam Altman as CEO. However, after strong support from employees, he returned five days later with a new board of directors.
2024–2025: New Tools and Growth
In early 2024, OpenAI showed the world its next amazing tool: Sora. This AI can create realistic videos from text commands.
The company also made important partnerships. In June 2024, Apple announced it would build ChatGPT into its products, like the iPhone.
Throughout 2024 and 2025, OpenAI continued to release new and more powerful AI models. This included the o1 model, which is designed to be better at reasoning and solving complex problems. The company also began working with other companies to design its own computer chips for AI.
Management
OpenAI is led by a team of experienced people from the tech industry.
Key People
- CEO and co-founder: Sam Altman
- President and co-founder: Greg Brockman
- Chief Scientist: Jakub Pachocki
- Chief Financial Officer: Sarah Friar
Board of Directors
The non-profit part of OpenAI is guided by a board of directors. Their job is to make sure the company follows its mission to benefit humanity. The board includes:
- Bret Taylor (Chairman), former co-CEO of Salesforce
- Sam Altman
- Lawrence Summers, former U.S. Secretary of the Treasury
- Adam D'Angelo, CEO of Quora
- Sue Desmond-Hellmann, former CEO of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
- Paul Nakasone, former Director of the U.S. National Security Agency
Strategy and Safety
OpenAI has thought a lot about the best way to build AI safely.
At first, some founders believed the safest thing was to give AI to everyone. The idea was that if everyone had AI, no single person or group could become too powerful. But others disagreed, arguing that giving powerful tools to everyone could be risky.
A big focus for OpenAI today is AI alignment. This means making sure that AI systems share human values and goals. They want to teach AI to be helpful and harmless, especially as it gets smarter. OpenAI believes that making sure a future super-smart AI is "aligned" is a very important and difficult problem.
In 2024, some researchers who focused on AI safety left the company. They had different ideas about how quickly to build new AI and how to best make sure it stays safe.
Products and Applications
OpenAI has created many well-known AI models and tools. Some of the most important ones are:
- ChatGPT
- DALL-E
- GPT-2, GPT-3, and GPT-4
- OpenAI o1
- Sora (text-to-video model)
- Whisper (speech recognition system)
See also
 In Spanish: OpenAI para niños
In Spanish: OpenAI para niños
- Anthropic
- Center for AI Safety
- Future of Life Institute
- Google DeepMind
- Machine Intelligence Research Institute
- Model Context Protocol
- xAI (company)