Parliament of Malaysia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Parliament of MalaysiaParlimen Malaysia |
|
|---|---|
| 15th Parliament | |
 |
|
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | |
| History | |
| Founded | 11 September 1959 |
| Preceded by | Federal Legislative Council |
| Leadership | |
|
Ibrahim Iskandar
Since 31 January 2024 |
|
|
President of the Dewan Negara
|
Awang Bemee Awang Ali Basah, GPS–PBB
Since 22 July 2024 |
|
Speaker of the Dewan Rakyat
|
Johari Abdul, PH–PKR
Since 19 December 2022 |
|
Hamzah Zainudin, PN–BERSATU
Since 19 December 2022 |
|
| Structure | |
| Seats | Dewan Negara: 70 Dewan Rakyat: 222 |
 |
|
|
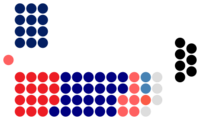
Dewan Negara political groups
|
As of 25 August 2025[update] Government (49) PH (20)
BN (12)
GPS (7)
GRS (4)
Independent (6) Opposition (8) PN (8)
|
 |
|
|
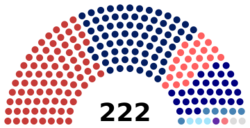
Dewan Rakyat political groups
|
As of 2 June 2024[update]
Government (153)
BN (30)
GPS (23)
GRS (6)
WARISAN (3) KDM (1) PBM (1) Independent (7) Opposition (69)
|
| Dewan Negara committees |
4
Committee of Selection
House Committee Committee of Privileges Standing Orders Committee |
| Dewan Rakyat committees |
5
Committee of Selection
Public Accounts Committee House Committee Committee of Privileges Standing Orders Committee |
| Elections | |
| Indirect election and appointments | |
| First-past-the-post | |
|
Dewan Rakyat last election
|
19 November 2022 |
|
Dewan Rakyat next election
|
By 17 February 2028 |
| Meeting place | |
 |
|
| Malaysian Houses of Parliament, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia | |
The Parliament of Malaysia (also called Parlimen Malaysia in Malay) is the main law-making body for the country of Malaysia. It works like the British Parliament, following a system called the Westminster system.
Malaysia's Parliament has two main parts:
- The Dewan Rakyat (which means "People's Assembly" or House of Representatives).
- The Dewan Negara (which means "State Assembly" or Senate).
The Yang di-Pertuan Agong, who is the King of Malaysia and the country's head of state, is also an important part of how Parliament works.
Parliament meets in the Malaysian Houses of Parliament building, located in Kuala Lumpur, the capital city.
When people talk about a "Member of Parliament" (or MP), they usually mean someone from the Dewan Rakyat. A "Senator" is a member of the Dewan Negara.
Contents
History of Malaysia's Parliament
How Malaysia's Parliament Started
Before Malaysia became an independent country, the different states did not have their own parliaments. However, Sarawak had a special council called the Council Negeri since 1863. This allowed local people to help with governing.
The British government, who ruled Malaysia before independence, allowed some legislative councils to be formed. But these councils were not the main law-makers. They had to follow the British High Commissioner.
When Malaya became independent in 1957, a group called the Reid Commission helped create its Constitution. They designed the government to be like the British system. This meant having two houses in Parliament: one where people voted for members, and another with members chosen by the King.
The first elections after independence happened in 1959. This is when the first Parliament of Malaya was chosen.
At first, Parliament met in an old building. But in 1962, a new Parliament House was finished. It had a main building for both houses to meet and a tall tower for offices. Both the Dewan Negara and Dewan Rakyat moved into this new, special building.
Parliament of Malaysia is Formed
In 1963, Malaya, Sabah, Sarawak, and Singapore joined together to form Malaysia. The Parliament of Malaya then became the Parliament of Malaysia. More representatives from the new states joined both the Dewan Rakyat and Dewan Negara.
Later, in 1965, Singapore left Malaysia. So, it no longer had representatives in the Malaysian Parliament.
Over time, the way the Dewan Negara (Senate) was made up changed. At first, most senators were chosen by the state assemblies. But later, more senators were appointed by the King. This meant the states had fewer elected representatives in the Senate.
Times of Suspension
Parliament has been temporarily stopped twice in Malaysia's history.
The first time was in 1969, during a period of national difficulty. A state of emergency was declared, and a special council ran the country for two years. Parliament started meeting again in 1971.
The second time was in January 2021, during the COVID-19 pandemic. A state of emergency was declared because of rising infections. This suspension lasted for six months, and Parliament met again in July 2021.
Debates and Broadcasts
Sometimes, important debates in Parliament, like when the national budget is presented, are shown on TV and radio.
Since 2013, parliamentary debates are broadcast live on the state television channel TV1. This allows more people to watch and understand what happens in Parliament.
How Malaysia's Parliament Works
What Parliament Does
Parliament is the highest law-making body in Malaysia. Its job is to create new laws, change old ones, and remove laws that are no longer needed.
The King, the Yang di-Pertuan Agong, is above Parliament. This means Parliament works under the King's authority, as stated in the Constitution of Malaysia.
The Dewan Rakyat: Your Representatives
The Dewan Rakyat has 222 members, called Members of Parliament (MPs). These MPs are chosen by people aged 18 and above in general elections.
Malaysia is divided into areas called constituencies. Each constituency elects one MP.
General elections happen every five years. Or, the King can dissolve Parliament earlier if the Prime Minister advises him to.
If an MP leaves their seat (for example, if they resign), a special election called a by-election is held. This happens unless the next general election is very soon.
