Parliamentary system facts for kids
A parliamentary system is a way a country's government is set up. In this system, the main leaders (the executive branch) get their power and support from the parliament. The parliament is the group of people who make the laws. This support is often shown by a special vote called a vote of confidence. If the parliament loses trust in the leaders, they can remove them.
In a parliamentary system, the different parts of government work closely together. The people who run the country (the executive) and the people who make laws (the legislature) are connected. This is different from a presidential system, where these parts are more separate.
Most parliamentary systems have two main leaders:
- The head of government is usually called the prime minister. This person has the most real power and makes many important decisions.
- The head of state is often a president (who might be elected) or a king or queen (whose role is usually more symbolic).
How it Works
In a parliamentary system, citizens vote for members of parliament. The political party that wins the most seats in parliament usually forms the government. The leader of that party then becomes the prime minister.
The prime minister chooses other members of parliament to be part of the government. These people are called ministers, and they lead different parts of the government, like education or health. Together, the prime minister and the ministers form the cabinet.
The cabinet needs the support of the parliament to stay in power. If parliament votes against a major government plan or passes a "no confidence" motion, the government might have to resign. This means new elections could be called. This close connection between the government and the parliament is called responsible government.
Countries with Parliamentary Systems
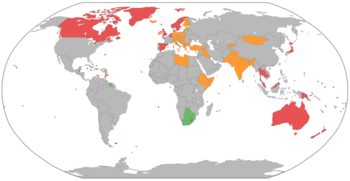
Many countries around the world use a parliamentary system. This includes nations in Africa, the Americas, Asia, Europe, and Oceania. Some well-known examples are Canada, India, the United Kingdom, Australia, and Germany. Each country has its own unique way of making this system work.
- In countries like Canada and Australia, the leader of the party with the most votes in parliament becomes the Prime Minister. The Governor-General (who represents the King or Queen) formally appoints them.
- In India, the President appoints the leader of the majority party in parliament as the Prime Minister.
- In Germany, the parliament (called the Bundestag) elects the Chancellor, who then forms the government.
- In Japan, the National Diet (parliament) chooses the Prime Minister.
These examples show how the parliament plays a central role in choosing and overseeing the government.
Images for kids
-
The Congress of Deputies, the lower house of the Spanish Parliament.
-
Parliament of Australia at dusk.
-
The New Zealand Parliament building.
-
The Palace of Westminster in London, United Kingdom. This is where the British Parliament meets.
-
The Reichstag Building in Berlin, Germany.
-
Jatiya Sangsad Bhaban, the parliament building of Bangladesh.
See also
 In Spanish: Parlamentarismo para niños
In Spanish: Parlamentarismo para niños
















