Parliament of Poland facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Parliament of PolandParlament Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej |
|
|---|---|
| 9th term Sejm and 10th term Senate | |
 |
|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | |
|
Term limits
|
4 years |
| Leadership | |
|
Elżbieta Witek, PiS
Since 9 August 2019 |
|
| Structure | |
| Seats | |
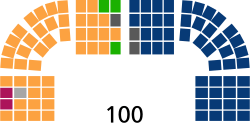 |
|
|
Senate political groups
|
Government (48)
Opposition (52)
|
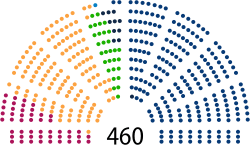 |
|
|
Sejm political groups
|
Government (235)
Opposition (225)
|
| Elections | |
| First-past-the-post voting | |
| Proportional representationa | |
|
Senate last election
|
13 October 2019 |
|
Sejm last election
|
13 October 2019 |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
| Sejm chamber, Warsaw | |
 |
|
| Senate chamber, Warsaw | |
| Footnotes | |
| a Open-list proportional representation in 41 constituencies (5% national electoral threshold, 8% national electoral threshold for coalitions). | |
The Parliament of Poland is where laws are made for the country. It has two main parts, like two different teams working together. One part is called the Senate, which is the upper house. The other part is the Sejm, known as the lower house. Both of these groups meet in the same building complex in Warsaw, the capital city of Poland. The official name for Poland's law-making body is simply "the Sejm and the Senate," as stated in the Polish Constitution.
People in both the Senate and the Sejm are chosen by direct elections. This means citizens vote for them directly. These elections usually happen every four years. The Sejm has 460 members, who are called deputies. The Senate has 100 members, called senators. For any new law to be created, both the Sejm and the Senate must agree to it.
Contents
What is the Polish Parliament?
The Parliament of Poland is the main law-making body in the country. It is made up of two separate groups: the Sejm and the Senate. This system, having two houses, is called bicameralism. It helps ensure that new laws are carefully reviewed before they are passed.
The Sejm: The Lower House
The Sejm is the larger of the two houses, with 460 members. These members are called deputies. They are elected by the people of Poland. The Sejm is very important because it is where most new laws begin. The head of the Sejm is called the Marshal of the Sejm. Currently, Elżbieta Witek holds this position.
The Senate: The Upper House
The Senate is the smaller house, with 100 members called senators. Senators are also elected by the people. The Senate's job is to review the laws passed by the Sejm. They can suggest changes or even reject a law. If they reject a law, the Sejm can still pass it with enough votes. The head of the Senate is called the Marshal of the Senate. Tomasz Grodzki is the current Marshal of the Senate.
How Laws Are Made
Making a new law in Poland involves both the Sejm and the Senate.
- First, a proposed law, called a bill, is usually introduced in the Sejm.
- The Sejm debates and votes on the bill. If it passes, it moves to the Senate.
- The Senate then reviews the bill. They can approve it, suggest changes, or reject it.
- If the Senate suggests changes or rejects the bill, it goes back to the Sejm. The Sejm can then decide whether to accept the Senate's changes or pass the original bill again.
- Once both houses agree, the bill goes to the President of Poland to be signed into law.
Who Leads the Parliament?
Each house of the Polish Parliament has its own leader.
- The leader of the Senate is the Marshal of the Senate. They are in charge of meetings and making sure rules are followed.
- The leader of the Sejm is the Marshal of the Sejm. They have similar duties for the Sejm.
These leaders are important for keeping the parliamentary process running smoothly.
Elections and Terms
Members of both the Sejm and the Senate are elected for a term of four years. This means they serve for four years before new elections are held. The last elections for both houses were on 13 October 2019.
How Members Are Elected
- For the Senate, members are elected using a system called First-past-the-post voting. This means the candidate who gets the most votes in a specific area wins.
- For the Sejm, members are elected using Proportional representation. This system tries to make sure that the number of seats a political party gets in the Sejm is similar to the percentage of votes they received nationwide. This is done in 41 different voting areas across Poland.
Where They Meet
Both the Sejm and the Senate meet in the Sejm complex in Warsaw. This complex includes separate chambers for each house.
- The Sejm meets in the Sejm chamber.
- The Senate meets in the Senate chamber.
These buildings are important places where the future of Poland is discussed and decided.
Political Groups in Parliament
Inside both the Sejm and the Senate, members form groups based on their political parties. These groups are divided into the Government (the parties that are in power) and the Opposition (the parties that are not in power).
Political Groups in the Senate
In the Senate, there are 100 members.
- The current Government group has 48 senators, mainly from the United Right coalition.
- The Opposition group has 52 senators. This includes groups like Civic Coalition, Polish Coalition, and The Left, along with some independent senators.
Political Groups in the Sejm
In the Sejm, there are 460 members.
- The current Government group has 235 deputies, mostly from the United Right coalition.
- The Opposition group has 225 deputies. This includes groups like Civic Coalition, The Left, Polish Coalition, and Confederation, plus a few independent members.
These groups work together and debate to shape the laws of Poland.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sejm para niños
In Spanish: Sejm para niños