To become an MP, you must be 18 years old or older.
The Dewan Negara: The Senate
The Dewan Negara has 70 members, called Senators.
- 26 Senators are chosen by the 13 state assemblies (two from each state).
- 4 Senators represent the three federal territories (two for Kuala Lumpur, one for Putrajaya, and one for Labuan). The King appoints these.
- The remaining 40 Senators are appointed by the King, usually based on the Prime Minister's advice.
Senators must be 30 years old or older. They serve for three years and can be re-appointed only once.
Even if the Dewan Rakyat is dissolved for an election, the Dewan Negara continues its work.
Freedom of Speech in Parliament
Members of Parliament can speak freely on many topics inside Parliament. This is called Parliamentary immunity. It protects them from being criticized outside Parliament for what they say during debates.
However, there are some important rules. MPs cannot criticize the King or judges. Also, they cannot question certain parts of the Constitution that are very important for national unity. These rules help keep peace and harmony in the country.
The Government and Parliament
The government of Malaysia includes the Prime Minister and their Cabinet. These leaders are usually chosen from among the members of Parliament.
The King appoints the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister is usually the MP who has the most support from the Dewan Rakyat.
The Prime Minister then suggests a list of other MPs to the King to become Ministers in the Cabinet. These Ministers work together to create government policies and draft new laws.
If the Prime Minister loses the support of the Dewan Rakyat, they must either resign or ask the King to dissolve Parliament for a new election.
Women in Leadership
After the 2008 general elections, Wan Azizah Wan Ismail became the first woman in Malaysian history to be the Leader of the Opposition. This was an important moment for women in Malaysian politics.
How Laws Are Made
Parliament usually meets from Monday to Thursday. The Dewan Rakyat also meets on some Fridays, especially when the national budget is presented.
Steps to Create a Law
1. Idea and Draft: A government minister or ministry first comes up with an idea for a new law. They write a first version, called a 'bill'.
2. Cabinet Discussion: The Cabinet discusses the bill. If they agree, it is shared with all MPs.
3. Readings in Dewan Rakyat: The bill goes through three "readings" in the Dewan Rakyat:
- First Reading: The minister officially presents the bill.
- Second Reading: MPs discuss and debate the bill. Most debates are in Malay, the national language.
- Third Reading: MPs vote on whether to approve the bill. Sometimes a simple majority (more than half) is enough, but for some important changes, two-thirds of the votes are needed.
4. Dewan Negara Review: If the bill passes in the Dewan Rakyat, it goes to the Dewan Negara (Senate). The Senate also has three readings and can discuss the bill.
- The Dewan Negara can delay a bill for up to a year if they don't agree with it. But after that time, the bill is considered passed.
5. Royal Assent: After passing both houses, the bill is sent to the Yang di-Pertuan Agong (King). The King has 30 days to review it.
- If the King suggests changes, Parliament reconsiders them.
- If the King approves, or if 30 days pass without his approval after reconsideration, the bill becomes law.
6. Publication: The new law is officially published in the Government Gazette. Only then does it take effect.
Bills from Other Members
While most bills come from the government, individual MPs can also propose their own bills. These are called "Private Member's Bills." However, this happens less often.
Parliament and the Government
Parliament is meant to keep the government in check. This means Parliament makes sure the government is doing its job well.
How Parliament Checks the Government
- Question Time: MPs can ask ministers questions about government policies. This helps everyone understand what the government is doing.
- Committees: Special groups called Select Committees are formed to look closely at specific issues.
Parliament also controls laws and how the government spends money. If Parliament votes to reject the government's budget, it means they no longer have confidence in the government. This can lead to the government resigning or new elections.
Dewan Negara

The Dewan Negara (Malay for Senate, or National Council) is the upper house of the Parliament of Malaysia. It has 70 senators.
- 26 senators are chosen by the state legislative assemblies (two from each state).
- The other 44 senators are appointed by the Yang di-Pertuan Agong (King). This includes four senators who represent the federal territories.
Senators serve for 3 years and can be re-appointed once.
The Dewan Negara usually reviews laws that have been passed by the lower house, the Dewan Rakyat. All bills must pass both houses before they go to the King for approval. If the Dewan Negara rejects a bill, it can only delay it for a maximum of one year.
Like the Dewan Rakyat, the Dewan Negara meets at the Malaysian Houses of Parliament in Kuala Lumpur.
Dewan Rakyat

The Dewan Rakyat (Malay for House of Representatives, or People's Hall) is the lower house of the Parliament of Malaysia. It has 222 Members of Parliament (MPs). These MPs are chosen by people in elections from different areas called federal constituencies.
MPs serve for a maximum of 5 years and can be re-elected many times. However, an MP cannot also be a senator at the same time.
Ministers or deputy ministers must be either an MP or a senator. If a senator becomes a minister, they can attend the Dewan Rakyat to answer questions. But they do not vote in the Dewan Rakyat.
The Dewan Rakyat is where most new laws, called 'bills', are first proposed. All bills must usually be passed by both the Dewan Rakyat and the Dewan Negara, before they are sent to the King for approval.
Like the Dewan Negara, the Dewan Rakyat meets at the Malaysian Houses of Parliament in Kuala Lumpur.
Fun Facts About Parliament
Members of Parliament are allowed to wear Malaysian batik clothing on Thursdays during parliamentary sessions. Wearing batik in Parliament is a choice, not a rule.
See also
 In Spanish: Parlamento de Malasia para niños
In Spanish: Parlamento de Malasia para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |

